Abstract
Objective: The effects of slow diurnal hemodialysis (slow HD) on amino acid losses and nitrogen balance were studied.
Design: Slow HD was conducted for 10 h during the day at the dialysate flow rate of 30 ml/min. The patients received total parenteral nutrition including 40 g of amino acids (6.08 g of nitrogen). The amino acid concentrations in plasma and dialysate were determined and the daily nitrogen balance was calculated from the urea nitrogen appearance.
Patients: Six critically ill patients with renal failure were entered into the study.
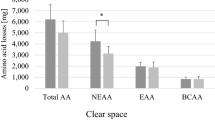
Results: Slow HD eliminated 48.5±4.4 mmol (6.2±0.6 g) of amino acids, representing 16% of the daily amino acid load. The estimated nitrogen balance was –2.3±1.3 g/day. Amino acid nitrogen lost in the dialysate was 1.0±0.1 g, contributing 43% of the daily negative nitrogen balance.
Conclusion: The amount of amino acid losses during slow HD should be taken into consideration when designing nutritional schedules for maintaining positive nitrogen balance in critically ill patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 December 1995 Accepted: 3 September 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kihara, M., Ikeda, Y., Fujita, H. et al. Amino acid losses and nitrogen balance during slow diurnal hemodialysis in critically ill patients with renal failure. Intensive Care Med 23, 110–113 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050299
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050299