Abstract
Objective: Capillary leakage syndrome (CLS) is a frequent complication in sepsis, characterized by loss of intravasal fluids leading to generalized edema and hemodynamic instability despite massive fluid therapy. In spite of its importance no standardized diagnostic criteria are available for CLS.
Design: Prospective clinical study.
Setting: 1800-bed university hospital
Patients: Six septic shock patients with CLS were compared to six control patients.
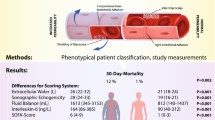
Measurements and results: CLS was clinically determined by generalized edema, positive fluid balance, and weight gain. Plasma volume was measured by indocyanine green, red blood cell volume by chromium-51 labeled erythrocytes, and colloid osmotic pressure before and 90 min after the administration of 300 ml 20% albumin. Extracellular water (ECW) was measured using the inulin distribution volume and bioelectrical impedance analysis. Red blood cells averaged 20.2±1.0 ml/kg body weight in CLS patients and 23.3±4.1 in controls. ECW was higher in CLS patients than in controls (40.0±6.9 vs. 21.7±3.7 l; p<0.05). ECW of inulin was correlated with that measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (r=0.74, p<0.01). The increase in colloid osmotic pressure over the 90 min was less in CLS patients than in controls (1.1±0.3 vs. 2.8±1.3 mmHg; p<0.05).
Conclusion: These results suggest that measurements of an increased ECW using bioelectrical impedance analysis combined with a different response of colloid osmotic pressure to administration of albumin can discriminate noninvasively between patients with and those without CLS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Final revision received: 19 April 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marx, G., Vangerow, B., Burczyk, C. et al. Evaluation of noninvasive determinants for capillary leakage syndrome in septic shock patients. Intensive Care Med 26, 1252–1258 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340000601
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340000601