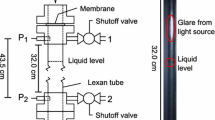
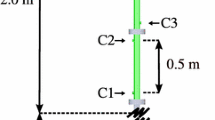
Abstract
Measurements of film condensation were made behind the incident shock wave propagating through a vapor-liquid two-phase medium. Major objective of the study is to identify condensing heat transfer rates of the vapor to the shock-tube side wall as well as to learn the condensing main flow field. Ethanol and E-10 (a heavy liquid named Afluid by the manufacturer) were extensively used as working fluid. Steady accumulation of the condensing vapor was confirmed on the wall surface, as similarly seen in the end-wall experiment conducted elsewhere. A most significant result is that “dual-step” shock pressurization was observed in E-10. The first pressure rise is a normal one created by an incident shock front, whereas the second pressure rise is taken place by some large disturbance in the main flow. The reason for this is not certain yet, but is speculated to be a long relaxation time or inefficient compressibility of the fluid. The visualized shock front and its vicinity of E-10 is completely different from those of normal gases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bratos M, Meier GEA (1979) Shock wave induced condensation in the retrograde vapor. Archives of Mechanics 31:679
Dettliff G (1979) An experimental study of liquefaction shock waves. J. Fluid Mech. 95:279
Duff RE (1959) Shock-tube performance at low initial pressure. Physics of Fluids 2:207
Fujikawa S, Okuda M, Akamatsu T, Goto T (1987) Non-equilibrium vapour condensation on a shock-tube endwall behind a reflected shock waves. J. Fluid Mech. 183:293
Kobayashi Y (1989) Vapor condensation behind a shock wave propagating through vapor-liquid two-phase media. In: Proc. IUTAM Symposium. pp 59–68
Maerafat M, Fujikawa S, Akamatsu T, Goto T (1989) An experimental study of non-equilibrium vapour condensation in a shock-tube. Experiments in Fluids 7:513
Roshko A (1960) On flow duration in low-pressure shock tubes. Physics of Fluids 3:835
Smolders HJ (1992) Non-linear wave phenomena in a gas-vapour mixture with phase transition. Ph.D. Thesis of University of Technology, Einhoven, The Netherlands
Thompson PA (1975) On possibility of complete condensation shock wave in retrograde fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 70:639
Thompson PA, Carofano GC, Kim YG (1986) Shock waves and phase change in a large-heat-capacity fluid emerging form a tube. J. Fluid Mech. 166:57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, Y., Watanabe, T. & Nagai, N. Vapor condensation behind a shock wave propagating through a large molecular-mass medium. Shock Waves 5, 287–292 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425221
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425221