Abstract
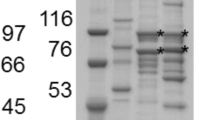
Clostridium thermocellum, strain JW20 (ATCC 31449) when growing in cellulose produces a cellulolytic enzyme system, that at the early stage of the fermentation is largely bound to the substrate. As cellulose is consumed the bound enzyme is released as free enzyme to the culture fluid. The bound enzyme fraction extracted with distilled water from the cellulose contains two major components, a large complex (Mr≃100×106) and a small complex Mr≃4.5×106) which were separated by gel filtration and sucrose solved by affinity chromatography into a complex that binds to the column and into a non-bindable mixture of proteins. All four fractions have endo-β-glucanase activity but only the two bound complexes and the free bindable complex hydrolyze crystalline cellulose with cellobiose as the main product. These three complexes are qualitatively similar in that they each contain about 20 different polypeptides (Mr values from 45,000 to 200,000) of which about ten are major components. However, the relative amounts of some of the peptides in the complexes differ. At least four polypeptides of the complexes have endo-β-glucanase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CM:
-
cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose
- CMCase:
-
carboxymethyl cellulase cosidered endo-β-1,4-glucanase
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
- YAS:
-
yellow affinity substance
- YAS-cellulose:
-
yellow affinity substance-cellulose complex
References
Ait N, Cruezet N, Forget P (1979) Partial purification ofcellulase from Clostridium thermocellum. J Gen Microbiol 113: 399–402
Almin KE, Ericsson KE, Jansson C (1967) Enzymic degradation of polymers. II. Viscometric determination of cellulase activity in absolute terms. Biochim Biophys Acta 139: 248–253
Bayer EA, Kenig R, Lamed R (1983) Adherence of Clostridium thermocellum to cellulose. J Bacteriol 156: 818–827
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Cornet P, Millet J, Beguin P, Aubert JP (1983) Characterization of two cell (cellulose degradation) genes of Clostridium thermocellum coding for endoglucanases. Bio/Technol 1: 580–594
Coughlan MP, Hon-nami K, Hon-nami H, Ljungdahl LG, Paulin JJ, Rigsby WE (1985) The cellulolytic enzyme complex of Clostridium thermocellum is very large. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 130: 904–909
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28: 350–356
Hon-nami K, Coughlan MP, Hon-nami H, Carreira LH, Ljungdahl LG (1986) Properties of the cellulolytic enzyme system of Clostridium thermocellum. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp (in press)
Johnson EA, Demain AL (1984) Probable involvement of sulfhydryl groups and a metal as essential components of the cellulase of Clostridium thermocellum. Arch Microbiol 137: 135–138
Johnson EA, Reese ET, Demain AL (1982a) Inhibition of Clostridium thermocellum cellulase by end products of cellulolysis. J Appl Biochem 4: 64–71
Johnson EA, Sakajoh M, Halliwell G, Madia A, Demain AL (1982b) Saccharification of complex cellulosic substrates by the cellulase system from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol 43: 1125–1132
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Lamed R, Kenig R, Setter E, Bayer EA (1985) Major characteristics of the cellulolytic system of Clostridium thermocellum coincide with those of the purified cellulosome. Enzyme Microb Technol 7: 37–41
Lamed R, Setter E, Bayer EA (1983) Characterization of cellulosebinding, cellulase-containing complex in Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol 156: 828–836
Ljungdahl LG, Carreira LH, Wiegel J (1981) Production of ethanol from carbohydrates using anaerobic thermophilic bacteria. In: The Ekman-Days International Symposium on Wood and Pulping Chemistry, vol 4. SPCI, Stockholm, pp 24–28
Ljungdahl LG, Pettersson B, Eriksson KE, Wiegel J (1983) A yellow affinity substance involved in the cellulolytic system of Clostridium thermocellum. Curr Microbiol 9: 195–200
McHale A, Coughlan MP (1980) Synergistic hydrolysis of crystalline cellulose by components of the extracellular cellulase system of Talaromyces emersonii. FEBS Lett 117: 319–322
Millet J, Petre D, Beguin P, Raynaud O, Aubert JP (1985) Cloning of ten distinct DNA fragments of Clostridium thermocellum coding for cellulases. FEMS Microbiol Lett 29: 145–149
Ng TK, Zeikus JG (1981) Purification and characterization of an endoglucanase (1,4-β-d-glucan glucanohydrolase) from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochem J 199: 341–350
Petre J, Longin R, Millet J (1981) Purification and characterization of an endo-β-1,4-glucanase from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochimie 63: 629–639
Segrest JP, Jackson RL (1972) Molecular weight determination of glycoproteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Meth Enzymol 28: 54–63
Weber K, Osborn MJ (1969) The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem 244: 4406–4412
Wiegel J, Dykstra M (1984) Clostridium thermocellum adhesion and sporulation while adhered to cellulose and hemicellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20: 59–65
Wiegel J, Ljungdahl LG (1980) Ethanol as fermentation product of extreme thermophilic, anaerobic bacteria. In: Dellweg H (ed) Viertes Symposium Technische Mikrobiologie. Verlag Versuchs- und Lehranstalt für Spiritusfabrikation und Fermentationstechnologie, Berlin, pp 117–127
Wu JHD, Demain AL (1985) Purification of the extracelular cellulase system of Clostridium thermocellum. Ann Meet Am Soc Microbiol, Abstr. 079:248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hon-nami, K., Coughlan, M.P., Hon-nami, H. et al. Separation and characterization of the complexes constituting the cellulolytic enzyme system of Clostridium thermocellum . Arch. Microbiol. 145, 13–19 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413021
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413021