Abstract
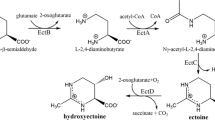
The halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halochloris is able to synthesize both nitrogen-containing (betaine, ectoine) and nitrogen-free (trehalose) compatible solutes. In the absence of external ammonium and under nitrogen-limited growth conditions ectoine was metabolized and trehalose partly replaced betaine. The cytoplasmic trehalose concentration did not exceeded 0.5 mol/kg water (approx. 30% of total compatible solutes). A decreasing content of betaine in cells growing under nitrogen limitation is a result of decreased biosynthesis. Apparently, the betaine pool cannot be used as a nitrogen source, not even in a situation of total nitrogen depletion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BrownAD (1976) Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev 40: 803–846
Galinski EA (1986) Salzadaptation durch kompatible Solute bei halophilen phototrophen Bakterien. Ph D thesis, University of Bonn
GalinskiEA, TrüperHG (1982) Betaine, a compatible solute in the extremely halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halochloris. FEMS Microbiol Lett 13: 357–360
GalinskiEA, PfeifferHP, TrüperHG (1985) 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid, a novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur J Biochem 149: 135–139
HerzogRM, GalinskiEA, TrüperHG (1990) Degradation of the compatible solute trehalose in Ectothiorhodospira halochloris: isolation and characterization of trehalase. Arch Microbiol 153: 600–606
ImhoffJF, TrüperHG (1977) Ectothiorhodospira halochloris sp. nov., a new extremely halophilic phototrophic bacterium containing bacteriochlorophyll b. Arch Microbiol 114: 115–121
KromMD (1980) Spectrophotometric determination of ammonia: A study of a modified Berthelot reaction using salicylate and dichloroisocyanurate. Analyst 105: 303–316
LanyiJK (1974) Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 38: 272–290
LawJH, SlepeckyRA (1961) Assay of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid. J Bacteriol 82: 33–36
LoewusFA (1952) Improvement in the anthron method for determination of carbohydrate. Anal Chem 24: 219
LowryOH, RosebroughNJ, FarrAL, RandallRF (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
MackayMA, NortonRS, BorowitzkaLJ (1984) Organic osmoregulatory solutes in cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 130: 2177–2191
MohammadFAA, ReedRH, StewartWDP (1983) The halophilic cyanobacterium Synechocystis DUN 52 and its osmotic responses. FEMS Microbiol Lett 16: 287–290
ReedRH, RichardsonDL, WarrSRC, StewartWDP (1984) Carbohydrate accumulation and osmotic stress in cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 130: 1–4
ReistadR (1970) On the composition and nature of the bulk protein of extremely halophilic bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol 71: 353–360
SchmidtK, Liaen-JensenS, SchlegelHG (1963) Die Carotinoide der Thiorhodaceae. I. Okenon als Hauptcarotinoid von chromatium okenii Perty. Arch Mikrobiol 46: 117–126
StumpfDK (1984) Quantitation and purification of quarternary ammonium compounds from halophyte tissue. Plant Physiol 75: 273–274
SutherlandIW, WilkinsonJF (1971) Chemical extraction methods of microbial cells. In: NorrisJR, RibbonsDW (eds) Methods in microbiology, vol 5 B. Academic Press, London, pp 345–384
TakacsFP, MatulaTI, l MacLeodRA (1964) Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XIII. Intracellular concentrations of sodium and potassium ions in a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol 87: 510–518
TrüperHG, GalinskiEA (1986) Concentrated brines as habitats for microorganisms. Experientia 42: 1182–1187
Tschichholz I, Trüper HG (1990) Fate of compatible solutes during dilution stress in Ectothiorhodospira halochloris. FEMS Microbiology Ecology (in press)
VialleJ, KoloskyM, RoccaJL (1981) Determination of betaine in sugar and wine by liquid chromatography. J Chromatog 204: 429–435
VisentinLP, ChowC, MathesonAT, YaguchiM, RollinF (1972) Halobacterium cutirubrum ribosomes. Properties of the ribosomal proteins and ribonucleic acid. Biochem J 130: 103–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galinski, E.A., Herzog, R.M. The role of trehalose as a substitute for nitrogen-containing compatible solutes (Ectothiorhodospira halochloris). Arch. Microbiol. 153, 607–613 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00245273
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00245273