Abstract
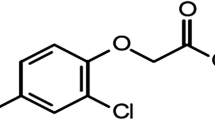
Chronic dieldrin administration to rats (5 mg/kg/day) produced pathological changes in liver and kidney tissues. Dieldrin treated rats showed high levels of liver ascorbic acid and increased activities of inorganic pyrophosphatase in brain and glucose-6-phosphatase in liver. The activities of Mg2+-ATPase in liver and acetylcholinesterase in brain were decreased under toxic doses of dieldrin. L-Ascorbic acid supplements in treated animals could partially prevent the pathological alterations, as observed histologically in liver and kidney tissues. Administration of this vitamin could also prevent alterations in some enzyme activities produced by toxic dieldrin doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakraborty D, Bhatacharyya A, Mazumdar K, Chatterjee K, Sen A, Chatterjee GC (1978a) Studies on L-ascorbic acid metabolism in rats under chronic toxicity due to organophosphorus insecticides: Effects of supplementation of L-ascorbic acid in high doses. J Nutr 108: 973–980
Chakraborty D, Bhattacharyya A, Chatterjee J, Chatterjee K, Sen A, Chatterjee S, Mazumdar K, Chatterjee GC (1978b) Biochemical studies on polychlorinated biphenyl toxicity in rats: Manipulation by Vitamin C. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 48 (1): 22–31
Chatterjee K, Banerjee SK, Tiwari R, Mazumdar K, Bhattacharyya A, Chatterjee GC (1981) Studies on the protective effects of L-ascorbic acid in chronic chlordane toxicity. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 51 (3): 254–265
Chatterjee GC, Chatterjee S, Chatterjee K, Sahu A, Bhattacharyya A, Chakraborty D, Das PK (1979) Studies on the protective effects of ascorbic acid in rubidium toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 51: 47–58
Chatterjee GC, Roy RK, Sasmal N, Banerjee SK, Mazumdar PK (1973) Effects of chromium and tungsten on L-ascorbic acid metabolism in rats and chicks. J Nutr 103: 509–514
Hiddemen JW, Cornish HH (1970) Dieldrin induced hyperglycemia in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 17: 277–289
Hutterer F, Klion FM, Wengraf A, Schaffner F, Popper H (1969) Hepatocellular adaptation and injury: Structural and biochemical changes following dieldrin and methyl butter yellow. Lab Invest 20: 455–464
Stevens JT, Oberholser KM, Wagner SR, Greene FE (1977) Content and activities of microsomal electron transport components during the development of dieldrin induced hypertrophic hypoactive endoplasmic reticulum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 39: 411–421
Street JC, Chadwick RW (1975) Ascorbic acid requirements and metabolism in relation to organochlorine pesticides. Ann NY Acad Sci 258: 132–143
Walker AIT, Stevenson DE, Robinson J, Thorpe E, Roberts M (1969) The toxicology and pharmacodynamics of dieldrin (HEOD): Two year oral exposures of rats and dogs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 15: 345–373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandyopadhyay, S.K., Tiwari, R.K., Mitra, A. et al. Effects of L-ascorbic acid supplementation on dieldrin toxicity in rats. Arch Toxicol 50, 227–232 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310854
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310854