Abstract
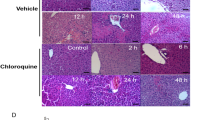
Chlordecone (CD) pretreatment is known to markedly potentiate CCl4 hepatotoxicity. Previous studies have shown that prior exposure to CD obtunds the increased hepatocellular regeneration and repair observed in non-treated rats challenged with a single, low dose of CCl4. These observations allowed us to hypothesize that suppression of hepatic regeneration and tissue repair by CD + CCl4 combination treatment might be involved in this interaction. To test this hypothesis, CCl4 hepatotoxicity was evaluated in actively regenerating livers using CD-treated (10 ppm in the diet for 15 days), surgically partially hepatectomized (PH) male Sprague-Dawley rats. Rats undergoing no surgical manipulation (CTRL) and sham operation (SH) were included as appropriate controls. Surgical manipulations were conducted on day 15 of the dietary protocol. Based on liver-to-body weight ratios (LW/BW), mitotic indices, hepatic cytochrome P-450 content, and hepatic glutathione (GSH and GSSG) levels, PH-induced hepatocellular regeneration was not affected by pretreatment with CD. Thus, the PH model was considered valid for assessing the effects of CD + CCl4 combination treatment. CCl4 (100 μl/kg; i.p.) was administered 1, 2, 4 or 7 days after the surgical manipulations. Hepatotoxicity was assessed 24 h later by measuring LW/BW and serum enzymes (SGPT, SGOT and ICD) in all four groups. Hepatic histopathological, histomorphometric and lethal effects were assessed in animals receiving CCl4 1 or 7 days after the surgical manipulations. CCl4-induced increases in LW/BW were observed in CD + PH rats receiving CCl4 4 or 7 days post-PH, but not in the 1 or 2 day post-PH groups in which the hepatocellular regeneration was maximal. CCl4-induced serum enzyme elevations were significantly less in the CD + PH rats as compared to CD + SH. This decrease in the serum enzyme elevations was most prominent in the 1 day post-PH group, where the hepatocellular mitotic activity was most pronounced. CCl4 lethality, assessed in the 1 day post-surgical manipulation group, was also decreased in the CD + PH rats in comparison to CD + SH rats. Such a protection was not observed in rats receiving CCl4 7 days post-PH. These data are consistent with and are supportive of the hypothesis that a suppression of otherwise normally stimulated hepatocellular regeneration following low-dose CCl4 administration is involved in the marked amplification of CCl4 toxicity by CD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
chlordecone
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- GSSG:
-
oxidized glutathione
- PH:
-
partial hepatectomy
- SH:
-
shamhepatectomy
- CTRL:
-
control, not surgically manipulated
- N:
-
normal diet
- LW/BW:
-
liver weight-to-body weight ratio
- SGPT:
-
serum glutamic; pyruvic transaminase
- SGOT:
-
serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase
- ICD:
-
isocitrate dehydrogenase
References
Agarwal AK, Mehendale HM (1984) Excessive hepatic accumulation of intracellular Ca2+ in chlordecone potentiated CCl4 toxicity. Toxicology 30: 17–24
Agarwal AK, Mehendale HM (1986) Effect of chlordecone on carbon tetrachloride-induced increase in calcium uptake in isolated perfused liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 83: 342–348
Barker EA, Arcasoy M, Smuckler EA (1969) A comparison of the effects of partial surgical and partial chemical (CCl4) hepatectomy on microsomal cytochrome b5 and P-450 and oxidative demethylation. Agents Actions 1: 27–34
Bucher NLR (1967) Experimental aspects of hepatic regeneration. N Engl J Med 227: 686–696
Chang LW, Perieria MA, Klaunig JE (1985) Cytotoxicity of halogenated alkanes in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes from normal partial hepatectomized and preneoplastic/neoplastic liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 80: 274–283
Curtis LR, Mehendale HM (1980) Specificity of chlordecone-induced potentiation of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Dispos 8: 23–27
Curtis LR, Williams WL, Mehendale HM (1979) Potentiation of hepatotoxicity of carbon tetrachloride following pre-exposure to chlordecone (Kepone) in the male rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 51: 283–293
Curtis LR, Thureson-Klein AK, Mehendale HM (1981) Ultrastructural and biochemical correlates of the specificity of chlordecone-potentiated carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. J Toxicol Environ Health 7: 499–517
Davis ME, Mehendale HM (1980) Functional and biochemical correlates of chlordecone exposure and its enhancement of CCl4 hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 15: 91–103
Digernes V, Bronstad G, Danol TE, Christoferson T (1982) The proliferative response of rat liver parenchymal cell after partial hepatectomy. Cell Tissue Kinet 15: 521–528
Egle JL, Fernandez SB, Guzelian PS, Borzelleca JF (1978) Distribution and excretion of chlordecone (Kepone) in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos 6: 91–95
Garner RC, McLean AEM (1969) Increased susceptibility to carbon tetrachloride poisoning in the rat after treatment with oral phenobarbitone. Biochem Pharmacol 18: 645–650
Henderson PT, Kersten KJ (1970) Metabolism of drugs during rat liver regeneration. Biochem Pharmacol 19: 2343–2352
Hewitt WR, Miyajima H, Cote MG, Plaa GL (1979) Modification of haloalkane-induced hepatotoxicity by exogenous ketones and metabolic ketosis. Fed Proc 39: 3118–3123
Higgins GM, Anderson RM (1931) Experimental pathology of the liver. I. Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol 12: 186–202
Iwata T, Ota K (1969) Effect of anticancer drugs on DNA synthesis and mitosis in regenerating rat liver. Gann 60: 13–22
Jackson CD, Irving CC (1973) Effects of α-acetyl aminofluorene on liver cell proliferation after partial hepatectomy of female rats. Cancer Res 33: 397–401
King J (1967) Thesis, Institute of Medical Laboratory Technology, London. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 2, 2nd Edn. Academic Press, New York
Klingensmith JS (1982) Metabolism of CCl4 in rats pretreated with chlordecone, mirex and phenobarbital. Doctoral Dissertation, pp 118–121
Klingensmith JS, Mehendale HM (1982a) Potentiation of CCl4 lethality by chlordecone. Toxicol Lett 11: 149–154
Klingensmith JS, Mehendale HM (1982b) In vivo metabolism of CCl4 by rats pretreated with chlordecone, mirex or phenobarbital. Pharmacologist 24: 136
Klingensmith JS, Mehendale HM (1983) Hepatic microsomal metabolism of CCl4 after pretreatment with chlordecone, mirex or phenobarbital in male rats. Drug Metab Dispos 11: 329–334
Lockard VG, Mehendale HM, O'Neal RM (1983a) Chlordeconeinduced potentiation of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity: a light and electron microscopic study. Exp Mol Pathol 39: 230–245
Lockard VG, Mehendale HM, O'Neal RM (1983b) Chlordeconeinduced potentiation of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity: a morphometric and biochemical study. Exp Mol Pathol 39: 246–255
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Malamud D, Gonzalez EM, Chiu H, Malt RA (1972) Inhibition of cell proliferation by azothioprine. Cancer Res 32: 1226–1229
McLean AEM, McLean EK (1966) The effect of diet and 1, 1, 1, trichloro -2, 2-bis- (p-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) on microsomal hydroxylating enzymes and on sensitivity of rats to carbon tetrachloride poisoning. Biochem J 100: 564–571
Mehendale HM (1977) Effect of pre-exposure to kepone on the biliary excretion of imipramine and sulfobromophthalein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 40: 247–259
Mehendale HM (1981) Onset and recovery from chlordecone and mirex-induced hepatobiliary dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 58: 132–139
Mehendale HM (1984) Potentiation of halomethane hepatotoxicity: chlordecone and carbon tetrachloride. Fund Appl Toxicol 4: 295–308
Omura T, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem 239: 2370–2378
Ord MG, Stocken LA (1984) Functional restoration and compensatory hyperplasia in mammalian systems. In: Cell and tissue regeneration. John Wiley & Son, New York, pp 50–52
Reed DJ, Babson JR, Beatty PW, Brodie AE, Ellis WW, Potter DW (1980) High performance liquid chromatography analysis of nanomole levels of glutathione, glutathione disulfide and related thiols and disulfides. Anal Biochem 106: 55–62
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28: 53–56
Roberts E, Ahluwalia MB, Lee G, Chan C, Sharma DSR, Farber E (1983) Resistance to hepatotoxins acquired by hepatocytes during liver regeneration. Cancer Res 43: 28–34
Ruch RJ, Klaunig JE, Pereira MA (1985) Selective resistance to cytotoxic agents in hepatocytes isolated from partially hepatectomized and neoplastic mouse liver. Cancer Lett 26: 295–301
Schwartz HS, Garofalo M, Stenberg SS, Philips FS (1965) Hydroxyurea: Inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in regenerating liver of rats. Cancer Res 25: 1867–1870
Weibel ER, Staubli W, Guagi HR, Hess FA (1969) Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. J Cell Biol 42: 68–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
These studies were made possible by a grant from the US Environmental Protection Agency R-811072
A. N. Bell is a Predoctoral Toxicology Trainee and Robert A. Young is a Postdoctoral Trainee supported by Toxicology Training grant from National Institute of Environmental Health Science ES-07045
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bell, A.N., Young, R.A., Lockard, V.G. et al. Protection of chlordecone-potentiated carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity and lethality by partial hepatectomy. Arch Toxicol 61, 392–405 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334621
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334621