Abstract
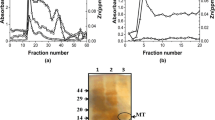
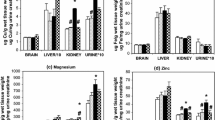
Metallothionein (MT) is one of the stress proteins which can easily be induced by various kind of heavy metals. However, MT in the brain is difficult to induce because of blood-brain barrier impermeability to␣most heavy metals. In this paper, we have attempted to induce brain MT in rats by exposure to methylmercury (MeHg) or metallic mercury vapor, both of which are known to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and cause neurological damage. Rats treated with MeHg (40 μmol/kg per day × 5 days, p.o.) showed brain Hg levels as high as 18 μg/g with slight neurological signs 10␣days after final administration, but brain MT levels remained unchanged. However, rats exposed to Hg vapor for 7 days showed 7–8 μg Hg/g brain tissue 24 h after cessation of exposure. At that time brain MT levels were about twice the control levels. Although brain Hg levels fell gradually with a half-life of 26 days, MT levels induced by Hg exposure remained unchanged for >2␣weeks. Gel fractionation revealed that most Hg was in the brain cytosol fraction and thus bound to MT. Hybridization analysis showed that, despite a significant increase in MT-I and -II mRNA in brain, MT-III mRNA was less affected. Although significant Hg accumulation and MT induction were observed also in kidney and liver of Hg vapor-exposed rats, these decreased more quickly than in brain. The long-lived MT in brain might at least partly be accounted for by longer half-life of Hg accumulated there. The present results showed that exposure to Hg vapor might be a suitable procedure to provide an in vivo model with enhanced brain MT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 June 1997 / Accepted: 4 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasutake, A., Nakano, A. & Hirayama, K. Induction by mercury compounds of brain metallothionein in rats: Hg0 exposure induces long-lived brain metallothionein. Arch Toxicol 72, 187–191 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050486
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050486