Abstract
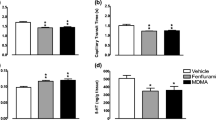
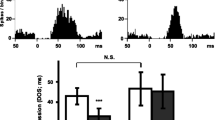
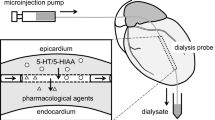
Rats were administered the selective serotonin (5-HT) uptake blocker citalopram or saline for 14 days to determine if prolonged treatment would lead to changes in extracellular 5-HT or autoreceptor sensitivity. One day after drug withdrawal, dialysis probes were implanted in the frontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus. Dialysis experiments were carried out using chloral hydrate anesthetized rats. The experimental protocol comprised the administration of three consecutive drug challenges: (1) After stable baseline levels were obtained, citalopram was infused through the dialysis probes to locally block uptake in the forebrain. (2) Subsequently, a 5-HT1B receptor agonist (RU24969 or CP93,129) was infused through the probe to test for changes in terminal autoreceptor sensitivity. (3) Last, citalopram was administered systemically to test the effect of indirect activation of somatodendritic autoreceptors. Under these conditions, with uptake already blocked locally in the forebrain, systemic citalopram produces a decrease in extracellular 5-HT, an effect that can be inhibited by pretreatment with antagonists of 5-HT1A receptors. The results indicate that during local infusion of citalopram extracellular 5-HT was significantly higher in the dorsal hippocampus of the chronic citalopram as compared to saline treatment group. This difference persisted throughout the full time course of the experiment. However, the decreases in 5-HT levels produced by local infusion of a 5-HT1B receptor agonist or after systemic citalopram administration were not significantly different between the chronic citalopram and saline treated groups. There were no significant differences between chronic citalopram and saline treated animals in frontal cortex. These results suggest that prolonged inhibition of 5-HT uptake may produce a selective change in the regulation of release from median raphe 5-HT neurons, but this change could not be clearly linked to a change in nerve terminal or somatodendritic autoreceptor sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1978) Feedback regulation of central monoaminergic neurons: evidence from single cell recording studies. In: Youdim MBH, Lovenberg W, Sharman DF, Lagnado JR (eds) Essays in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology. Wiley, New York, pp 2–32
Arnt J, Fredricson Overø K, Hyttel J, Olsen R (1984) Changes in rat dopamine- and serotonin function in vivo after prolonged administration of the specific 5-HT reuptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 84:457–465
Auerbach SB, Minzenberg MJ, Wilkinson LO (1989) Extracellular serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in hypothalamus of the unanesthetized rat measured by in vivo dialysis coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: dialysate serotonin reflects neuronal release. Brain Res 499:281–290
Auerbach SB, Rutter JJ, Juliano PJ (1991) Substituted piperazine and indole compounds increase extracellular serotonin in rat diencephalon as determined by in vivo microdialysis. Neuropharmacology 30:307–311
Auerbach SB, Lundberg JF, Hjorth S (1995) Differential inhibition of serotonin release by 5-HT and NA reuptake blockers after systemic administration. Neuropharmacology 34:89–96
Bel N, Artigas F (1993) Fluvoxamine preferentially increases extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in the raphe nuclei: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol 229:101–103
Blier P, De Montigny C, Chaput Y (1987) Modifications of the serotonin system by antidepressant treatments: implications for the therapeutic response in major depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 7:24S-35S
Blier P, Serrano A, Scatton B (1990) Differential responsiveness of the rat dorsal and median raphe 5-HT systems to 5-HT1 receptor agonists and p-chloroamphetamine. Synapse 5:120–133
Bosker FJ, Van Esseveldt KE, Klompmakers AA, Westenberg HGM (1995) Chronic treatment with fluvoxamine by osmotic minipumps fails to induce persistent functional changes in central 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors, as measured by in vivo microdialysis in dorsal hippocampus of conscious rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 117:358–363
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1978) Effects of antidepressant agents on the synthesis of brain monoamines. J Neural Transm 43:73–91
Chaput Y, De Montigny C, Blier P (1986) Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:342–348
Cox RF, Meller E, Waszczak BL (1993) Electrophysiological evidence for a large receptor reserve for inhibition of dorsal raphe neuronal firing by 5-HT1A agonists. Synapse 14:297–304
Delgado PL, Price LH, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1992) Neurochemistry of affective disorders. In: Paytkel ES (ed) Handbook of affective disorders. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 219–253
Fredricson Overø K (1982) Kinetics of citalopram in test animals; drug exposure in safety studies. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:297–309
Hajós M, Gartside SE, Sharp T (1995) Inhibition of median and dorsal raphe neurones following administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351:624–629
Hjorth S (1993) Serotonin 5-HT1A autoreceptor blockade potentiates the ability of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor citalopram to increase nerve terminal output of 5-HT in vivo — a microdialysis study. J Neurochem 60:776–779
Hjorth S, Auerbach SB (1994a) Further evidence for the importance of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the action of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI). Eur J Pharmacol 260:251–255
Hjorth S, Auerbach SB (1994b) Lack of 5-HT1A autoreceptor desensitization following chronic citalopram treatment, as determined by in vivo microdialysis. Neuropharmacol 33:331–334
Hjorth S, Magnusson T (1988) The 5-HT1A agonist 8-OH-DPAT preferentially activates cell body 5-HT autoreceptors in rat brain in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338:463–471
Hjorth S, Tao R (1991) The putative 5-HT1B receptor agonist CP-93,129 suppresses rat hippocampal 5-HT release in vivo: comparison with RU 24969. Eur J Pharmacol 209:249–252
Hjorth S, Carlsson A, Lindberg P, Sanchez D, Wikström H, Arvidsson L-E, Hacksell U, Nilsson JLG (1982) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, 8-OH-DPAT, a potent and selective simplified ergot congener with central 5-HT-receptor stimulating activity. J Neural Transm 55:169–188
Hyttel J, Fredricson Overø K, Arnt J (1984) Biochemical effects and drug levels in rats after long-term treatment with specific 5-HT-uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 83:20–27
Invernizzi R, Belli S, Samanin R (1992) Citalopram's ability to increase the extracellular concentrations of serotonin in the dorsal raphe prevents the drug's effect in the frontal cortex. Brain Res 584:322–324
Invernizzi R, Bramante M, Samanin R (1994) Chronic treatment with citalopram facilitates the effect of a challenge dose on cortical serotonin output: role of presynaptic 5-HTIA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 260:243–246
Jolas T, Haj-Dahmane S, Kidd EJ, Langlois X, Lanfumey L, Fattaccini CM, Vantalon V, Laporte AM, Adrien J, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1994) Central pre- and postsynaptic 5-HTIA receptors in rats treated chronically with a novel antidepressant, cericlamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1432–1443
Maura G, Raiteri M (1984) Functional evidence that chronic drugs induce adaptive changes of central autoreceptors regulating serotonin release. Eur J Pharmacol 97:309–313
Meltzer HY, Lowy MT (1987) The serotonin hypothesis of depression. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology: The third generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 513–526
Moret C, Briley M (1990) Serotonin autoreceptor subsensitivity and antidepressant activity. Eur J Pharmacol 180:351–356
O'Hearn E, Molliver ME (1984) Organization of raphé-cortical projections in rat: a quantitative retrograde study. Brain Res Bull 13:709–726
Paul IA, Nowak G, Layer RT, Popik P, Skolnick P (1994) Adaptation of the N-Methyl-spd-Aspartate receptor complex following chronic antidepressant treatments}. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269:95–102
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Rutter JJ, Gundlah C, Auerbach SB (1995) Systemic uptake inhibition decreases serotonin release via somatodendritic autoreceptor activation. Synapse 20:225–233
Rutter JJ, Gundlah C, Auerbach SB (1994) Increase in extracellular decotonin produced by uptake inhibitors is enhanced after chronic treatment with fluoxetine. Neurosci Lett 171:183–186
Schoups AA, De Potter WP (1988) Species dependence of adaptations at the pre- and postsynaptic serotonergic receptors following long-term antidepressant drug treatment. Biochem Pharmacol 37:4451–4460
Sharp T (1992) Biochemical measurement of serotonergic neurotransmission in vivo: effect of antidepressant and anxiolytic treatments. In: Elliott JM, Heal DJ, Marsden CA (eds) Experimental approaches to anxiety and depression. Wiley, New York, pp 117–149
Sharp T, Hjorth S (1990) Application of brain microdialysis to study the pharmacology of the 5-HT1A autoreceptor. J Neurosci Methods 34:83–90
Sharp T, Bramwell SR, Clark D, Grahame-Smith DG (1989a) In vivo measurements of brain extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine using microdialysis: changes in relation to 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neuronal activity. J Neurochem 53:234–240
Sharp T, Bramwell SR, Grahame-Smith DG (1989b) 5-HT1 agonists reduce 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat hippocampus in vivo as determined by brain microdialysis. Br J Pharmacol 96:283–290
Sinton CM, Fallon SL (1988) Electrophysiological evidence for a functional differentiation between subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 157:173–181
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1987) Electrophysiological responses of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse 1:3–9
Stark P, Fuller RW, Wong DT (1985) The pharmacologic profile of fluoxetine. J Clin Psychiatry 46:7–13
Tao R, Hjorth S (1992) α2-Adrenoceptor modulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat ventral hippocampus in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345:137–143
Törk I (1990) Anatomy of the serotonergic system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 600:9–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auerbach, S.B., Hjorth, S. Effect of chronic administration of the selective serotonin (5-HT) uptake inhibitor citalopram on extracellular 5-HT and apparent autoreceptor sensitivity in rat forebrain in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 352, 597–606 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171317
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171317