Summary
The binding of phenol red and digitoxin to bovine albumin has been measured by means of equilibration dialysis and characterized by the following parameters: binding constant K 1, number of binding sites per albumin molecule n, and free binding energy DF o.
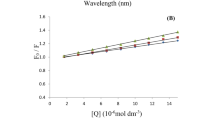
Protein binding of phenol red yields a saturation type curve with saturation at about 11.3 mmole/l.
Phenylbutazon and probenecid were able to displace phenol red from albumin binding sites in concentrations which are regularly reached after therapeutic doses.
With digitoxin because of its hydrophobic character plasma binding could not be measured beyond concentrations of 0.82 mmole/l. Though in principle there is no difference between phenol red and digitoxin binding (a digitoxin binding curve could be calculated also for high concentrations) no displacement effect was seen with probenecid, phenylbutazon, salicylic acid and benzbromaron up to tenfold therapeutic plasma levels.
These drugs were effective, however, in the displacement of digitoxin in diluted plasma albumin solutions. This indicates that for an effective displacement multiple molar concentrations of bound and displacing drug with respect to the binding protein are necessary. Displacement from plasma protein therefore plays no role in the possible interference of drugs if one of them is applied in doses far below the molar concentration of the binding proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Anton, A. H.: The relation between the binding of sulfonamides to albumin and their antibacterial efficacy. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 129, 282 (1960).
Bennhold, H., Kylin, E., Rusznyak, S.: Die Eiweißkörper des Blutplasmas. Leipzig: Steinkopf 1938.
Goldstein, A., Aronow, L., Kalman, S. M.: Principles of drug action, pp. 34–40. New York-Evanston-London: Harper and Row 1968.
Jähnchen, E., Kriegelstein, I., Kuschinsky, G.: Über den Einfluß saurer Substanzen auf die Bindung von Promazin an Rinderalbumin. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 260, 147 (1968).
Jeliffe, R. W., Blankenhorn, D. H.: Effect of phenobarbital on digitoxin metabolism. Clin. Res. 14, 160 (1966).
Josephson, B., Furst, P.: Sulfonamides competing with bilirubin for conjugation to albumin. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 18, 51 (1966).
Keen, P. M.: The displacement of three anionic drugs from binding to bovine serum albumin by various anionic compounds. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 26, 704–712 (1966).
Klotz, J. M.: The application of the Law of Mass Action to the binding by proteins. Interactions with Calcium. Arch. Biochem. 9, 109 (1946).
Klotz, J. M., Walter, F. M., Pivan, K. B.: The binding of organic ions by proteins. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 68, 1486 (1946b).
Krüger-Thiemer, E., Dettli, L., Spring, P., Diller, W.: Mathematical problems in the calculation of protein binding of drugs with digital computers. Estratto dal Volume degli Atti des 3° Congresso Internazionale di Medicina Cibernetica. Napoli 1964.
Kuschinsky, K.: Über die Bindungseigenschaften von Plasmaproteinen für Herzglykoside. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 262, 388 (1969).
Lukas, D. S., Martino, A. G. de: Binding of digitoxin and some related cardenolides to human plasma proteins. J. clin. Invest. 48, 1041 (1969).
Nemethy, G.: Hydrophobe Wechselwirkungen. Angew. Chem. 79, 260 (1967).
Odell, G. B.: Studies in kernicterus. I. The protein binding of bilirubin. J. clin. Invest. 38, 823 (1959).
Rodkey, F. L.: The binding of phenol red by serum and by bovine serum albumin. Arch. Biochem. 94, 38–47 (1961).
Rodkey, F. L.: Binding of phenol red by human serum albumin. Arch. Biochem. 94, 526–531 (1961b).
Scatchard, G.: The attractions of protein for small molecules and ions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 51, 660 (1949).
Scholtan, W.: Die Bindung der Sulfonamide an Eiweißkörper. (4. Mitteilung: Konzentrations-und Temperaturabhängigkeit der Eiweißbindung). Arzneimittel-Forsch. 14, 1139 (1964).
Scholtan, W., Schlossmann, K., Rosenkranz, H.: Bestimmung der Eiweißbindung von Digitalispräparaten mittels Ultrazentrifuge. Arzneimittel-Forsch. 16, 109 (1966).
Solomon, H. M., Reich, M. O. S., Spirt, O. S. N., Abrams, W. B.: Interactions between digitoxin and other drugs in vitro and in vivo. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 179, 362 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beeck, R., Braun, W., Damm, K.H. et al. Über den Einfluß verschiedener Pharmaka auf die Eiweißbindung von Phenolrot und Digitoxin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 275, 277–287 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500056
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500056