Summary
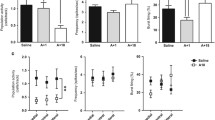
5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine lesions directed towards the central nucleus of the amygdala produced an apparently selective and localised destruction of 5HT terminals within the amygdaloid complex, without damage to dopamine neurons. Such lesions attenuated the biting responses produced by both amphetamine and apomorphine, suggesting that 5HT within this area may play an important role in the mediation of these behavioural effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azmitia, E. C., Segal, D. S.: An autoradiographic analysis of the differential ascending projections of the dorsal and median raphé nuclei in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 179, 641–668 (1978)
Baldessarini, R. J., Amatruda, T. T., Griffith, F. F., Gershon, S.: Differential effects of serotonin on turning and stereotypy induced by apomorphine. Brain Res. 93, 158–163 (1975)
Baumgarten, H. G., Victor, S. J., Lovenberg, W.: Effect of intraventricular injection of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine on regional tryptophan hydroxylase of rat brain. J. Neurochem. 21, 251–253 (1973)
Carter, C. J.: A study of the influences of central 5-hydroxytryptamine systems upon central dopaminergic function. Ph. D. Thesis, Bristol 1979
Carter, C. J., Pycock, C. J.: Differential effects of central serotonin manipulation on hyperactive and stereotyped behaviour. Life Sci. 23, 953–960 (1978)
Carter, C. J., Pycock, C. J.: The effects of 5,7-dihydroxytrayptamine lesions of extrapyramidal and mesolimbic sites on spontaneous motor behaviour, and amphetamine-induced stereotypy. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 308, 51–54 (1979)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J.: Stereotyped and circling behaviour induced by dopaminergic agonists after lesions of the midbrain raphe nuclei. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 29, 206–222 (1974)
Costall, B., Marsden, C. D., Naylor, R. J., Pycock, C. J.: Stereotyped behaviour patterns and hyperactivity induced by amphetamine and apomorphine after discrete 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of extrapyramidal and mesolimbic nuclei. Brain Res. 123, 89–111 (1977)
Cuello, A., Hiley, R., Iversen, L. L.: Use of catechol-O-methyltransferase for the enzyme radiochemical assay of dopamine. J. Neurochem. 21, 1337–1340 (1973)
Curzon, G., Green, A. R.: Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindole-acetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 39, 653–655 (1970)
DeGroot, J.: The rat forebrain in stereotaxic coordinates. Vehr. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 52, 14–39 (1959)
Emson, P. C., Björklund, A., Lindvall, O., Paxinos, G.: Contributions of different afferent pathways to the catecholamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine-innervation of the amygdala: a neurochemical and histochemical study. Neuroscience 4, 1347–1357 (1979)
Fuxe, K., Ungerstedt, U.: Histochemical, biochemical and functional studies on central monoamine neurons after acute and chronic amphetamine administration. In: Amphetamines and related compounds (E. Costa, S. Garattini, eds.), pp. 257–288. New York: Raven Press 1970
Grabowska, M.: Influence of apomorphine on brain serotonin turnover rate. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 3, 589–591 (1975)
Grabowska, M.: The involvement of serotonin in the mechanism of central action of apomorphine. Pol. J. Pharmacol. Pharm. 28, 389–394 (1976)
Grabowska, M., Michaluk, J., Antkiewicz, L.: Pharmacologic effects of apomorphine in rats with altered levels of brain serotonin. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz.) 23, 517–526 (1975)
Kerwin, R. W., Pycock, C. J.: Specific stimulating effect of glycine on 3H-dopamine efflux from substantia nigra slices of the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 54, 93–98 (1979)
Krettek, J. E., Price, J. L.: Amygdaloid projections to subcortical structures within the basal forebrain and brainstem in the rat and cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 178, 225–254 (1978)
Mogilnicka, G., Scheel-Kruger, J., Klimek, V., Golembiowska-Nikitin, J.: The influence of antiserotonergic agents on the action of dopaminergic drugs. Pol. J. Pharmacol. Pharm 29, 31–38 (1977)
Pycock, C. J., Horton, R. W., Carter, C. J.: Interactions of 5-hydroxytryptamine and aminobutyric acid with dopamine. Advances in Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 19, 323–341 (1978)
Rotrosen, J., Angrist, B. M., Wallach, M. B., Gershon, S.: Absence of serotonergic influence on apomorphine-induced stereotypy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 20, 133–138 (1972)
Saavedra, J. M., Brownstein, M., Palkovits, M.: Serotonin distribution in the limbic system of the rat. Brain Res. 79, 437–441 (1978)
Segal, D. S.: Differential effects of parachlorophenylalanine on amphetamine-induced locomotion and stereotypy. Brain Res. 116, 267–277 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, C.J., Pycock, C.J. 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine lesions of the amygdala reduce amphetamine-and apomorphine-induced stereotyped behaviour in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 312, 235–238 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499152
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499152