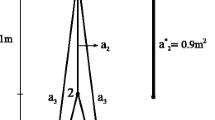
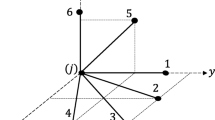
Abstract
A heuristic algorithm for optimal design of trusses is presented with account for stress and buckling constraints. The design variables are constituted by cross-sectional areas, configuration of nodes and the number of nodes and bars. Similarly to biological growth models, it is postulated that the structure evolves with the characteristic size parameter and the “bifurcation” of topology occurs with the generation of new nodes and bars in order to minimize the cost function. The first-order sensitivity derivatives provide the necessary information on topology variation and the optimality conditions for configuration and cross-sectional parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendsøe, M.P. 1995:Optimization of structural topology, shape and material. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer
Birker, T. 1996.New developments in structural optimization using optimality criteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Essen University. Also: Fortschrittberichte VDI, Nr. 199. Düsseldorf: VDI Verlag
Bojczuk, D.; Mróz, Z. 1998: Optimal design of trusses with account for topology variation.Mech. Struct. Mach. 26, 21–40
Gerdes, D. 1995:Strukturoptimierung unter Anwendung der Optimalitätskriterien auf diskretisierte Tragwerke bei besonderer Berücksichtigung der Stabilität (in German). Ph.D. Thesis, Essen University. Also: Düsseldorf: VDI Verlag
Kirsch, U. 1989: Optimal topologies of structures.Appl. Mech. Rev. 42, 223–239
Kirsch, U. 1996: Integration of reduction and expansion processes in layout optimization.Struct. Optim. 11, 13–18
Oberndorfer, J.M.; Achtziger, W.; Hörnlein, H.R.E.M. 1996: Two approaches for truss topology optimization: a comparison for practical use.Struct. Optim. 11, 137–144
Pedersen, P. 1992: Topology optimization of three-dimensional trusses. In: Bendsøe, M.P.; Mota-Soares, C.A. (eds.)Topology design of structures, pp. 19–30. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Rozvany, G.I.N. 1996: Difficulties in truss topology optimization with stress local buckling and system buckling constraints.Struct. Optim. 11, 213–217
Rozvany, G.I.N.; Birker, T. 1994: On singular topologies in exact layout optimization.Struct. Optim. 8, 228–235
Rozvany, G.I.N.; Birker, T. 1995: Generalized Michell structures — exact least-weight truss layouts for combined stress and displacement constraints. Part I—General theory for plane trusses.Struct. Optim. 9, 78–86
Rozvany, G.I.N.; Bendsøe, M.P., Kirsch, U. 1995: Layout optimization of structures.Appl. Mech. Rev. 48, 41–119.
Timoshenko, S.P.; Gere, J.M. 1961:Theory of elastic stability. New York: McGraw-Hill
Zhou, M. 1996: Difficulties in truss topology optimization with stress and local buckling constraints.Struct. Optim. 11, 134–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bojczuk, D., Mróz, Z. Optimal topology and configuration design of trusses with stress and buckling constraints. Structural Optimization 17, 25–35 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197710
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197710