Abstract
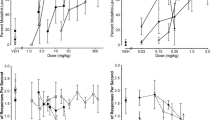
To investigate a dopaminergic component in the discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone, rats were trained to discriminate 2.5 mg/kg buspirone from saline, using a two lever, food-rewarded, fixed ratio 10 operant procedure. To test the dopamine-2(D2) antagonist action of buspirone, a second group of rats was trained to discriminate 0.16 mg/kg apomorphine from saline. In addition to a complete generalization to 8-OH-DPAT, the D2 antagonists haloperidol, R 79598 and sulpiride showed a partial generalization to buspirone. The benzodiazepine ligands chlordiazepoxide and bretazenil did not generalize to the buspirone cue. Buspirone (2.0 mg/kg) completely blocked the apomorphine cue in the apomorphine trained rats. Haloperidol, R 79895 and sulpiride also blocked the apomorphine cue, although at doses much smaller than the doses needed to evoke buspirone responding in the buspirone trained group. 8-OH-DPAT did not antagonize apomorphine. It was concluded that the D2 action of buspirone partially contributes to its discriminative stimulus properties. Mediation of the buspirone cue by 5-HT1a receptor activation seemed predominant. Further, buspirone can act as a full D2 antagonist in drug discrimination. A model was proposed suggesting a compound discriminative stimulus complex of buspirone with a dominant 5-HT1a component that overshadows a less pronounced D2 component.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ator NA (1991) Discriminative stimulus effects of the novel anxiolytic buspirone. Behav Pharmacol 2:3–14
Barrett JE, Witkin JM (1991) Buspirone in animal models of anxiety. In: Tunnicliff G, Eison AS, Taylor DP (eds) Buspirone: mechanisms and clinical aspects. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 37–79
Barrett JE, Witkin JM, Mansbach RS, Skolnick P, Weissman BA (1986) Behavioural studies with anxiolytic drugs. III. Antipunishment actions of buspirone in pigeons do not involve benzodiazepine receptor mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238S: 1009–1013
Barrett JE, Gleeson S, Nader MA, Hoffman SM (1989) Anticonflict effects of the 5-HT1a compound flesinoxan. J Psychopharmacol 3(1):64–69
Bergman J, Madras BK, Spealman RD (1991) Behavioural effects of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:910–917
Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (1982) Drug discrimination: applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier Amsterdam
Colpaert FC, Niemergeers CJE, Kuyps JJMD, Janssen PAJ (1975) Apomorphine as a discriminative stimulus, and its antagonism by haloperidol. Eur J Pharmacol 32:383–386
Cory-Slechta DA, Widzowski DV, Newland MC (1989) Behavioral differentiation of the stimulus properties of a dopaminergic D1 agonist from a D2 agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250 [3]:800–808
Cunningham KA, Callahan PM, Appel JB (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of lisuride revisited: involvement of dopamine D2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241 [1]:147–151
Davis M, Cassella JV, Kehne JH (1988) Serotonin does not mediate anxiolytic effects of buspirone in the fear-potentiated startle paradigm: comparison with 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone. Psychopharmacology 94:14–20
Gleeson S, Ahlers ST, Mansbach RS, Foust JM, Barrett JE (1989) Behavioral studies with anxiolytic drugs. VI. Effects on punished responding of drugs interacting with serotonin receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:809–817
Goa KL, Ward A (1986) Buspirone. A preliminary review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy as an anxiolytic. Drugs 32:114–129
Haefely WE (1984) Pharmacological profile of two benzodiazepine partial agonists: Ro 16–6028 and Ro 17–1812. Clin Neuropharmacol 7 [suppl. 1]:670–671
Hendry JS, Balster RL, Rosecrans JA (1983) Discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone compared to central nervous system depressants in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 19:97–101
Kamien JB, Woolverton WL (1989) Failure of SCH 23390 to function as a discriminative stimulus in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:337–340
Kamien JB, Woolverton WL (1990) Buspirone blocks the discriminative stimulus effects of apomorphine in monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:117–120
Kamien JB, Goldberg LI, Woolverton WL (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of D1 and D2 dopamine agonists in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242 [3]:804–811
Mansbach RS, Barrett JE (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone in the pigeon. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:364–369
McMillen BA (1991) Buspirone and the dopaminergic system. In: Tunnicliff G, Eison AS, Taylor DP (eds) Buspirone: mechanisms and clinical aspects. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 163–176
McMillen BA, Matthews RT, Sanghera MK, Shepard PD, German DC (1983) Dopamine receptor antagonism by the novel antianxiety drug, Buspirone. J Neurosci 3:733–738
Meert TF, Awouters FHL, De Haes PLAJ, Vermote PCM (1991) In: Olivier B, Mos J, Slangen JL (eds) Animal models in psychopharmacology. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 375–379
Montgomery AMJ, Rose IC, Herberg LJ (1991) 5-HT1a agonists and dopamine: the effects of 8-OH-DPAT and buspirone on brain-stimulation reward. J Neural Transm [GenSect] 83:139–148
Nader MA (1991) Behavioral effects of chronic buspirone administration in the pigeon — comparison to midazolam. Pharmacol. Biochem Behav 38:611–616
Nader MA, Hoffmann SM, Gleeson S, Barrett JE (1989) Further characterization of the discriminative stimulus effects of buspirone using monoamine agonists and antagonists in the pigeon. Behav Pharmacol 1:57–67
Pich EM, Samanin R (1986) Disinhibitory effects of buspirone and low doses of sulpiride and haloperidol in two experimental anxiety models in rats: possible role of dopamine. Psychopharmacology 89:125–130
Rijnders HJ, Slangen JL (1991) Haloperidol substitutes partially for buspirone in rats trained to discriminate buspirone from saline. In: Olivier B, Mos J, Slangen JL (eds) Animal models in psychopharmacology. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 381–386
Rijnders HJ, Järbe TUC, Slangen JL (1990) Extinction and reacquisition of differential responding in rats trained to discriminate between chlordiazepoxide and saline. Psychopharmacology 102:404–410
Rijnders HJ, Järbe TUC, Slangen JL (1991) The pentylenetetrazolecue antagonist actions of bretazenil (Ro 16–6028) as compared to midazolam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:129–132
Skarsfeldt T, Larsen JJ (1988) SCH 23390 — a selective dopamine D-1 receptor antagonist with putative 5-HT1 receptor agonistic activity. Eur J Pharmacol 148:389–395
Taylor DP, Riblet LA, Stanton HC, Eison AS, Eison MS, Temple DL (1982) Dopamine and antianxiety activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17 [suppl 1]:25–35
Tricklebank MD, Neil J, Kidd EJ, Fozard JR (1987) Mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of 8-OH-DPAT by the putative 5-HT1a receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 133:47–56
Tunnicliff G, Eison AS (1991) Clinical pharmacology of buspirone action. In: Tunnicliff G, Eison AS, Taylor DP (eds) Buspirone: mechanisms and clinical aspects. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 19–34
Tunnicliff, G, Eison, AS, Taylor, DP (1991) Buspirone: Mechanisms and clinical aspects. Academic Press, San Diego
Ukai M, Hiraiwa E, Kameyama T (1991) Pentazocine-like discriminative stimulus effects of morphine are blocked by the dopmaine D-1 antagonist SCH 23390, but not by the dopamine D-2 antagonist sulpiride. Brain Res 541:146–148
Weissman BA (1991) Interaction of buspirone with receptor binding sites. In: Tunnicliff G, Eison AS, Taylor DP (eds) Buspirone: mechanisms and clinical aspects. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 119–137
Woolverton WL, Kamien JB, Goldberg LI (1985) Effects of selective dopamine receptor agonists in rats trained to discriminate apomorphine from saline. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:577–581
Ybema CE, Slangen JL, Olivier B, Mos J (1990) Discriminative stimulus properties of flesinoxan. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:781–784
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rijnders, H.J., Slangen, J.L. The discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone involve dopamine-2 receptor antagonist activity. Psychopharmacology 111, 55–61 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257407
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257407