Abstract
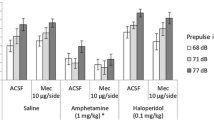
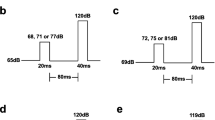
Separate experiments conducted in two different laboratories assessed the importance of the prepulse intensity in the ability of apomorphine to reduce prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle responses. Rats were presented with noise bursts alone or noise bursts 100 ms after presentation of prepulse stimuli ranging from 70 to 85 or 90 dB. Throughout testing, the background noise was maintained at 65 dB. In both laboratories, apomorphine markedly decreased the absolute magnitude of prepulse inhibition when the prepulse stimuli were no more than 10 dB above the background. With more intense prepulse stimuli, apomorphine had no significant effect on prepulse inhibition. Hence, apomorphine does not interfere with the inhibitory process which actually mediates prepulse inhibition, but appears to affect the detectability of the prepulse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia: human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Braff DL, Stone C, Callaway E, Geyer MA, Glick ID, Bali L (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15:339–343
Carlsson A (1978) Mechanism of action of neuroleptic drugs. In: Lipton MA, DiMascio A, Killam KF (eds), Psychopharmacology: a generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 1057–1070
Cassella JV, Davis M (1986) The design and calibration of a startle measurement system. Physiol Behav 36:377–383
Davis M (1988) Apomorphine,d-amphetamine, strychnine and yohimbine do not alter prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 95:151–156
Freedman R, Adler LE, Waldo MC, Pachtman E, Franks RD (1983) Neurophysiological evidence for a defect in inhibitory pathways in schizophrenia: comparison of medicated and drug-free patients. Biol Psychiatry 18:537–552
Geyer MA, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1987) Dopamine agonists and antagonists in an animal model of sensory gating and schizophrenia. Proc Soc Biol Psychiatry, p 156
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1990) Startle response models of sensorimotor gating and habituation deficits in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull (in press)
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. Some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 2:175–189
Leitner DS, Cohen ME (1985) Role of the inferior colliculus in the inhibition of acoustic startle in the rat. Physiol Behav 34:65–70
Leitner DS, Cohen ME (1988) Tectal modulation of acoustic startle in the rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 14:1100
Leitner DS, Powers AS, Stitt CL, Hoffman HS (1981) Midbrain reticular formation involvement in the inhibition of acoustic startle. Physiol Behav 26:259–268
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
Moore BCJ (1982) An introduction to the psychology of hearing. Academic Press, New York
Parisi T, Ison JR (1979) Development of the acoustic startle response in the rat: ontogenetic changes in the magnitude of inhibition by prepulse stimulation. Dev Psychobiol 12:219–230
Peng RY, Mansbach RS, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) A D2 dopamine receptor agonist disrupts sensorimotor gating in rats: implications for dopaminergic abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:211–218
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA, Koob GF (1986) Central dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21:23–33
Swerdlow NR, Koob GF, Geyer MA, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1988) A cross-species model of psychosis: mesolimbic dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. In: Soubrie P (ed) Animal models of psychiatric disorders. Karger, Basel, pp 1–18
Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Pulvirenti L, Koob GF, Braff DL (1990) Amphetamine disruption of prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle is reversed by depletion of mesolimbic dopamine. Psychopharmacology 100:413–416
Weiss GT, Davis M (1976) Automated system for acquisition and reduction of startle response data. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:713–720
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, M., Mansbach, R.S., Swerdlow, N.R. et al. Apomorphine disrupts the inhibition of acoustic startle induced by weak prepulses in rats. Psychopharmacology 102, 1–4 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245735
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245735