Abstract
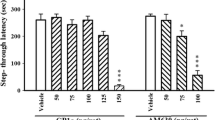
Previous research has demonstrated that low doses of anxiogenic central benzodiazepine receptor (CBR) ligands, the beta-carbolines, improve performance in various learning and memory tests in animals if administered prior to training. The present experiments compared the effect of a beta-carboline (FG 7142) with that of a pharmacologically distinct anxiogenic compound, a peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) ligand, 4′-chlorodiazepam (Ro5-4864), in two tests of learning and memory in rats. As expected, FG 7142 significantly improved performance in a passive avoidance test. Ro5-4864 was without effect. In a shuttlebox escape test, Ro5-4864 significantly impaired performance while FG 7142 had no effect. The effect of Ro5-4864 was antagonized by the specific peripheral benzodiazepine receptor antagonist, PK 11195. These results indicate that the differential impact of CBR and PBR anxiogenic ligands on performance in aversively-motivated learning tests may be a reflection of their distinct pharmacologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anholt RRH, Murphy KMM, Mack GE, Snyder SH (1984) Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in the central nervous system: localization to olfactory nerves. J Neurosci 4:5993–6003
Anholt RRH, Pederson PL, DeSouza EB, Snyder SH (1986) The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor: Localization to mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem 261:576–583
Basile AS, Skolnick P (1986) Subcellular localization of “peripheral-type” binding sites for benzodiazepines in rat brain. J Neurochem 461:305–308
Basile AS, Bolger GT, Lueddens HWM, Skolnick P (1989) Electrophysiological actions of Ro5-4864 on cerebellar Purkinje neurons: evidence for “peripheral” benzodiazepine receptor-mediated depression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:463–468
Benavides J, Malgouris C, Imbault F, Begassat F, Uzan A, Renault C, Dubroeucq MC, Gueremy C, Le Fur G (1983a) Peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites in rat adrenals: binding studies with [3H]PK 11195 and autoradiographic localization. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 266:38–49
Benavides J, Quarteronet D, Imbault F, Malgouris C, Uzan A, Renault C, Dubreucq MC, Gueremy C, Le Fur G (1983b) Labeling of ‘peripheral-type’ benzodiazepine binding sites in the rat brain using [3H]PK 11195, an isoquinoline carboxamide derivative: kinetic studies and autoradiographic localization. J Neurochem 41:1744–1750
Benavides F, Guilloux DE, Allam A, Uzan J, Mizoule J, Renault MC, Dubroeucq MC, Gueremy C, Le Fur G (1984) Opposite effects of an agonist, Ro5-4864, and an antagonist, PK 11195, of the peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites on audiogenic seizures in DBA/J2 mice. Life Sci 34:2613–2620
Bolger GT, Mezey E, Cott J, Weissman BA, Paul SM, Skolnick P (1984) Differential regulation of ‘central’ and ‘peripheral’ benzodiazepine binding sites in the rat olfactory bulb. Eur J Pharmacol 105:143–148
Braestrup C, Nielsen M (1986) Benzodiazepine receptor binding in vivo and efficacy. In: Olsen RW, Venter JC (eds) Benzodiazepine/GABA receptors and chloride channels: structural and functional properties. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 167–184
Braestrup C, Squires RF (1977) Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity [3H]diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3805–3809
Braestrup C, Nielsen M, Honore T, Jensen LH, Petersen EN (1983) Benzodiazepine ligands with positive and negative efficacy. Neuropharmacology 22:1451–1457
Corda MG, Blaker WD, Mendelion WB, Guidotti A, Costa E (1983) Beta-carbolines enhance the shock-induced suppression of drinking in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2072–2078
Costa E, Guidotti A (1979) Molecular mechanisms in the receptor action of benzodiazepines. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 19:531–545
Davies LP, Huston V (1981) Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites in heart and their interaction with dipyridamole. Eur J Pharmacol 73:209–211
Doble A, Malgouris M, Daniel M, Daniel F, Imbault F, Basbaum A, Uzan A, Gueremy C, Le Fur G (1987) Labelling of peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites in human brain with [3H]PK 11195: anatomical and subcellular distribution. Brain Res Bull 18:49–61
Drugan RC, Maier SF, Skolnick P, Crawley JN (1985) An anxiogenic benzodiazepine receptor ligand induces learned helplessness. Eur J Pharmacol 113:453–457
Drugan RC, Basile AS, Crawley JN, Paul SM, Skolnick P (1986) Inescapable shock reduces [3H] Ro5-4864 binding to peripheral type binding receptors in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:1673–1677
Drugan RC, Basile AS, Crawley JN, Paul SM, Skolnick P (1988) Characteristics of stress-induced alterations in [3H] Ro5-4865 binding to peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in rat heart and kidney Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:1015–1020
Drugan RC, Morrow AL, Weizman R, Weizman A, Deutsch SI, Crawley JN, Paul SM (1989) Stress-induced behavioral depression in the rat is associated with a decrease in GABA-receptor-mediated chloride ion flux and brain benzodiazepine receptor occupancy. Brain Res 487:45–51
File S, Pellow S (1988) Low and high doses of benzodiazepine inverse agonists respectively improve and impair performance in passive avoidance but do not affect habituation. Behav Brain Res 30:31–36
Gee K (1987) Phenylquiolines PK 8165 and PK 9084 allosterically modulate [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate binding to a chloride ionophore in rat brain via a novel Ro5-4864 binding site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:747–753
Karp L, Weizman A, Tyano S, Gavish M (1989) Examination stress, platelet peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites and plasma hormone levels. Life Sci 44:1077–1082
Maier SF, Seligman MEP (1976) Learned helplessness: theory and evidence. J Exp Psychol 105:3–46
Massotti M, Lucantoni D (1986) The peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand Ro5-4864 induces supraspinal convulsions in rabbits. Reversal by the central benzodiazepine antagonist Ro15-1788. Psychopharmacology 88:336–340
Medina JH, Novas ML, DeRobertis E (1986) Regulation of the benzodiazepine receptor: in vivo and in vitro experiments, In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol: GABAergic transmission and anxiety. Raven Press, New York, pp 107–121
Mizoule J, Gauthier A, Uzan A, Renault C, DuBroeuque M, Gueremy C, LeFur G (1985) Opposite effects of two ligands for peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites, PK11195 and Ro5-4864, in a conflict situation in the rat. Life Sci 36:1059–1068
Mohler H, Okada T (1977) Benzodiazepine receptors: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science 198:849–851
Novas PT, Medina JH, Calvo D, DeRobertis E (1987) Increase in peripheral binding sites in kidney and olfactory bulb in acutely stressed rats. Eur J Pharmacol 135:243–246
Paul SM, Marangos PJ, Skolnick P (1981) The benzodiazepine/GABA-chloride ionophore receptor complex: site of minor tranquilizer action. Biol Psychiatry 16:213–229
Pellow S, File S (1984) Behavioural actions of Ro5-4864: a peripheral type benzodiazepine? Life Sci 35:229–240
Rastogi SK, Ticku MK (1985) A possible role of a GABAergic mechanism in the convulsant action of Ro5-4864. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:285–288
Schoemaker H, Boles RG, Horst D, Yamamura HI (1983) Specific high-affinity binding sites for [3H]Ro5-4864 in rat brain and kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:61–66
Simmonds MA (1985) Antagonism of flurazepam and other effects of RO15-1788, PK 8165 and Ro5-4864 on the GABAA receptor complex in rat cuneate nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol 117:51–60
Tallman JF (1983) Agonist and antagonist interactions at benzodiazepine receptors. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Benzodiazepine recognition site ligands: biochemistry and pharmacology. Raven Press, New York
Ticku MK (1983) Benzodiazepine/GABA receptor-ionophore complex: current concepts. Neuropharmacology 22:1459–1470
Ticku MK, Ramanjaneyulu R (1984) Ro5-4864 inhibits binding of [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate to rat brain membranes. Life Sci 34:631–638
Trullas RH, Havoundjian H, Zamir H, Paul SM, Skolnick P (1987) Environmentally-induced modification of the benzodiazepine/GABA receptor coupled chloride ionophore. Psychopharmacology 97:384–390
Venault P, Chapouthier G, Prado de Carvalho L, Simiand J, Morre M, Dodd RH, Rossier J (1986) Benzodiazepine impairs and beta-carboline enhances performance in learning and memory tasks. Nature 321:864–866
Walker JM, Dixon W (1982) A solid state device for studying sensitivity to thermal pain. Physiol Behav 30:481–483
Wang JKR, Taninguchi T, Spector S (1980) Properties of [3H]diazepam binding sites on rat blood platelets. Life Sci 27:1881–1888
Weissman BA, Cott J, Paul SM, Skolnick P (1983) Ro5-4864: a potent benzodiazepine convulsant. Eur J Pharmacol 90:149–150
Weissman BA, Cott J, Jackson JA, Bolger GT, Weber KH, Horst WD, Paul SM, Skolnick P (1985) “Peripheral type” binding sites for benzodiazepines in brain: relationship to the convulsant actions of Ro5-4864. J Neurochem 44:1494–1499
Weizman R, Tanne Z, Granek M, Karp L, Golomb M, Tyano S, Gavish M (1987) Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites on platelet membranes are increased during diazepam treatment of anxious patients. Eur J Pharmacol 138:282–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmes, P.V., Drugan, R.C. Differential effects of anxiogenic central and peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands in tests of learning and memory. Psychopharmacology 104, 249–254 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244187
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244187