Abstract
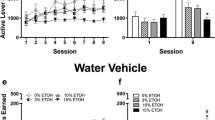
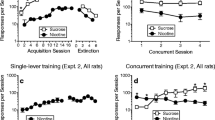
Rationale: The concepts of appetitive and consummatory behaviors provide a framework for examining ethanol-drinking behavior. However, traditional studies of ethanol self-administration using dipper procedures make separating the appetitive from the consummatory components difficult. Objective: This study compared the ability to initiate ethanol self-administration using a new sipper-tube self-administration procedure with the older established sucrose-substitution initiation model that employed dipper presented reinforcement. The new model was developed to allow for an assessment of the appetitive and consummatory components in ethanol self-administration. Methods: For the sipper-tube procedure, the rats were initiated to self-administer ethanol using a sucrose-substitution procedure that provided limited access to a sipper tube containing ethanol. This procedure required the completion of a fixed ratio requirement (FR4) in order to gain access to a sipper tube for 20 min. Initially, a 20% sucrose solution with no ethanol was provided in the sipper tube. Over sessions, the concentration of sucrose was reduced and the ethanol concentration increased, until 10% ethanol in water was the solution presented. A second group of animals was initiated to self-administer ethanol using the dipper-presentation procedure employed in our laboratory for many years. This group was used for comparison of the effectiveness of initiation in the sipper-tube procedure. Results: Following initiation, the sipper-tube rats self-administered 10% ethanol in water with intakes averaging 0.75 g/kg during the 20-min drinking period. Increasing the ethanol concentrations as high as 20%, increased intakes as high as 1.5 g/kg. The ethanol intakes observed were similar to those obtained with the dipper initiation procedure but occurred in one-third of the time. Conclusions: The sipper-tube procedure employed here results in similar ethanol self-administration behavior as has been found with a dipper presentation procedure. More importantly, however, it allows for a separation of the appetitive and consummatory components of ethanol self-administration. This separation may prove useful for examining the strength of ethanol-seeking behaviors without the confound of increasing levels of ethanol interacting with the appetitive seeking behaviors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 January 1999 / Final version: 28 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samson, H., Sharpe, A. & Denning, C. Initiation of ethanol self-administration in the rat using sucrose substitution in a sipper-tube procedure. Psychopharmacology 147, 274–279 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051167
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051167