Abstract
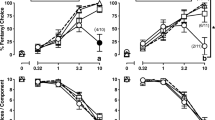
Rationale: Discriminative stimulus effects of mu opioids vary systematically as a function of training dose. Differences among training doses may arise from multiple mechanisms. Objectives: In vivo apparent pA2 analyses were used to examine the contributions of opioid mechanisms to stimulus control by low and high training doses of the mu opioid fentanyl. Methods: Saline and one of two doses of fentanyl, administered s.c., were established as discriminative stimuli in two groups of rats (low training dose group: 0.01 mg/kg; high training dose group: 0.04 mg/kg). Generalization tests and in vivo apparent pA2 analyses were used to evaluate receptor mechanisms of stimulus control. Results: Fentanyl, etonitazene, methadone, and morphine evoked full fentanyl generalization in both groups but were more potent in the low-dose group. Spiradoline and d-amphetamine did not evoke generalization in either group. Naltrexone antagonized stimulus and rate-altering effects of fentanyl in both groups, with apparent pA2 values of 7.6 in the low-dose group and 7.5 in the high-dose group. Nalbuphine and nalorphine evoked full generalization in the low-dose group but less than 40% generalization in the high-dose group. In the high-dose group, nalbuphine and nalorphine antagonized the stimulus and rate-altering effects of fentanyl with apparent pA2 values of 5.3 and 6.1, respectively, demonstrating lower efficacy mu actions. Conclusions: Changes in fentanyl training dose preserved the mu opioid selectivity of stimulus control but altered the intensity of the transduced mu opioid stimulus required for generalization. These differences in intensity of the fentanyl stimulus determined whether low efficacy mu opioids would evoke or antagonize fentanyl generalization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 February 1999 / Final version: 31 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Walker, E., Sutherland II, J. et al. Discriminative stimulus effects of two doses of fentanyl in rats: pharmacological selectivity and effect of training dose on agonist and antagonist effects of mu opioids. Psychopharmacology 148, 136–145 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050035
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050035