Abstract
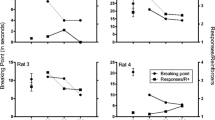
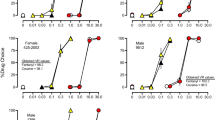
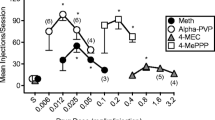
Rationale: Previous results suggested that naltrexone had opioid-selective effects on behavior reinforced by orally delivered drugs and food. The present study explores the possibility that previous results were due to presentation of the reinforcers in a closed economy (all reinforcers earned by subjects) and that naltrexone’s effect may be nonselective under conditions of an open economy (earned reinforcers supplemented by unearned). Objectives: The purpose of this experiment was to compare the effect of naltrexone on ethanol-, phencyclidine-(PCP), and food-reinforced responding under several open-economy conditions and compare them with those from a previous report using a closed economy. Methods: Ethanol (8% w/v), PCP (0.25 mg/ml), and food were available under independent, concurrent, progressive-ratio (PR) schedules with water, and side positions were alternated daily. Three naltrexone doses (0.1, 0.3, and 1.0 mg/kg) were administered in a nonsystematic order for 5 days, with the 5-day pretreatment period serving as a control. Four economic conditions were compared: data for the closed economy were taken from a recently completed experiment using the same monkeys. The open-economy condition was varied by allowing free access to 1, 2 or 3 times the amount of drug or food that was earned during session later during a post-session time-out period. Results: In an open economy, naltrexone nonselectively suppressed ethanol, PCP, and food-maintained behavior, in contrast to results in the previous study which used a closed economy, wherein naltrexone did not significantly suppress food- or PCP self-administration. As the economy for PCP, ethanol, and food became more open, the suppressant effects of naltrexone increased and, in many animals, behavioral measures decreased to zero. Conclusion: These results indicated that the economy under which drugs and food are self-administered is an important determinant of the effectiveness of naltrexone’s ability to suppress drug- and food-reinforced behavior. The results also suggest that testing medications for drug abuse using a food control condition under a closed economy can bias the results toward a conclusion of selectivity of the treatment medication for drug-reinforced behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 June 1999 / Final version: 27 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carroll, M., Cosgrove, K., Campbell, U. et al. Reductions in ethanol, phencyclidine, and food-maintained behavior by naltrexone pretreatment in monkeys is enhanced by open economic conditions. Psychopharmacology 148, 412–422 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050071