Abstract
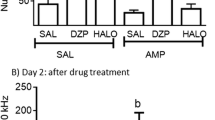
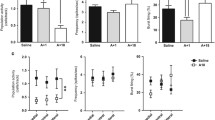
Reliable aggression was seen in rats which were grouped 30 days after undergoing continuous withdrawal from morphine. This withdrawal aggression, associated with long-lasting effects of morphine dependence, was blocked by morphine or lesions of the nigrostriatal bundle, but not by lesions of the median forebrain bundle. When the nigrostriatal lesioned rats were treated with a small dose of apomorphine, the aggression was reinstated. Apomorphine reduced the turnover of dopamine in the 30-day withdrawn rats at doses which were ineffective in similarly housed non-dependent rats. These results suggest that animals undergoing protracted morphine abstinence show aggression due to a latent dopaminergic supersensitivity, similar to that previously reported during acute narcotic withdrawal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anden, N. E., Carlson, A., Dahlstrom, A., Fuxe, K., Hillarp, N., Larsson, K.: Demonstration and mapping out of nigro neostriatal dopamine neurons. Life Sci. 3, 523–530 (1964)
Anden, N. E., Robenson, A., Fuxe, K., Hokfelt, T.: Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 627–629 (1967)
Carlsson, A., Waldeck, A.: A fluorometric method for the determination of dopamine. Acta physiol. scand. 44, 293–298 (1958)
Costa, E., Neff, N. H.: Isotopic and non-isotopic measurements of catecholamine biosynthesis. In: Biochemistry and pharmacology of the basal ganglia, pp. 141–156. E. Costa, L. Cote, and M. P. Yahr, Eds. New York: Raven Press 1966
Drawbaugh, R., Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M. D., Lal, H.: Self-multilation and bizarre behaviors in rats with nigrostriatal lesions given apomorphine or amphetamine: Antagonism by butyrophenones. Pharmacologist 15, 254 (1973)
Ernst, A. M.: Relation between the action of dopamine and apomorphine and their O-methylated derivatives upon the CNS. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 7, 391–399 (1965)
Himmelsbach, C. K.: Clinical studies of drug addiction. Physical dependence, withdrawal and recovery. Arch. intern. Med. 69, 766–772 (1942)
Himmelsbach, C. K.: Studies of the relation of drug addiction to the autonomic nervous system: Results of cold pressor test. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 73, 91–98 (1941)
Khazan, N., Colasanti, B.: EEG correlates of morphine challenge in post-addict rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 56–63 (1971)
Lal, H., O'Brien, J., Pitterman, A., Gianutsos, G., Reddy, C.: Aggression after amphetamines and dihydroxyphenylalanine. Fed. Proc. 31, 529 (1972)
Lal, H., O'Brien, J., Puri, S. K.: Morphine-withdrawal aggression: sensitization by amphetamines. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 217–223 (1971)
Lal, H., Puri, S. K.: Morphine-withdrawal aggression: Role of dopaminergic stimulation. In: Drug addiction, vol. 1, pp. 301–310. J. Singh, L. H. Miller and H. Lal, Eds. Mount Kisco, N.Y.: Futura Press 1972
Martin, W. R., Jasinski, D. R.: Physiologic parameters of morphine dependence in man-tolerance, early abstinence, protracted abstinence. J. Psychiat. Res. 7, 9–17 (1969)
Martin, W. R., Jasinski, D. R., Sapira, J. D., Flanery, H. G., Kelly, O. A., Thompson, A. K., Logan, C. R.: The respiratory effects of morphine during a cycle of dependence. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 162, 182–189 (1968)
Martin, W. R., Sloan, J. W.: The pathophysiology of morphine dependence and its treatment with opioid antagonists. Pharmakopsychiat. Neuro-Psychopharmak. 1, 260–270 (1968)
Martin, W. R., Wikler, A., Eades, C. G., Pescor, F. T.: Tolerance to and physical dependence on morphine in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 4, 247–260 (1963)
Nash, P., Colasanti, B., Khazan, N.: Long-term effects of morphine on the electroencephalogram and behavior of the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 29, 271–276 (1973)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of dopaminergic stimulation or blockade on morphine-withdrawal aggression. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 113–118 (1973)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of morphine, haloperidol, apomorphine and benzotropine on dopamine turnover in rat corpus striatum: Evidence showing morphine induced reduction in CNS dopaminergic activity. Fed. Proc. 32, 758 (1973a)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of apomorphine, benzotropine or morphine on striatal dopamine turnover: Evidence for latent supersensitivity of dopaminergic receptors in morphine dependent rats. Pharmacologist 15, 247 (1973b)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Reduced threshold to pain induced aggression specifically related to morphine dependence. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) (in press) (1974)
Puri, S. K., Reddy, C. R., Lal, H.: Blockade of central dopaminergic receptors by morphine: Effect of haloperidol, apomorphine or benztropine. Res. Comm. Chem. Path. Pharmacol. 5, 389–401 (1973)
Seevers, M. H., Deneau, G. A.: Physiological aspects of tolerance and physical dependence. In: Physiological pharmacology, Vol. 1, pp. 565–640. W. S. Root and F. G. Hofmann, Eds. New York: Academic Press 1963
Spano, P. F., Neff, N. H.: Procedure for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in brain. Analyt. Biochem. 42, 113–118 (1971)
Thor, D. H.: Chemical induction of traumatic fighting behavior. Proc. Amer. psychol. Ass. 4, 883–884 (1969)
Wikler, A.: Some implications of conditioning theory for problems of drug abuse. Behav. Sci. 16, 92–97 (1971)
Wikler, A., Pescor, F. T.: Classical conditioning of a morphine abstinence phenomenon, reinforcement of opioid drinking behavior and “relapse” in morphine addicted rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 255–284 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M.D., Puri, S.K. et al. Effect of apomorphine and nigrostriatal lesions on aggression and striatal dopamine turnover during morphine withdrawal: Evidence for dopaminergic supersensitivity in protracted abstinence. Psychopharmacologia 34, 37–44 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421218
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421218