Abstract
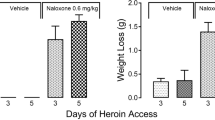
An intravenous infusion method is described for rapidly producing physical dependence in rats. Rats were infused with morphine or meperidine for 24 or 48 h at constant rates and the development of physical dependence was assessed by body weight loss after naloxone challenge. Naloxone challenge induced body weight losses that were dependent upon magnitude, rate and duration of infusion. The steady-state concentrations of morphine (4 mg/kg/h) in serum and meperidine (6 mg/kg/h) in plasma were 4 and 2.5 μg/ml, respectively. Morphine concentration in the brain in the steady-state (4 mg/kg/h) was 0.7 μg/g and in the serum was proportional to the infusion rate. Maximum body weight loss was significantly correlated with total amount of infused morphine, but not with the steady-state concentration of the drug in the serum. These results suggest that total doses of infused morphine, not steady-state concentrations, are critical in producing body weight loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akera T, Brody TM (1968) The addiction cycle to narcotics in the rat and its relation to catecholamines. Biochem Pharmacol 17:675–688
Bhargava HN (1977) Rapid induction and quantitation of morphine dependence in the rat by pellet implanation. Psychopharmacology 52:55–62
Bläsig J, Herz A, Reinhold K, Zieglgänsberger S (1973) Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia 33:19–38
Collier HOJ, Francis DL, Schneider C (1972) Modification of morphine withdrawal by drugs interacting with hormonal mechanisms: some contradictions and their interpretation. Nature 237:220–223
Cox BM, Ginsburg M, Osman OH (1968) Acute tolerance to narcotic analgesic drugs in rats. Br J Pharmacol 33:245–256
Domino EF, Wilson A (1973) Effect of narcotic analgesic agonists and antagonists on rat brain acetylcholine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 184:18–32
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Goode PG (1971) An implanted reservoir of morphine solution for rapid induction of physical dependence in rats. Br J Pharmacol 41:558–566
Horning MG, Gregory P, Nowlin J, Stafford M, Lertratanangkoon K, Butler C, Stillwell WG, Hill RM (1974) Isolation of drugs and drug metabolites from biological fluids by use of salt-solvent pairs. Clin Chem 20:282–287
Hosoya E (1959) Some withdrawal symptoms of rats to morphine. Pharmacologist 1:77
Huidobro F, Maggiolo C (1961) Some features of the abstinence syndrome to morphine in mice. Acta Physiol Lat Am 11:201–209
Martin WR, Wikler A, Eades CC, Pescor FT (1963) Tolerance to and physical dependence on morphine in rats. Psychopharmacologia 4:247–260
Mucha RF, Kalant H, Linseman MA (1979) Quantitative relationships among measures of morphine tolerance and physical dependence in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:397–405
Nozaki M (1976) Assessment of morphine type physical dependence liability: a screening method using the rat. Psychopharmacology 47:225–235
Numan R, Smith N, Lal H (1975) A versatile procedure for rapid induction of narcotic addiction in the rat utilizing intravenous injections. Physiol Psychol 3:261–262
Patrick GA, Dewey WL, Huger FP, Daves ED, Harris LS (1978) Disposition of morphine in chronically infused rats: relationship to antinociception and tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 205:556–562
Way EL, Loh HH, Shen F (1969) Simultaneous quantitative assessment of morphine tolerance and physical dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 167:1–8
Wikler A, Green CP, Smith HD, Presor FT (1960) Use of dilute solution (5 μg/ml) of a benzimidazole derivative with potent morphine-like actions orally as a presumptive reinforcing agent in conditioning of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Fed Proc 19:22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakaki, T., Saito, M., Nakadate, T. et al. Acute physical dependence induced by continuous intravenous infusion of morphine or meperidine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 73, 215–218 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422405
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422405