Abstract
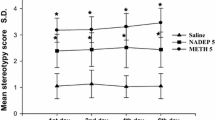
Pretreatment with the opiate antagonist naloxone, at 1.25–5 mg/kg, increased the intensity of methamphetamine stereotypy, had no effect (over a range of 0.3125–5 mg/kg) on apomorphine stereotypy, and antagonized haloperidol catalepsy in rats at 1.25–5 mg/kg. It is suggested that naloxone, by blocking the opiate receptors located on the nigro-striatal and mesolimbic dopamine (DA) nerve terminals, releases the DA systems from endogenous inhibition, presumably caused by endogenous opiate systems, and thereby potentiates methamphetamine stereotypy and antagonizes haloperidol catalepsy. However, the possibility that naloxone might have affected methamphetamine stereotypy and haloperidol catalepsy by modulating the activity of the central noradrenergic and GABAergic systems, which are reported to influence dopaminergically mediated behaviours, also needs to be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnoli A, Ruggieri S, Falaschi P, Mearelli S, Del Roscio S, D'Urso R, Frajese G (1980) Are the enkephalins involved in Parkinson's diesease? Clinical and neuroendocrine responses to naloxone administration. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communication. Raven Press, New York, pp 511–521
Al-Shabibi UMH, Doggett NS (1978) On the central noradrenergic mechanism involved in haloperidol-induced catalepsy in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 30:529–531
Andén NE, Butcher SG, Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Ungerstedt U (1970) Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur J Pharmacol 11:303–314
Arnsten AFT, Segal DS, Loughlin SE, Roberts DCS (1981) Evidence for an interaction of opioid and noradrenergic locus coeruleus systems in the regulation of environmental stimulus-directed behavior. Brain Res 222:351–363
Bianchine JR (1980) Drugs for Parkinson's disease; centrally acting muscle relaxants. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Macmillan Publishing Co, New York, pp 475–493
Bjørndal N, Casey DE, Gerlach J (1980) Enkephalin, morphine, and naloxone in tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 69:133–136
Braestrup C (1977) Changes in drug-induced stereotyped behaviour after 6-OHDA lesions in noradrenaline neurons. Psychopharmacology 51:199–204
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1963) Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Kbh) 20:140–144
Costa E, Fratta W, Hong JS, Moroni F, Yang HYT (1978) Interactions between enkephalinergic and other neuronal systems. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) The endorphins. Raven Press, New York, pp 217–226
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1974a) Mesolimbic involvement with behavioural effects indicating antipsychotic activity. Eur J Pharmacol 27:46–58
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1974b) On catalepsy and catatonia and the predictability of the catalepsy test for neuroleptic activity. Psychopharmacologia 34:233–241
Creese I, Iversen SD (1975) The pharmacological and anatomical substrates of the amphetamine response in the rat. Brain Res 83:419–436
Czlonkowski A, Höllt V, Herz A (1978) Binding of opiates and endogenous opioid peptides to neuroleptic receptor sites in the corpus striatum. Life Sci 22:953–962
Dingledine R, Iversen LL, Breuker E (1978) Naloxone as a GABA antagonist: evidence from iontophoretic, receptor binding and convulsant studies. Eur J Pharmacol 47:19–27
Hornykiewicz O (1975) Parkinsonism induced by dopaminergic antagonists. In: Calne DB, Chase TN, Barbeau A (eds) Dopaminergic mechanisms. Raven Press, New York, pp 155–164
Jaffe JH, Martin WR (1980) Opioid analgesics and antagonists. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Macmillan Publishing Co, New York, pp 494–534
Jorgensen A, Fog R, Veilis B (1979) Synthetic enkephalin analogue in treatment of schizophrenia. Lancet I:935
Klawans HL, Goetz C, Westheimer R (1976) The pharmacology of schizophrenia. In: Klawans HL (ed) Clinical neuropharmacology, vol 1 Raven Press, New York, pp 1–28
Leysen JE, Tollenaere JP, Koch MHJ, Laduron P (1977) Differentiation of opiate and neuroleptic receptor binding in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 43:253–267
Loh HH, Brase DA, Sampath-Khanna S, Mar JB, Way EL, Li CH (1976) β-Endorphin in vitro inhibition of striatal dopamine release. Nature 264:567–568
Mason ST, Roberts DCS, Fibiger HC (1978) Noradrenergic influences on catalepsy. Psychopharmacology 60:53–57
Moon BH, Feigenbaum JJ, Klawans HL (1979) Naloxone enhancement of amphetamine-induced dopamine release. Fed Proc 38:860
Namba MM, Quock RM, Malone MH (1981) Effects of narcotic antagonists on l-dopa reversal of reserpine-induced catalepsy and blepharoptosis in mice. Life Sci 28:1629–1636
Peroutka SJ, U'Prichard DC, Greenberg DA, Snyder SH (1977) Neuroleptic drug interactions with norepinephrine alpha receptor binding sites in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 16:549–556
Pollard H, Llorens C, Bonnet JJ, Costentin J, Schwartz JC (1977a) Opiate receptors on mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons. Neurosci Letters 7:295–299
Pollard H, Llorens-Cortes C, Schwartz JC (1977b) Enkephalin receptors on dopaminergic neurones in rat striatum. Nature 268:745–747
Pollard H, Llorens C, Schwartz JC, Gros C, Dray F (1978) Localization of opiate receptors and enkephalins in the rat striatum in relationship with the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system: lesion studies. Brain Res 151:392–398
Pycock C (1977) Noradrenergic involvement in dopamine dependent stereotyped and cataleptic responses in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 298:15–22
Pycock CJ, Horton RW, Carter CJ (1978) Interactions of 5-hydroxytryptamine and γ-aminobutyric acid with dopamine. In: Roberts PJ, Woodruff GN, Iversen LL (eds) Dopamine. Raven Press, New York, pp 323–341
Raiteri M, Del Carmine R, Bertollini A, Levi G (1977) Effect of sympathomimetic amines on the synaptosomal transport of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Eur J Pharmacol 41:133–143
Randrup A, Munkvad I (1974) Pharmacology and physiology of stereotyped behaviour. J Psychiatr Res 11:1–10
Snyder SH (1978) The opiate receptor and morphine-like peptides in the brain. Am J Psychiatry 135:645–652
Snyder SH, Childers SR (1979) Opiate receptors and opioid peptides. Ann Rev Neurosci 2:35–64
Subramanian N, Mitznegg P, Spruegel W, Domschke W, Domschke S, Wunsch E, Demling L (1977) Influence of enkephalin on K+ evoked efflux of putative neurotransmitters in rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 299:163–165
Wallach MB (1974) Drug-induced stereotyped behaviour: Similarities and differences. In: Usdin E (ed) Neuropsychopharmacology of monoamines and their regulatory enzymes. Raven Press, New York, pp 241–260
Worms P, Willigens MT, Lloyd KG (1978) GABA involvement in neuroleptic-induced catalepsy. J Pharm Pharmacol 30:716–718
Zetler G (1981) Differential cataleptogenic and antistereotypic effects of caerulein and haloperidol. Neuropharmacology 20:681–686
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balsara, J.J., Nandal, N.V., Burte, N.P. et al. Effects of naloxone on methamphetamine and apomorphine stereotypy and on haloperidol catalepsy in rats. Psychopharmacology 82, 237–240 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427781
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427781