Abstract
Administration of haloperidol (1.4–1.6 mg/kg/day) for up to 12 months or sulpiride (102–109 mg/kg/day) for between 6 and 12 months increased the frequency of purposeless chewing jaw movements in rats. N,n-propylnorapomorphine (NPA) (0.25–2.0 mg/kg SC) did not induce hypoactivity in haloperidol-treated rats at any time; sulpiride treatment for 9 and 12 months caused a reduction in the ability of NPA to induce hypoactivity. Haloperidol, but not sulpiride, treatment enduringly inhibited low dose apomorphine effects (0.125 mg/kg SC). After 12 months, sterotypy induced by high doses of apomorphine (0.5–1.0 mg/kg) was exaggerated in haloperidol-, but not sulpiride-treated rats.
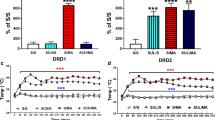
Bmax for specific striatal 3H-spiperone binding was increased by haloperidol, but not sulpiride, treatment throughout the study. Bmax for 3H-NPA binding was elevated only after 12 months of both haloperidol and sulpiride treatment. Bmax for 3H-piflutixol binding was not alfered by chronic haloperidol or sulpiride treatment. Striatal dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity was inhibited for the 1st month of haloperidol treatment, thereafter returning to control levels; dopamine stimulation was increased after 12 months of sulpiride treatment. Striatal acetylcholine content was increased after 3 and 12 months of treatment with haloperidol, but was not affected by sulpiride.
Chronic administration of sulpiride does not induce identical changes in striatal dopamine function to those caused by haloperidol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts JL (1983) Survey on extrapyramidal side-effects induced by sulpiride. Presented at symposium on sulpiride, Paris
Bannet J, Gillis S, Ebstein RP, Belmaker RH (1980) The effect of chronic sulpiride on striatal spiperone binding. Int Pharmacopsychiatr 15:334–335
Brown JR, Arbuthnott GW (1983) The electrophysiology of dopamine (D2) receptors: a study of the actions of dopamine on corticostriatal transmission. Neuroscience 10:349–355
Chang HC, Gaddum JH (1983) Choline esters in tissue extracts. J Physiol 79:755–785
Clow A, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1979a) Changes in dopamine-mediated behaviour during one year's neuroleptic administration. Eur J Pharmacol 57:365–375
Clow A, Jenner P, Theodorou A, Marsden CD (1979b) Striatal dopamine receptors become supersensitive while rats are given trifluoperazine for six months. Nature 278:59–61
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1975) Detection of the neuroleptic properties of clozapine, sulpiride and thioridazine. Psychopharmacology 43:69–74
Costall B, Hui S-CG, Naylor RJ (1980) Differential actions of substituted benzamides on pre- and postsynaptic dopamine receptor mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:594–596
Costall B, Naylor RJ, Owen RT (1978) Behavioural correlates of modified dopaminergic/anticholinergic responses following chronic treatment with neuroleptic agents of differing activity spectra. Eur J Pharmacol 48:29–36
Creese I, Stewart K, Snyder SH (1979) Species variations in dopamine receptor binding. Eur J Pharmacol 60:55–66
Di Chiara G, Porceddu ML, Vargiu L, Argiolas P, Gessa GL (1976) Evidence for dopamine receptors mediating sedation in mouse brain. Nature 264:564–566
Elliott PNC, Jenner P, Huizing G, Marsden CD, Miller R (1977) Substituted benzamides as cerebral dopamine antagonists in rodents. Neuropharmacology 16:333–342
Feldberg W (1945) Synthesis of acetylcholine by tissue of the central nervous system. J Physiol 103:367–402
Fleminger S, Rupniak NMJ, Hall MD, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1983a) Changes in apomorphine-induced stereotypy as a result of subacute neuroleptic treatment correlates with increased D-2 receptors, but not with increases in D-1 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 32:2921–2927
Fleminger S, van de Waterbeemd H, Rupniak NMJ, Reavill C, Testa B, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1983b) Potent lipophilic substituted benzamides are not selective D-1 dopamine receptor antagonists in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 35:363–368
Fuxe K, Ogren S-O, Hall H, Agnati LF, Anderson K, Kohler C, Schwarcz R (1980) Effect of chronic treatment with 1-sulpiride and haloperidol on central monoaminergic mechanisms. In: Cattabeni F, Racagni G, Spano PF, Costa E (eds) Long-term effects of neuroleptics. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 24:193–197
Hall MD, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1981) Characteristics of in vitro binding of 3H-N,n-propylnorapomorphine to rat striatal preparations. Neurosci Lett (Suppl) 7:363
Hattori T, Singh VK, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1976) Immunhistochemical localisation of choline acetyltransferase-containing neostriatal neurones and their relationship with dopaminergic synapses. Brain Res 102:164–173
Howells RB, Iversen SD (1979) Behavioural hypersentivity and spontaneous motor abnormalities following chronic fluphenazine treatment in the rat. Neurosci Lett (Suppl) 3:210
Jenner P, Elliott PNC, Clow A, Reavill C, Marsden CD (1978) A comparison of in vitro and in vivo dopamine receptor antagonism produced by substituted benzamide drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 30:46–48
Jenner P, Hall MD, Murugaiah K, Rupniak N, Theodorou A, Marsden CD (1982) Repeated administration of sulpiride for three weeks produces behavioural and biochemical evidence for cerebral dopamine receptor supersensitivity. Biochem Pharmacol 31:325–328
Jenner P, Kerwin R, Marsden CD, Rupniak NMJ (1983) Alterations of striatal acetylcholine and glutamate release following acute and chronic neuroleptic administration to rats. Br J Pharmacol 78:15P
Klawans HL (1973) The pharmacology of extrapyramidal movement disorders. In: Cohen MM (ed) Monographs in neural sciences. Karger, Basel, pp 1–137
Kohler C, Haglund L, Ogren S-O, Angeby T (1981) Regional blockade by neuroleptic drugs of in vivo 3H-spiperone binding in the rat brain. Relation to blockade of apomorphine-induced hyperactivity and stereotypies. J Neural Transm 52:168–173
Leysen JE, Gommeren W (1981) Optimal conditions for 3H-apomorphine binding and anomalous equilibrium binding of 3H-apomorphine and 3H-spiperone to rat striatal membranes: involvement of surface phenomena versus multiple binding sites. J Neurochem 36:201–219
Leysen JE, Gommeren W, Laduron PM (1978) Spiperone: a ligand of choice for neuroleptic receptors. I. Kinetic and characteristics of in vitro binding. Biochem Pharmacol 27:307–316
Miller RJ, Horn AS, Iversen LL (1974) The action of neuroleptic drugs on dopamine-stimulated adenosine 3,5-monophosphate production in rat neostriatum and limbic forebrain. Mol Pharmacol 10:759–766
Murugaiah K, Theodorou A, Mann S, Clow A, Jenner P, Marsden CD, (1982) Chronic administration of neuroleptic drugs alters cerebral dopamine receptors and increases spontaneous dopaminergic action in the striatum. Nature 296:570–572
Puech AJ, Simon P, Boissier JR (1976) Antagonism by sulpiride of three apomorphine-induced effects in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 36:439–441
Rupniak NMJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1983) Cholinergic manipulation of perioral behaviour induced by chronic neuroleptic administration to rats. Psychopharmacology 79:226–230
Rupniak NMJ, Kilpatrick G, Hall MD, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1984) Differential alterations in striatal dopamine receptor sensitivity induced by repeated administration of clinically equivalent doses of haloperidol, sulpiride or clozapine in rats. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Sethy VH, van Woert MH (1974) Regulation of striatal acetylcholine concentration by dopamine receptors. Nature 251:529–530
Stoof JC, Kebabian JW (1981) Opposing roles for D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature 294:366–368
Theodorou AE, Hall MD, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1980) Cation regulation differentiates specific binding of 3H-sulpiride and 3H-spiperone to rat striatal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:441–444
Titeler M, Seeman P (1980) Radioreceptor labeling of pre- and postsynaptic dopamine receptors. In: Cattabeni F, Racagni G, Spano PF, Costa E (eds) Long-term effects of neuroleptics. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 24:159–165
Trabucchi M, Longoni R, Fresia P, Spano PF (1975) Sulpiride: a study of the effects on dopamine receptors in rat neostriatum and limbic forebrain. Life Sci 17:1551–1556
Trabucchi M, Memo M, Battaini F, Reggiani A, Spano PF (1980) Effect of long term treatment with haloperidol and sulpiride on different types of dopaminergic receptors. In: Cattabeni F, Racagni G, Spano PF, Costa E (eds) Long term effects of neuroleptics. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 24:275–281
Wiesel F-A, Alfredsson G, Ehrenbo M, Sedvall G (1980) The pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral sulpiride in healthy human subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17:385–391
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rupniak, N.M.J., Mann, S., Hall, M.D. et al. Differential effects of continuous administration for 1 year of haloperidol or sulpiride on striatal dopamine function in the rat. Psychopharmacology 84, 503–511 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431457
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431457