Abstract
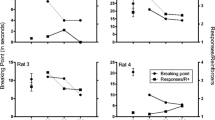
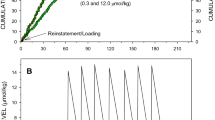
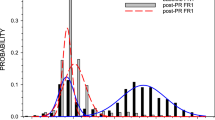
Key pressing by rats was maintained under spaced-responding and random-ratio schedules of food delivery, and rates of responding were reliably different for each schedule. When responding was maintained under a multiple schedule, appropriate doses of d-amphetamine (1.0 and 1.7 mg/kg) markedly increased low rates of spaced responding while markedly decreasing high rates of ratio responding. These drug-produced changes in response rate resulted in decreased food presentation during both schedule components. When 1.0 mg/kg d-amphetamine was given daily, tolerance developed to initially decreased ratio responding in six to nine sessions, but did not develop to initially increased spaced responding. However, when the ratio schedule was removed, tolerance developed very quickly to increases under the spaced-responding schedule, and associated food frequency returned to control levels. When the ratio schedule was reinstated, spaced responding was once again increased, and its associated frequency of food delivery was again decreased. The development of tolerance to the behavioral effects of d-amphetamine was influenced more by global changes in response consequences during entire experimental sessions than by local changes in response consequences in single components of those sessions. Whenever the concept of “response cost” is used, it should be understood in terms of total “cost.”
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackman DE (1968) Response rate, reinforcement frequency, and conditioned suppression. J Exp Anal Behav 11:503–516
Chung SH (1965a) Effects of effort on response rate. J Exp Anal Behav 8:1–7
Chung SH (1965b) Effects of delayed reinforcement in a concurrent situation. J Exp Anal Behav 8:439–444
Clody DE, Carlton PL (1980) Stimulus efficacy, chlorpromazine, and schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 69:127–131
Dews PB (1958) Studies of behavior. IV. Stimulant actions of methamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 122:137–147
Dews PB (1964) A behavioral effect of amobarbital. Nauyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 248:296–307
Geller I, Seifter J (1960) The effects of meprobamate, barbiturates, d-amphetamine, and promazine on experimentally induced conflict in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 1:482–492
Hanson HM, Witoslawski JJ, Campbell EA (1967) Drug effects in squirrel monkeys trained on a multiple schedule with a punishment contingency. J Exp Anal Behav 10:565–569
Kelleher RT, Morse WH (1968) Determinants of the specificity of the behavioral effects of drugs. Ergebn Physiol 60:1–56
Laties VG, Wood RW, Rees DC (1981) Stimulus control and the effects of d-amphetamine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 75:277–282
Laties VG, Weiss B (1966) Influence of drugs on behavior controlled by internal and external stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 152:388–396
McKearney JW (1970) Rate-dependent effects of drugs: Modification by discriminative stimuli of the effects of amobarbital on schedule-controlled behavior. J Exp Anal Behav 14:167–175
McKearney JW (1976) Punishment of responding under schedules of stimulus-shock termination: Effects of d-amphetamine and pentobarbital. J Exp Anal Behav 26:281–287
McKearney JW, Barrett JE (1978) Schedule-controlled behavior and the effects of drugs. In: Blackman DE, Sanger DJ (eds) Contemporary research in behavioral pharmacology, Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–68
McKearney JW, Barrett JE (1975) Punished behavior: Increases in responding after d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacologia 41:23–26
McMillan DE (1973) Drugs and punished responding I: Rate-dependent effects under multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav 19:133–145
Schuster CR, Dockens WS, Woods JH (1966) Behavioral variables affecting the development of amphetamine tolerance. Psychopharmacologia 9:170–182
Smith JB (1974) Effects of response rate, reinforcement frequency and the duration of a stimulus preceding response-independent food. J Exp Anal Behav 21:215–221
Smith JB, McKearney JW (1977) Changes in the rate-increasing effects of d-amphetamine and pentobarbital by response consequences. Psychopharmacology 53:151–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, J.B. Effects of chronically administered d-amphetamine on spaced responding maintained under multiple and single-component schedules. Psychopharmacology 88, 296–300 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180827
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180827