Abstract
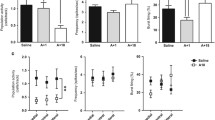
Rats were trained to escape from aversive electrical brain stimulation delivered to the mesencephalic reticular formation (MRF). The threshold for this escape behavior was determined by a modification of the classic psychophysical method of limits. Escape thresholds were determined after the administration of morphine alone, d-amphetamine alone, and the combination of d-amphetamine and an ineffective dose of morphine. Morphine alone caused a dose-dependent raising of the escape threshold (1.0–16.0 mg/kg IP) while d-amphetamine alone (0.06–2.0 mg/kg IP) had no effect or caused a slight lowering of threshold. For each animal, a dose of morphine that produced no change in escape threshold was then selected to be administered concomitantly with various doses of d-amphetamine. The co-administration of morphine and d-amphetamine resulted in a significant, dose-dependent increase in the escape threshold, which was not seen with d-amphetamine alone and was as great or greater in magnitude than the increase seen with the highest dose of morphine tested. The results of this study clearly demonstrate that opiate analgesia is potentiated by concomitant d-amphetamine administration. The mechanisms involved in this potentiation warrant further investigation for the clinical management of pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SS, Abraham GJS, Assari M (1970) Dose dependent modification of codeine analgesia by d-amphetamine in albino rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 184:240–244
Evans WO (1962) The synergism of autonomic drugs on opiate or opiate-induced analgesia: A discussion of its potential utility. Milit Med 127:1000–1003
Evans WO (1967) The effect of stimulant drugs on opiate induced analgesia. Arch Biol Med Exp 4:144–149
Evans WO, Bergner DP (1964) A comparison of the analgesic potencies of morphine, pentazocine, and a mixture of methamphetamine and pentazocine in the rat. J New Drugs 4:82–85
Forrest WH, Brown BW, Brown CR, Defalque R, Gold M, Gordon HE, James KE, Katz J, Mahler DL, Schroff P, Teutsch G (1977) Dextroamphetamine with morphine for the treatment of postoperative pain. New Engl J Med 296 (13):712–715
Gunne L-M (1963) Catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in morphine tolerance and withdrawal. Acta Physiol Scand 204 (58):1–91
Ivy AC, Goetzl FR, Burrill DY (1944) Morphine-dextroamphetamine analgesia. War Med 6:67–71
Marcus R, Kornetsky C (1974) Negative and positive intracranial reinforcement thresholds: effects of morphine. Psychopharmacologia 38:1–13
Nott MW (1968) Potentiation of morphine analgesia by cocaine in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 5:93–99
Richards RK (1975) A study of the effect of d-amphetamine on the toxicity, analgesic potency and swimming impairment caused by potent analgesics in mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 216:225–245
Sasson S, Kornetsky C (1983) Naloxone lowers brain-stimulation escape thresholds. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:231–233
Sasson S, Kornetsky C (1986) Evidence for a supraspinal analgesic effect with cyclazocine and pentacozine. Life Sci 38:21–26
Sloan J, Brooks J, Eisenmann A, Martin W (1963) The effects of addiction to and abstinence from morphine on rat tissue catecholamine and serotonin levels. Psychopharmacologia 4:261–270
Verri RA (1967) Antagonism of morphine analgesia by reserpine and alpha-methyltyrosine and the role played by catecholamines in morphine analgesic action. J Pharm Pharmacol 19:264
Wheeling HS, Sasson S, Kornetsky C (1981) Tolerance to the effects of morphine on escape from reticular formation stimulation. Substance and Alcohol Actions/Misuse 2:107–114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasson, S., Unterwald, E.M. & Kornetsky, C. Potentiation of morphine analgesia by d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 90, 163–165 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181233
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181233