Summary
-
1.
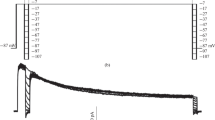
Voltage clamp experiments were carried out on frog myelinated fibres to study the origin of the transient inward current occuring when the membrane is repolarized after long lasting depolarizing pulses (tail current denominated “I p” by Frankenhaeuser).
-
2.
The “tail” of inward current measured during repolarization after break of the depolarizing pulse is insensitive to external application of TTX, is abolished by external treatment with TEA or Cs and decreases when the outward K-current during the pulse is diminished.
-
3.
The time course of the “tail” current is exponential. Its direction depends on the duration of the depolarizing pulse and on the membrane potential level at repolarization.
-
4.
It is concluded that the tail of inward current during repolarization is carried by K-ions accumulated in the perinodal space during a depolarizing pulse. The data suggest that the tail reflects the time course of the restoration of the K-concentration to its initial level. The tail current itself contributes to this restoration depending on the Em value at repolarization.
-
5.
It is shown that one of the two phenomenological models proposed by Frankenhaeuser and Hodgkin to account for the external potassium accumulation observed in the squid giant axon may be also applied to the Ranvier node. Assuming that the thickness of the space is 2900 Å and that the K-permeability of the barrier is 0.019 cm/sec, it is possible to account for the observed changes in [K]0 during a long lasting depolarizing pulse.
-
6.
The existence of such a barrier would introduce an electrical resistance in series with the nodal membrane of roughly 150000 Ω.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelman, W. J., Palti, Y., Senft, J. P.: Potassium ion accumulation in a periaxonal space and its effects on the measurement of membrane potassium ion conductance. J. Membrane. Biol.13, 387–410 (1973)
Adelman, W. J., Senft, J. P.: Dynamic asymmetries in the squid axon membrane. J gen. Physiol.51, 102s-114s (1968)
Armstrong, C. M., Hille, B.: The inner quaternary ammonium ion receptor in potassium channels of the node of Ranvier. J. gen. Physiol.59, 388–400 (1972)
Bergman C.: Increase of sodium concentration near the inner surface of the nodal membrane. Pflügers Arch.317, 287–302 (1970)
Bergman, C., Nonner, W., Stämpfli, R.: Sustained spontaneous activity of Ranvier nodes induced by the combinated actions of TEA and lack of calcium. Pflügers Arch.302, 24–37 (1968)
Bezanilla, F., Armstrong, C. M.: Negative conductance caused by entry of sodium and cesium ions into the potassium channels of squid axons. J. gen. Physiol.60, 588–608 (1972)
Dodge, F. A., Frankenhaeuser, B.: Membrane currents in isolated nerve fibres under voltage clamp conditions. J. Physiol. (Lond.)143, 76–90 (1958)
Drouin, H., Neumcke, B.: Specific and unspecific charges at the sodium channel of the nerve membrane. Pflügers Arch.351, 207–229 (1974)
Dubois, J. M., Bergman, C.: Late sodium current in the node of Ranvier. Pflügers Arch.357, 145–148 (1975a)
Dubois, J. M., Bergman, C.: Cesium induced rectifications in frog myelinated fibres. Pflügers Arch.355, 361–364 (1975b)
Frankenhaeuser B.: Instantaneous potassium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus leavis. J. Physiol. (Lond.)160, 46–53 (1962)
Frankenheuser, B.: A quantitative description of potassium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.)169, 424–430 (1963)
Frankenhaeuser, B., Hodgkin, A. L.: The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.)131, 341–376 (1956)
Hille, B.: The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J. gen. Physiol.59, 637–658 (1972)
Hille, B.: Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. J. gen. Physiol.61, 669–686 (1973)
Huxley, A. F., Stämpfli, R.: Direct determination of membrane resting and action potential in single myelinated nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)112, 476–495 (1951)
Koppenhöfer, E.: Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf die Membranströme Ranvierscher Schnürringe von Xenopus laevis. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.293, 34–55 (1967)
Koppenhöfer, E., Schmidt, H.: Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. I. Die Permeabilitäten PNa und PK. Pflügers Arch.303, 133–149 (1968)
Koppenhöfer, E., Vogel, W.: Wirkung von Tetrodotoxin und Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid an der Innenseite der Schnürrings membran von Xenopus laevis. Pflügers Arch.313, 361–380 (1969)
Meves, H.: Die Nachpotentiale isolierte markhaltiger Nervenfasern des Frosches bei tetanischer Reizung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.272, 336–359 (1961)
Nonner, W.: A new voltage clamp method for Ranvier nodes. Pflügers Arch.309, 116–192 (1969)
Nonner, W., Rojas, E., Stämpfli, R.: Displacement currents in the node of Ranvier. Voltage and time dependence. Pflügers Arch.354, 1–18 (1975)
Ulbricht, W.: Der zeitliche Verlauf des Kalium-depolarisation der Schnürringsmembran bei verschiedenen Calcium-Konzentrationen und anodischer Polarisation. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.277, 270–284 (1963)
Vierhaus, J., Ulbricht, W.: Effect of a sudden change in sodium concentration on repetitively evoked action potentials of single nodes of Ranvier. Pflügers Arch.326, 76–87 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants of the C.N.R.S. and D.G.R.S.T.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubois, J.M., Bergman, C. Potassium accumulation in the perinodal space of frog myelinated axons. Pflugers Arch. 358, 111–124 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583922
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583922