Abstract
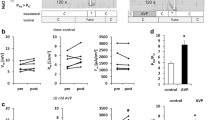
Experiments were performed in anesthetized rats to investigate the time course of the adaptive changes in tubuloglomerular feedback reactivity and juxtaglomerular renin activity induced by DOCA and NaCl loading (isotonic saline as drinking fluid plus daily injections of 25 mg/kg DOCA). In these DOCA escaped rats we studied further the effect of acute volume depletion and repletion on the magnitude of feedback responses. A significant reduction of feedback reactivity was found on the fifth day after starting the DOCA-salt treatment with maximum depression being established after two weeks. In contrast, significant reduction of juxtaglomerular renin content required 10 days and maximum depression three weeks of DOCA-salt administration. In DOCA-salt treated animals with severely curtailed feedback responses acute volume depletion was induced by a single injection of furosemide (10 mg/kg) leading to an excretion of 0.49 ±0.17 mEq sodium and a mean decrease of body weight of 2.17±0.22% over a period of 60–70 min. Mean feedback response (expressed as percent change of early proximal flow rate caused by elevating loop of Henle flow rate from zero to 40 nl/min) was −43.9 ±4.0%, significantly greater than in the pre-depletion phase and indistinguishable from responses seen in normal control rats. Repletion of extracellular volume by infusing HCO3-Ringer solution over 20 min induced a reduction in feedback responsivity to −12.0±2.9%. Plasma and juxtaglomerular renin concentration increased with volume depletion and decreased with volume repletion, but remained considerably lower than observed in normal control rats. Our results suggest that the tubuloglomerular feedback system responds to acute alterations in extracellular volume with rapid adaptations in its reactivity which is consistent with its role in the control of sodium excretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailie MD, Rector FC, Seldin DW (1971) Angiotensin II in arterial and renal venous plasma and renal lymph in the dog. J Clin Invest 50:119–126
Dahlheim H, Granger P, Thurau K (1970) A sensitive method for determination of renin activity in the single juxtaglomerular apparatus of the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch 321:303–315
Dev B, Drescher C, Schnermann J (1974) Resetting of tubuloglomerular feedback sensitivity by dietary salt intake. Pflügers Arch 346:263–277
Führ J, Kaczmarczyk J, Krüttgen CD (1970) Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr 33:729–730
Granger P, Dahlheim H, Thurau K (1972) Enzyme activities of the single juxtaglomerular apparatus in the rat kidney. Kidney Int 1:78–88
Haber E, Koerner T, Page LB, Kliman B, Purnode A (1969) Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 29:1349–1355
Kaufman JS, Hamburger RJ, Flamenbaum W (1976a) Tubuloglomerular feedback: effect of dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol 231:1744–1749
Kaufman JS, Hamburger RJ, Flamenbaum W (1976b) Effect of renin angiotensin system activity on tubuloglomerular feedback in the rat. Fed Proc 35:541
Möhring J, Möhring B (1972) Reevaluation of DOCA escape phenomenon. Am J Physiol 223:1237–1245
Persson AEG, Schnermann J, Wright FS (1979a) Modification of feedback influence on glomerular filtration rate by acute isotonic extracellular volume expansion. Pflügers Arch 381:99–105
Persson AEG, Müller-Suur R, Selen G (1979b) Capillary oncotic pressure as a modifier for tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol 236:F97–F102
Ploth DW, Rudulph J, Thomas C, Navar LG (1978) Renal and tubuloglomerular feedback responses to plasma expansion in the rat. Am J Physiol 235:F156–F162
Schnermann J, Weber PC (1979) Restoration by PGI2 of tubuloglomerular feedback responsiveness during blockade induced by indomethacin or chronic DOCA administration. Kidney Int 16:835
Schnermann J, Hermle M, Schmidmeier E, Dahlheim H (1975) Impaired potency for feedback regulation of glomerular filtration rate in DOCA-escaped rats. Pflügers Arch 358:325–338
Schnermann J, Schubert G, Hermle M, Herbst R, Stowe NT, Yarimizu S, Weber PC (1979) The effect of inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis on tubuloglomerular feedback in the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch 379:269–279
Thurau K, Dahlheim H, Grüner A, Mason J, Granger P (1972) Activation of renin in the single juxtaglomerular apparatus by sodium chloride in the tubular fluid at the macula densa. Circ Res 30–31 Suppl. II:182–186
Weber PC, Held E, Uhlich E, Eigler JOC (1975) Reaction constants of renin in juxtaglomerular apparatus and plasma renin activity after renal ischemia and hemorrhage. Kidney Int 7:331–341
Wright FS, Schnermann J (1974) Interference with feedback control of glomerular filtration rate by furosemide, triflocin, and cyanide. J Clin Invest 53:1695–1708
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, L.C., Yarimizu, S., Schubert, G. et al. Dynamics of tubuloglomerular feedback adaptation to acute and chronic changes in body fluid volume. Pflugers Arch. 387, 39–45 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580842
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580842