Abstract
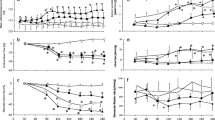
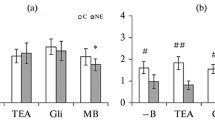
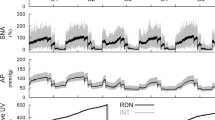
To assess the renal haemodynamic response to manipulations of the nitric oxide (NO) system, we examined subtotally nephrectomized (SNX) rats and control rats (CON) 28 days after their operation. Bolus infusions of the NO synthase inhibitor N G-nitro-l-arginine (l-NA) were given intravenously at doses of 2 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg. Blood pressure was measured intra-arterially, glomerular filtration rate was measured by inulin clearance and fractional changes in renal blood flow (RBF) were determined by a Doppler flow probe. Both doses of l-NA caused a similar and dose dependent increase in mean blood pressure in both SNX and CON rats. In contrast, the decrease in RBF and the increase in the renovascular resistance index (RVRI) was less in SNX rats as compared to CON rats (RBF = −70.1±2.2% of baseline vs −52.7±5.2%, P<0.01; RVRI = +177±9% of baseline vs +243±24%, P<0.05). These changes were not affected by autonomic blockade (hexamethonium), or by blockade of the angiotensin II receptor (Losartan). The exogenous NO donor sodium nitroprusside (0.5 and 1.5 μg · kg−1 · min−1) lowered mean blood pressure to a similar degree in SNX and CON rats; in contrast, RVRI decreased less in SNX rats (86.9±9.2% of baseline) than in CON rats (68.2±4.6%, P<0.05). We conclude that the reaction of the renal vasculature to manipulations of the NO system is altered in the SNX rats. The data suggest that in the remnant kidney, renovascular resistance is less dependent on endogenous NO and the vascular bed is less sensitive to exogenous NO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baylis C, Harton P, Engels K (1990) Endothelial derived relaxing factor controls renal haemodynamics in the normal rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 1:875–881
Baylis C, Mitruka B, Deng A (1992) Chronic blockade of nitric oxide synthesis in the rat produces systemic hypertension and glomerular damage. J Clin Invest 90:278–281
Bidani AK, Schwartz MM, Lewis EJ (1987) Renal autoregulation and vulnerability to hypertensive injury in remnant kidney. Am J Physiol 252:F1003-F1010
Boegehold MA (1992) Reduced influence of nitric oxide on arteriolar tone in hypertensive DAHL rats. Hypertension 19:920–925
Brenner BM (1985) Nephron adaptation to renal injury or ablation. Am J Physiol 249:F324-F337
Dworkin LD, Grosser M, Feiner HD, Ulian M, Parker M (1987) Renal vascular effects of antiphypertensive therapy in uninephrectomized SHR. Kidney Int 35:790–798
Ferrari AU, Daffonchio A, Gerosa S, Franzelli C, Paleari P, Ventura C, DiRienzo M, Mancia G (1993) Spontaneous variability of regional haemodynamics in unanaesthetized rats. J Hypertens 11:535–541
Folkow B (1971) The haemodynamic consequences of adaptive structural changes of the resistance vessels in hypertension. Clin Sci 41:1–9
Gardiner SM, Compton AM, Kemp PA, Bennett T (1990) Regional and cardiac haemodynamic responses to glyceryl trinitrate, acetylcholine, bradykinin and endothelin-1 in conscious rats: effects of N G-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester. Br J Pharmacol 101:625–631
Gardiner SM, Compton AM, Bennett T, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S (1990) Control of regional blood flow by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension 15:486–492
Grady HC, Bullivant EMA (1992) Renal blood flow varies during normal activity in conscious unrestrained rats. Am J Physiol 262:R926-R932
Haywood JRH, Shaffer RA, Fastenow C, Fink GD, Brody MJ (1981) Regional blood flow measurement with pulsed Doppler flowmeter in conscious rats. Am J Physiol 241:H273-H278
Horst P, Veelken R, Unger T (1988) A new method for collecting urine directly from the ureter in conscious unrestrained rats. Renal Physiol Biochem 11:902–908
Hostetter TH, Olson JL, Rennke HG, Venkatachalam MA, Brenner BM (1981) Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol 241:F85-F89
Kanagy NL, Fink GD (1993) Losartan prevents salt-induced hypertension in reduced renal mass rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:1131–6
King AJ, Troy JE, Anderson S, Neuringer JR, Gunning M, Brenner BM (1991) Nitric oxide: a potential mediator of amino acid-induced renal hyperemia and hyperfiltration. J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1271–1277
Lahera V, Salom MG, Fiksen-Olson MJ, Raju L, Romero JC (1990) Effects of N-monomethyl-l-arginine on acetylcholine renal response. Hypertension 15:659–663
Lahera V, Salom MG, Miranda F, Moncada S, Romero JC (1991) Effects of N-nitro-l-arginine methylester on renal function and blood pressure. Am J Physiol 261:F1033-F1037
Mayhan WG, Faraci FM, Heistad DD (1987) Impairment of endothelium-dependent responses of cerebral arterioles in chronic hypertension. Am J Physiol 253:H1435-H1440
Moncada SR, Palmer MJ, Higgs E (1991) Biosynthesis and endogenous roles of nitric oxide. Pharmacol Rev 43:109–142
Naess PA, Kirkeboen KA, Christensen G, Kiil F (1992) Inhibition of renal nitric oxide synthesis with N-monomethyl-l-arginien and N-nitro-l-arginine. Am J Physiol 262:F939-F942
Palmer RMJ, Ferrige AG, Moncada S (1987) Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 327:524–526
Rees DD, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S (1989) Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3375–3378
Rettig R, Folberth C, Stauss H, Kopf D, Waldherr R, Unger T (1990) Role of the kidney in primary hypertension: a renal transplantation study in rats. Am J Physiol 258:F606-F611
Rohmeiss P, Photiadis J, Rohmeiss S, Unger T (1990) Haemodynamic actions of intravenous endothelin in rats: comparison with sodium nitroprusside and methoxamine. Am J Physiol 258:H337-H346
Salazar FJ, Pinilla JM, Lopez F, Romero JC, Quesada T (1992) Renal effects of prolonged synthesis inhibition of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension 20:113–117
Unger T, Carolus S, Demmert G, Ganten D, Lang RE, Maser-Gluth C, Steinberg H, Veelken R (1988) Substance P induces a cardiovascular defense reaction in the rat: pharmacological characterization. Circ Res 63:812–820
Vallance P, Collier J, Moncada S (1989) Effect of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on peripheral tone in man. Lancet 2: 997–1000
Vallance P, Leone A, Calver A, Collier J, Moncada S (1992) Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet 339:572–575
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, J., Wystrychowski, A., Stauss, H. et al. Decreased renal haemodynamic response to inhibition of nitric oxide synthase in subtotally nephrectomized rats. Pflügers Arch. 430, 181–187 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374648
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374648