Summary
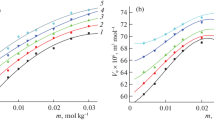
Interaction of urate with human and rat plasma was studied by a dialysis technique at different temperatures. At 4° C a certain fraction of urate is bound to proteins. However, this fraction diminishes with increasing temperature and at 37° C only some 7–8% (in man) and 2% (in rat) interact with proteins. The finding that urate is almost completely filtered in the glomerulus is discussed. In body areas exposed to low temperatures protein binding of urate may be of importance.
Urate uptake by erythrocytes is characterized by two components: a fast component equilibrating almost immediately at about 7% in man and 17% in rat and a slow component reaching equilibrium after 60 min, at 28% and 36%, respectively. The process is described by a mathematical formula. Lowering of the temperature mainly diminishes uptake by the slow component withQ 10-values ranging between 1.5 and 4.0. In the observed range of concentrations the uptake process does not saturate. The results at lower pH-values suggest that it is unionized uric acid which is transported by the slow component. Application of the data to kidney medulla supports the hypothesis that erythrocytes and, probably, to a lesser extent plasma proteins serve as vehicles for urate reabsorption in the countercurrent system. Such a temporary interaction enables uric acid to escape recirculation and to leave the kidney medulla.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvsaker, J. O.: Uric acid in human plasma. V. Isolation and identification o plasma proteins interacting with urate. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.18, 227–239 (1966)
Appleman, R. M., Hallenback, G. A., Shorter, R. G.: Effect of reciprocal allogenic renal transplantation between Dalmatian and non Dalmatian dogs on urinary excretion of uric acid. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)121, 1094–1097 (1966)
Bluestone, R., Kippen, I., Klinenberg, J. R.: Effects of drugs on urate binding to plasma proteins. Brit. med. J.1969 IV, 590–593
Deuticke, B., Dierkesmann, R., Bach, D.: Neuere Studien zur Anionen-Permeabilität menschlicher Erythrocyten. In: Stoffwechsel und Membranpermeabilität von Erythrocyten und Thrombocyten. Hrsg. von E. Deutsch, E. Gerlach u. K. Moser. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1968
Farell, P. C., Popovich, R. P., Babb, A. L.: Binding levels of urate ions in human serum albumin and plasma. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)243, 49–52 (1971)
Greger, R., Lang, F., Deetjen, P.: Renale Harnsäurebehandlung. Fortschritte der Nephrologie. VII. Symposion der Ges. für Nephrologie. Hrsg. A. Bohle. Stuttgart-New York: F. K. Schattauer 1971
Harvey, A. M., Christensen, H. N.: Uric acid transport system: Apparent absence in erythrocytes of Dalmatian coach hound. Science145, 826–827 (1964)
Isomäki, H., Kreus, K.: Serum and urinary uric acid in respiratory acidoses. Acta med. scand.184, 293 (1968)
Klinenberg, J. R., Kippen, I.: The binding of urate to plasma proteins determined by means of equilibrium dialysis. J. Lab. clin. Med.75, 503–510 (1970)
Lang, F., Greger, R., Deetjen, P.: Handling of uric acid by the rat kidney. II. Microperfusion studies on bidirectional transport of uric acid in the proximal tubule. Pflügers Arch.335, 257–265 (1972)
Lang, F., Greger, R., Deetjen, P.: Handling of uric acid by the rat kidney. III. Microperfusion studies on steady state concentration of uric acid in the proximal tubule. Consideration of free flow conditions. Pflügers Arch.338, 295–302 (1973)
Lassen, U. V.: Kinetics of uric acid transport in human erythrocytes. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)53, 557–569 (1961)
Lennox, W. G.: Increase of uric acid in the blood during prolonged starvation. J. Amer. med. Ass.82, 602 (1924)
Naftalin, R. J.: The effects of probenecid and salicylate on uric acid flux across red cell membranes. J. Physiol. (Lond.)211, 47 P (1970)
Overgaard, K., Lassen, U. V.: Active transport of uric acid through the human erythrocyte membrane. Nature (Lond.)184, 553–554 (1959)
Quehenberger, P., Lang, F., Greger, R., Deetjen, P.: pH-Measurements in loops of henle of the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch.347, R 68 (1974)
Sheikh, M. I., Moeller, J. V.: Binding of urate to proteins of human and rabbit plasma. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)158, 456–458 (1968)
Soerensen, L. B.: Excretion of uric acid in health and disease. Handbuch der Inneren Medizin. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer (in press)
Uhlich, E., Baldamus, C. A., Ullrich, K. J.: Verhalten von CO2-Druck und Bicarbonat im Gegenstromsystem des Nierenmarks. Pflügers Arch.303, 31–48 (1968)
Ullrich, K. J.: Das Nierenmark. Struktur, Stoffwechsel und Funktion. In: Ergebnisse der Physiologie. Hrsg. O. Krayer, E. Lehnartz, A. v. Muralt u. H. H. Weber. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1959
Yü, T. F., Gutman, A. B.: Ultrafiltrability of plasma urate in man. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. (N. Y.)84, 21–24 (1953)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Partially supported by “Österreichischer Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung”.
Receiving scholarships from “Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greger, R., Lang, F., Puls, F. et al. Urate interaction with plasma proteins and erythrocytes. Pflugers Arch. 352, 121–133 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587511
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587511