Abstract
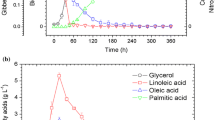
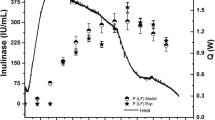
In the microbial lipid production system using the yeast Rhodotorula gracilis, CFR-1, kinetics of lipid accumulation and substrate utilisation at initial substrate concentrations in the range of 20–100 kg/m3 were investigated using shake flask experiments. A mathematical representation based on logistic model for biomass and Luedeking-Piret model for lipid accumulation gave reasonably good agreement between the theoretical and experimental values for substrate concentration less than 60 kg/m3. The kinetic expressions and parameters obtained through shake flask studies were directly applied to experiments in the laboratory fermentors also and the models were found to hold good for the prediction of the change of biomass, product as well as substrate with time. The attainment of a saturation in the intracellular lipid accumulation with time, however, was not predicted by the model which was shown to be an inherent feature of the Luedeking-Piret model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- S 0, P 0 kg/m3 :
-
Initial concentrations of sugar and lipid respectively
- S, S(t) kg/m3 :
-
Concentrations of sugar and lipid respeclively at any timet
- p,p(t) L kg/m3 :
-
Maximum concentration of lipid produced
- E %:
-
Maximum sugar utilised
- dP/dt kg/(m3 · h):
-
Rate of lipid production
- -dS/dt kg/(m3 · h):
-
Rate of sugar utilisation
- μ max h−1 :
-
Maximum specific growth rate
- X max kg/m3 :
-
Maximum biomass reached in a run
- P max kg/m3 :
-
Maximum product concentration
- m, n :
-
Constants used in Luedeking-Piret model in eq. (7)
- α, β :
-
Constants used to predict residual sugar
- k e :
-
maintainance coefficient
- Y x g/g:
-
Biomass yield based on sugar consumed
- Y p g/g:
-
Lipid yield based on sugar consumed
- (dP/d t)stat kg/(m3 · h):
-
Rate of lipid production at stationary phase
- (dS/dt)stat kg/(m3 · h):
-
Rate of sugar utilisation at stationary phase
References
Sattur, A. P.; Karanth, N. G.: Mathematical modeling of production of microbial lipids. I — Kinetics of biomass growth. Bioprocess Engg. 6 (1991)
Ratledge, C.: Microbial oils and fats — An assessment of their commencai potential. Prog. Ind Microbiol. 16 (1984) 119–206
Weiss, R. M.; Ollis, D. F.: Extracellular microbial polysaccharides. I. Substrate, biomass, and product kinetic equations for batch xanthan gum fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioengg. 22 (1980) 859–873
Yoon, R. H.; Rhee, J. S.: Quantitative physiology of Rhodotorula gracilis for microbial lipid production. Proc. Biochem. Oct (1983) 2–4
Evans, C. T.; Ratledge, C.: Effect of nitrogen source on lipid accumulation in oleaginous yeasts. J. Gen. Microbiol. 130 (1984) 1693–1704
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karanth, N.G., Sattur, A.P. Mathematical modeling of production of microbial lipids. Bioprocess Engineering 6, 241–248 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369553
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369553