Abstract
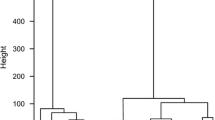
Artificial neural networks with unsupervised learning strategy known as Self-Organizing Maps were applied to classify ancient Roman glazed ceramics. Their clay ceramic bodies were analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy and the chemical composition obtained was processed by this neural algorithm. The results obtained provide two types of information: firstly, classification of ceramic samples with identification of several groups and secondly, differentiation between the elemental chemical information. It was found that there are certain chemical elements which can be considered as principal and which can serve to differentiate between ceramics, whereas other elements give redundant information and do not contribute to sample differentiation. Seven chemical elements were considered principal and provide the necessary information. Two types of element were identified: 1 – a group formed by common elements, such as: Ca, Fe, Mg, Mn and 2 – another formed by optional elements: K or Na and Ba or Sr and Al or Ti.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 October 1999 / Revised: 20 March 2000 / Accepted: 23 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez-Molinero, A., Castro, A., Pino, J. et al. Classification of ancient Roman glazed ceramics using the neural network of Self-Organizing Maps. Fresenius J Anal Chem 367, 586–589 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160000433
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160000433