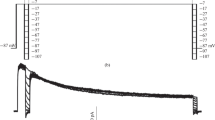
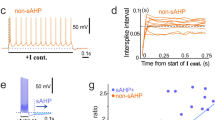
Abstract
Slowly inactivating outward currents were examined in neurons from rat anterior cortex dissociated at postnatal day 1 and recorded after 7–48 days in vitro by the use of whole-cell patch-clamp technique, in the presence of 0.5–0.8 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX), 50 μM carbachol and 1–5 mM CsCl2. Experiments were often carried out in the additional presence of 1–5 mM CsCl2, which blocks the anomalous, inwardly rectifying I Q, the fast Ca +2 -dependent K+ current (I C), and 50 μM carbachol, which depresses the I M current. These currents were evoked by depolarizing steps to -40+-5 mV from a conditioning hyperpolarization to -110+-10 mV. Their sensitivity to elevation from 2.5 to 12.5 mM in extracellular K+ concentration, together with their sensitivity to 5–15 mM tetraethylammonium, suggests that they are mainly carried by K+ ions. Their activation and inactivation curves show that the threshold for activation is -65 mV, that their inactivation is achieved at -75 mV and that potentials more negative than -120 mV are needed to abolish it. The time-dependence of de-inactivation gives a maximal current amplitude for conditioning hyperpolarizations of 2 s and is best described by a monoexponential function with a time constant of 0.7 s. Slow, transient K+ currents were depressed by low doses of 4-aminopyridine (30–100 μM), which indicates the occurrence of an I D-type component in the recorded K+ currents. No slowly declining K+ current was expressed when a recording solution containing 10 mM 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N, N,N′-N′-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA), instead of 1–5 mM BAPTA, was used. When recorded without Ca2+ chelator in the pipette, slowly declining K+ currents were blocked by bath-applied 40–50 μM BAPTA-aminoethoxy, revealing a large-amplitude, rapidly inactivating outward current. This residual component is insensitive to 50 μM 4-aminopyridine and may include a current more related to the I A-type. Our data provide evidence that, in cultured cortical neurons from rat, the expression of an I D-like K+ current is highly dependent on internal Ca2+ concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams PR, Halliwell JV (1982) A hyperpolarization-induced inward current in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 324:62–63P
Alonso A, Llinas R (1989) Subthreshold Na+-dependent theta-like rhythmicity in stellate cells of entorhinal cortex layer. II. Nature 342:175–177
Alzheimer C, Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1993) Postnatal development of a persistent Na+ current in pyramidal neurons from rat sensorimotor cortex. J Neurophysiol 69:290–292
Audinat E, Hermel JM, Crépel F (1989) Neurotensin-induced excitation of neurons of the rat's frontal cortex studied intracellularly in vitro. Exp Brain Res 78:358–368
Augustine GJ (1990) Regulation of transmitter release at the squid giant synapse by presynaptic delayed rectifier potassium current. J Physiol (Lond) 431:343–364
Baraban JM, Snyder SH, Alger BE (1985) Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:2538–2542
Barone P, Joseph IP (1989) Prefrontal cortex and spatial sequencing in macaque monkey. Exp Brain Res 78:447–464
Batuev AS, Pirogov AA, Orlov AA (1979) Unit activity of the prefrontal cortex during delayed alternation performance in monkey. Acta Physiol Hung 3:345–353
Batuev AS, Kursina NP, Shutov AP (1990) Unit-activity of the medial wall of the frontal cortex during delayed performance in rats. Behav Brain Res 41:95–102
Belluzzi O, Sacchi O, Wanke E (1985) Identification of delayed potassium and calcium currents in the rat sympathetic neurone under voltage clamp. J Physiol (Lond) 358:109–130
Brown DA, Constanti A, Adams PR (1983) Ca-activated potassium currents in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium 4:407–420
Byrne JH (1980) Quantitative aspects of ionic conductance mechanisms contributing to firing pattern of motor cells mediating inking behaviour in Aplysia californica. J Neurophysiol 43: 651–668
Choquet D, Korn H (1992) Mechanism of 4-aminopyridine action on voltage-gated potassium channels in lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol 99:217–240
Constanti A, Galvan M (1983) Fast inward-rectifying current accounts for anomalous rectification in olfactory cortex neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 335:153–178
Crépel V, Krnjevic K, Ben-Ari Y (1993) Sulphonylureas reduce the slowly inactivating D-type outward current in rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 466:39–54
Ficker E, Heinemann U (1992) Slow and fast transient potassium currents in cultured rat hippocampal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 445:431–455
Fuster J M (1973) Unit activity in prefrontal cortex during delayed-response performance: neuronal correlates of transient memory. J Neurophysiol 36:61–78
Galvan M, Sedlmeier C (1984) Outward currents in voltageclamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 356: 115–133
Goldman-Rakic PS (1987) Circuitry of primate prefrontal cortex and regulation of behaviour by representational memory. In: Plum F (ed) Higher functions of the brain (Handbook of physiology, sect 1, The nervous system, vol V) Am Physiol Assoc, Bethesda, pp 373–417
Greene RW, Haas HL, Reiner PB (1990) Two transient outward currents in histamine neurones of the rat hypothalamus in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 420:149–163
Guigon E, Dorizzi B, Burnod Y, Schultz W (1994) Neural correlates of learning in the prefrontal cortex of the monkey: a predictive model. Cerebral Cortex (In press)
Gustafsson B, Galvan M, Grafe P, Wigstrom H (1982) A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature 299:252–254
Halliwell JV, Adams PR (1982) Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 250:71–92
Hammond C, Crépel F (1992) The presence of a slowly inactivating K+ current and its role on the firing properties in prefrontal cortical cells. Eur J Neurosci 4:1087–1092
Hounsgaard J, Mintz I (1988) Calcium conductance and firing properties of spinal motoneurones in the turtle. J Physiol. (Lond) 398:591–603
Hounsgaard J, Hultborn H, Jespersen B, Kiehn O (1984) Intrinsic membrane properties causing a bistable behaviour of α-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res 55:391–394
Huguenard JR, Hamill OP, Prince DA (1988) Developmental changes in Na+ conductances in rat neocortical neurons: appearance of a slowly inactivating component. J Neurophysiol 59:778–795
Kikkawa U, Takai Y, Minakuchi R, Inohara S, Nishikuza Y (1982) Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. J Biol Chem 257:13341–13348
Kitai ST, Surmeier DJ (1993) Cholinergic and dopaminergic modulation of potassium conductances in neostriatal neurons. Adv Neurol 60:40–52
Krjnevic K, Crépel V, Ben-Ari Y (1991) Calcium dependence of I D in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17: 587–4
Malenka RC, Madison DV, Andrade R, Nicoll RA (1986) Phorbol esters mimic some cholinergic actions in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 6: 475–480
McCormick DA (1991) Functional properties of a slowly inactivating potassium current in guinea pig dorsal lateral geniculate relay neurons. J Neurophysiol 66:1176–1189
Numann RE, Wadman WI, Wong RKS (1987) Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guineapig. J Physiol (Lond) 393:331–353
Owen DG, Marsh SJ, Brown DA (1990) M-current noise and putative M-channels in cultured rat sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol (Lond) 431:269–290
Rudy B (1988) Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience 25:729–749
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic PS (1991) D1 dopamine receptors in prefrontal cortex: involvement in working memory. Science 251:947–950
Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1980) Properties of a persistent inward current in normal and TEA-injected motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 43:1700–1724
Schwindt PC, Spain WJ, Crill WE (1992) Effects of intracellular calcium chelation on voltage-dependent and calcium-dependent currents in cat neocortical neurons. Neuroscience 47: 571–578
Segal M, Barker JL (1984) Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol 51:1409–1433
Spain WJ, Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1991) Two transient potassium currents in layer V pyramidal neurones from cat sensorimotor cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 434:591–607
Stafstrom CE, Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1982) Negative slope conductance due to a persistent Subthreshold sodium current in cat neocortical neurons in vitro. Brain Res 236:221–226
Stafstrom CE, Schwindt PC, Chubb MC, Crill WE (1985) Properties of persistent sodium conductance and calcium conductance of layer V neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol 53:153–170
Stansfeld CE, Marsh SJ, Halliwell JV, Brown DA (1986) 4-aminopyridine and dendrotoxin induce repetitive firing in rat visceral sensory neurones by blocking a slowly inactivating outward current. Neurosci Lett 64:299–304
Storm J (1988) Temporal integration by a slowly inactivating K+ current in hippocampal neurons. Nature 336:379–381
Surmeier DJ, Stefani A, Foehring RC, Kitai ST (1991) Developmental regulation of a slowly-inactivating potassium conductance in rat neostriatal neurons. Neurosci Lett 122:41–46
Sutor B, Zieglgänsberger WA (1987) Low voltage activated, transient calcium current is responsible for the time-dependent inward rectification of rat neocortical neurons in vitro. Pflugers Arch 410:102–111
Tseng GF, Haberly LB (1989) Deep neurons in piriform cortex. II Membrane properties that underlie unusual synaptic responses. J Neurophysiol 62:386–399
Wagoner PK, Oxford GS (1990) Aminopyridines block an inactivating potassium current having slow recovery kinetics. Biophys J 58:1481–1489
Watanabe M (1986) Prefrontal unit activity during delayed conditional go/no-go discrimination in the monkey. I Relation to the stimulus. Brain Res 382:1–14
Watanabe M (1990) Prefrontal unit activity during associative learning in the monkey. Exp Brain Res 80:296–309
Zbicz KL, Weight FF (1985) Transient voltage and calcium-dependent outward currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 53:1038–1058
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamon, B., Audinat, E., Gibelin, N. et al. Calcium-dependent, slowly inactivating potassium currents in cultured neurons of rat neocortex. Exp Brain Res 107, 197–204 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230041
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230041