Abstract
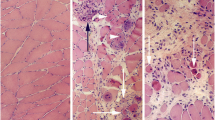
The density of substance P (SP)-, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-immunoreactive (ir) nerve endings was quantitatively evaluated in intact and inflamed gastrocnemius-soleus muscle of the rat. In persistently inflamed muscle (12 days after a single injection of Freund’s adjuvant into the muscle), the density of SP-ir fibres was significantly increased. CGRP- and VIP-ir fibres displayed an insignificant increase in density. The density of fibres ir for nerve growth factor (NGF) and for growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43/B-50), a marker for axonal sprouting, regeneration and synaptic reorganisation, increased significantly in persistently inflamed muscle. The data are consistent with the established contribution of NGF on the expression of SP and GAP-43 in afferent neurones under the influence of a persistent inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 September 1997 / Accepted: 12 February 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinert, A., Kaske, A. & Mense, S. Inflammation-induced increase in the density of neuropeptide-immunoreactive nerve endings in rat skeletal muscle. Exp Brain Res 121, 174–180 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050449
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050449