Summary
Stimulation of the lateral funicle was performed at different segmenta levels in the cat in order to investigate the connecxions of long propriospinal neurones with ipsilateral lumbosacral motoneurones and interneurones projecting directly to them.
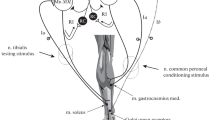
In one series of experiments the propriospinal contribution was assessed from the difference between the effect of maximal stimulation in C 1 (activating supraspinal descending fibres) and in more caudal segments (activating supraspinal and propriospinal fibres). In another series on cats with chronic hemisection in C 3 pure propriospinal effects were evoked by stimulation of the thoracic spinal cord. In both series it was shown that volleys in long propriospinal neurones evoke monosynaptic EPSPs and disynaptic EPSP and/or IPSP in many flexor and extensor motoneurones; an extracellular monosynaptic focal synaptic potential was recorded in lamina VII of Rexed.
The effects evoked by stimulation of the Th 11 segment after chronic C 3 hemisection were not found after chronic Th 10 hemisection. It is therefore tentatively suggested that they were due to stimulation of long descending propriospinal neurones originating in the lower cervical and upper thoracic segments, their axon trajectory being in the middle of the lateral funiculus and conduct at velocity 100 m/sec. Other effects evoked by stimulation of Th 11 after chronic Th 10 hemisection are ascribed to antidromic activation of axons of ascending neurones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, V.C.: Spino-spinal mechanisms in the chloralose anaesthetized cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 215, 755–768 (1971)
Abrahams, V.C., Falchetto, S.: Hind limb ataxia of cervical origin and cervico-lumbar spinal interactions with a supratiatonal pathway. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 203, 435–447 (1969)
Baldissera, F., Lundberg, A., Udo, M.: Activity evoked from the mesencephalic tegmentum in descending pathways other than the rubrospinal tract. Exp. Brain Res. 15, 133–150 (1972)
Barilari, M.G., Kuypers, H.G.J.M.: Propriospinal fibres interconnecting the spinal enlargements in the cat. Brain Res. 14, 321–330 (1969)
Bayev, K.V., Kostyuk, P.G.: Convergence of cortico- and rubrospinal influences on interneurones of cat cervical spinal cord. Brain Res. 52, 159–172 (1973).
Bergmans, J., Miller, S., Reitsma, D.J.: Influence of L-DOPA on transmission in long ascending propriospinal pathways in the cat. Brain Res. 62, 155–167 (1973)
Bruggencate, G. ten, Lundberg, A.: Facilitatory interaction in transmission to motoneurones from vestibulo-spinal fibres and contralateral afferents. Exp. Brain Res. (In press 1974)
Djalali, E.: Relations neurophysiologiques brachio-lombaires chez le chat spinal. Université d'Aix-Marseille I. Thèse (1970)
Eccles, J.C.: The Physiology of Synapses, p. 316. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1964
Eide, E., Lundberg, A., Voorhoeve, P.: Monosynaptically evoked inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in motoneurones. Acta physiol. scand. 53, 185–195 (1961)
Fry, F.J., Cowan, W.M.: A study of retrograde cell degeneration in the lateral mammillary nucleus of the cat, with special reference to the role of axonal branching in the preservation of the cell. J. comp. Neurol. 144, 1–24 (1972)
Gernandt, B.E., Gilman, S.: Vestibular and propriospinal interactions and protracted spinal inhibition by brain stem activation. J. Neurophysiol. 23, 269–287 (1960)
Gernandt, B.E., Megirian, D.: Ascending propriospinal mechanisms. J. Neurophysiol. 24, 364–376 (1961)
Grillner, S., Hongo, T.: Vestibulospinal effects on motoneurones and interneurones in the lumbosacral cord. In: Basic aspects of central vestibular mechanisms. Ed. by A. Brodal and O. Pompeiano. Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 37. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1972
Grillner, S., Hongo, T., Lund, S.: The vestibulospinal tract. Effects on alpha-motoneurones in the lumbosacral spinal cord in the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 10, 94–120 (1970)
Grillner, S., Lund, S.: The origin of a descending pathway with monosynaptic action on flexor motoneurones. Acta physiol. scand. 74, 274–284 (1968)
Hongo, T., Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A.: Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory action on interneurones in the lumbosacral cord. Exp. Brain Res. 1, 338–358 (1966)
Hongo, T., Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A.: The rubrospinal tract. I. Effects on alpha-motoneurones innervating hindlimb muscles in cats. Exp. Brain Res. 7, 344–364 (1969a)
Hongo, T., Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A.: The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp. Brain Res. 7, 365–391 (1969b)
Hongo, T., Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A.: The rubrospinal tract. IV. Effects on interneurones. Exp. Brain Res. 15, 54–78 (1972)
Hultborn, H., Jankowska, E., Lindström, S.: Recurrent inhibition of interneurones mono-synaptically activated from group Ia afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 215, 613–636 (1971)
Jankowska, E.: Identification of interneurones interposed in different spinal reflex pathways. Materials of the Golgi Centennial Symposium. Ed. by D. Purpura and M. Santini (in press, 1974)
Jankowska, E., Lindström, S.: Morphology of interneurones mediating Ia reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones in the spinal cord of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 226, 805–823 (1972)
Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A., Stuart, D.: Propriospinal control of last order interneurones of spinal reflex pathways in the cat. Brain Res. 53, 227–231 (1973)
Jankowska, E., Roberts, W.J.: An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 222, 597–622 (1972a)
Jankowska, E., Roberts, W.J.: Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 222, 623–642 (1972b)
Jankowska, E., Smith, D.O.: Antidromic activation of Renshaw cells and their axonal projections. Acta physiol. scand. 88, 198–214 (1973)
Kostyuk, P.G., Vasilenko, D.A., Lang, E.: Propriospinal pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus and their effects on lumbosacral motoneuronal pools. Brain Res. 28, 233–249 (1971)
Kostyuk, P.G., Vasilenko, D.A., Zadorozkuy, A.G.: Responses of motoneurons of lumbar spinal cord evoked by activity from the propriospinal pathways. Neurophysiology (Kiev) 1, 5–14 (1969)
Kubota, K., Kidokoro, Y., Susaki, J.: Postsynaptic inhibitions of trigeminal and lumbar motoneurons from the superficial radial nerve in the cat. Jap. J. Physiol. 18, 198–215 (1968)
Lloyd, D.P.C.: Activity in neurons of the bulbospinal correlation system. J. Neurophysiol. 4, 115–134 (1941)
Lloyd, D.P.C.: Mediation of descending long spinal reflex activity. J. Neurophysiol. 5, 435–458 (1942)
Lloyd, D.P.C., McIntyre, A.K.: Analysis of forelimb-hindlimb reflex activity in acutely decapitate cats. J. Neurophysiol. 11, 455–470 (1948)
Lund, S., Pompeiano, O.: Monosynaptic excitation of alpha motoneurones from supraspinal structures in the cat. Acta physiol. scand. 73, 1–21 (1968)
Lundberg, A., Voorhoeve, P.: Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta physiol. scand. 56, 201–219 (1962)
McCouch, G.P., Austin, G.M., Liu, C.N., Liu, C.Y.: Sprouting as a cause of spasticity. J. Neurophysiol. 21, 205–216 (1958)
Miller, S., Reitsma, D.J., van der Meché, F.G.A.: Functional organization of long ascending propriospinal pathways linking lumbosacral and cervical segments in the cat. Brain Res. 62, 169–188 (1973)
Miller, S., van der Burg, J.: The function of long propriospinal pathways in the co-ordination of quadrupedal stepping in the cat. In: Control of posture and locomotion. Ed. by Stein et. al. Plenum Press 1973
Raisman, G., Field, P.: A quantitative investigation of the development of collateral reinervation after partial deafferentation of the septal nuclei. Brain Res. 50, 241–264 (1973)
Ramón y Cajal, S.: Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertebrés. Vol. 1. Paris: Maloine 1909
Rexed, B.: A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 100, 297–379 (1954)
Rustioni, A.: Non primary afferents to the nucleus gracilis from the lumbar cord of the cat. Brain Res. 51, 81–95 (1973)
Rustioni, A., Kuypers, H.G.J.M., Holstege, G.: Propriospinal projections from the ventral and lateral funiculi to the motoneurones in the lumbosacral cord of the cat. Brain Res. 34, 255–275 (1871)
Ryall, R., Piercey, M.F., Polosa, C.: Intersegmental and intrasegmental distribution of mutual inhibition of Renshaw cells. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 700–707 (1971)
Scheibel, M.E., Scheibel, A.B.: A structural analysis of spinal interneurons and Renshaw cells. In: The Interneuron. Ed. by M.A.B. Brazier. UCLA Forum Med. Sci. No. 11, p. 159–208. Los Angeles: University of California Press 1969
Shapovalov, A.I.: Excitation and inhibition of spinal neurones during supraspinal stimulation. In: Muscular Afferents and Motor Control. Nobel Symposium I. Ed. by R. Granit, pp. 331–348. Stockholm: Almqvist & Wiksell 1966
Shapovalov, A.I.: Monosynaptic control of spinal motoneurons from different levels of the brain. Neirofiziologia 2, 203–215 (1970)
Shapovalov, A.I., Karamjan, O.A., Kurchavyj, G.G., Repina, Z.A.: Synaptic actions evoked from the red nucleus on the spinal alpha-motoneurones in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 32, 325–348 (1971)
Sherrington, C.S., Laslett, E.E.: Observations on some spinal reflexes and the interconnection of spinal segments. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 29, 58–96 (1903)
Sterling, P., Kuypers, H.G.J.M.: Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of cat. III. The propriospinal connections. Brain Res. 7, 419–443 (1968)
Stewart, D.H., Preston, J.B., Whitlock, D.G.: Spinal pathways mediating cortex evoked excitability changes in segmental motoneurones in pyramidal cats. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 928–937 (1968)
Wilson, V.J., Yoshida, M.: Comparison of effects of stimulation of Deiters' nucleus and medial longitudinal fasciculus on neck, forelimb and hindlimb motoneurones. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 743–758 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council (project No 94). D.S. held a special research fellowship (NS-2451) from the U.S.P.H.S.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A., Roberts, W.J. et al. A long propriospinal system with direct effect on motoneurones and on interneurones in the cat lumbosacral cord. Exp Brain Res 21, 169–194 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234388
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234388