Summary
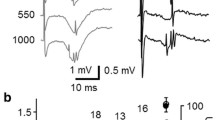
Spontaneous activity of single neurones in neocortex was sampled using pairs of microelectrodes in rats anaesthetised with urethane. In confirmation of previous studies, many cells recorded from middle layers characteristically fired in bursts, the onset times of which were synchronous both unilaterally and bilaterally. Iontophoresis of 2APV onto such cells either caused an abolition of bursts or a reduction in spikes per burst. In the latter case action potentials which occurred later in the burst were preferentially abolished. Iontophoresis of NMDA onto the same cells caused a prolongation of bursts with minimal effect on intraburst interspike interval. In interactive trials with the two drugs the effect of NMDA could be abolished by 2APV, and NMDA counteracted the effect of 2APV. It is concluded that spontaneous burst generation in neocortex during urethane anaesthesia is generated through a cortical NMDA/2APV-sensitive receptor mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong-James M, Fox K, Millar J (1980) A method of etching the tips of carbon fibre microelectrodes. J Neurosci Meth 2: 431–432
Armstrong-James M, Fox K, Kruk ZL, Millar J (1981) Quantitative ionophoresis of catecholamines using multibarrel carbon fibre microelectrodes. J Neurosci Meth 4: 385–406
Armstrong-James M, Fox K (1983) Effects of ionophoresed noradrenaline on the spontaneous activity of neurones in rat Sml cortex. J Physiol 335: 427–447
Armstrong-James M, Fox K (1984) Similarities in unitary cortical activity between slow wave sleep and light urethane anaesthesia. J Physiol 346: 55p
Armstrong-James M, Caan AW (1984) Sensory properties of units showing synchronous bursting activity in Sml cortex of urethane anaesthetized rat. J Physiol 357: 36p
Birley S, Collins JF, Perkins MN, Stone TW (1982) The effects of cyclic dicarboxylic acids on the spontaneous and amino acidevoked activity of rat cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol 77: 7–12
Creutzfeldt OD, Houchin J (1974) Neuronal basis of EEG-waves, pp 2C-5–2C-55. In: Creutzfeld OD (ed) Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology, Vol 2, Part C. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Evarts EV, Bental E, Bihari B, Huttenlocher PR (1962) Spontaneous discharge of single neurones during sleep and waking. Science 135: 726–728
Flatman JA, Schwindt PC, Crill WE, Stafstrom CE (1983) Multiple actions of NMDA on cat neocortical neurones in vitro. Brain Res 266: 169–173
Hubel DH (1959) Single unit activity in striate cortex of unanaes-thetised cats. J Physiol 147: 226–238
Llinas R, Sugimori M (1980) Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol 305: 171–213
Watkins JC, Evans RH (1981) Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 21: 165–204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong-James, M., Caan, A.W. & Fox, K. Threshold effects of N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) and 2-amino 5-phosphono valeric acid (2APV) on the spontaneous activity of neocortical single neurones in the urethane anaesthetised rat. Exp Brain Res 60, 209–213 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237036
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237036