Summary
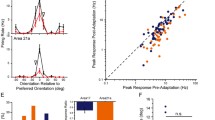
Responses of striate cortical neurones to bars of optimal orientation and width, moving with fixed velocity, were recorded in the lightly anaesthetized cat. Effects of periods of pre-adaptation with square-wave gratings of variable spatial frequency and velocity, drifting continuously in each cell's preferred or null directions, were investigated. Variations of cells' directional bias and responsiveness to oriented bars were assessed in relation to the degree and time-course of pre-adaptation to drifting gratings, compared with the preceding level of firing when exposed to uniform backgrounds of the same average luminance. All cells showed some susceptibility to pre-adapting moving gratings: subsequent responses to a bar were initially depressed in the direction of pre-adaptation and, in direction-biased or bidirectional cells, were enhanced in the opposite direction, compared with bar responses following exposure merely to a uniform background. These effects were strongest and most consistent amongst standard complex cells and weakest amongst special complex cells: maximal effects were obtained with adapting gratings of optimal velocity and spatial frequency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow HB, Hill RM (1963) Evidence for a physiological explanation of the Waterfall phenomenon and figurai after-effects. Nature 200: 1345–1347
Blakemore C, Campbell FW (1969) On the existence of neurones in the human visual system selectively sensitive to the orientation and size of retinal images. J Physiol (Lond) 203: 237–260
Hammond P (1980) A semi-chronic preparation for cortical recording. J Physiol (Lond) 298: 3–4P
Hammond P, Ahmed B (1985) Length summation of complex cells in cat striate cortex: a reappraisal of the “special”/“standard” classification. Neuroscience 15: 639–649
Hammond P, MacKay DM (1975) Differential responses of cat visual cortical cells to textured stimuli. Exp Brain Res 22: 427–430
Hammond P, MacKay DM (1983) Influence of luminance gradient reversal on simple cells in feline striate cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 337: 69–87
Hammond P, Smith AT (1982) On the sensitivity of complex cells in feline striate cortex to relative motion. Exp Brain Res 47: 457–460
Hammond P, Smith AT (1984) Sensitivity of complex cells in cat striate cortex to relative motion. Brain Res 301: 287–298
Maffei L, Fiorentini A, Bisti S (1973) Neural correlate of perceptual adaptation to gratings. Science 182: 1036–1038
Movshon JA, Lennie P (1979) Pattern-selective adaptation in visual cortical neurones. Nature 278: 850–852
Sekuler R, Pantle A, Levinson E (1978) Physiological basis of motion perception. In: Held R et al. (eds) Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol VIII: Perception. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Smith AT, Musselwhite MJ, Hammond P (1984) The influence of background motion on the motion after-effect. Vision Res 24: 1075–1082
Thompson P (1981) Velocity after-effects: the effects of adaptation to moving stimuli on the perception of subsequently seen moving stimuli. Vision Res 21: 337–345
Vautin RG, Berkley MA (1977) Responses of single cells in cat visual cortex to prolonged stimulus movement: neural correlates of visual after-effects. J Neurophysiol 40: 1051–1065
von der Heydt R, Hanny P, Adorjani C (1978) Movement after-effects in the visual cortex. Arch Ital Biol 116: 248–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammond, P., Mouat, G.S.V. & Smith, A.T. Motion after-effects in cat striate cortex elicited by moving gratings. Exp Brain Res 60, 411–416 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235938
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235938