Summary
-
1.
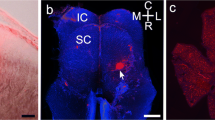
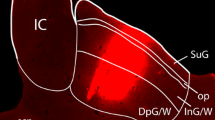
Cat retinal ganglion cells projecting to the superior colliculus (SC) were detected in flat whole-mounts of Nissl-stained retinas by means of unilateral intracollicular injections of horseradish peroxidase (HRP).
-
2.
With the purpose of drawing a comparison between HRP-labeled ganglion cells and the remaining population of unlabeled ganglion cells, the latter were classified according to their perikaryal characteristics into three groups: large, medium and small ganglion cells. Measurements of perikaryal sizes of ganglion cells distributed from the central area to the periphery of the retina showed that large cells ranged from 20 to 44 μm, medium cells from 15 to 30 μm and small cells from 8 to 17 μm.
-
3.
Peroxidase-labeled retinal ganglion cells (HRP-cells) occurred among representatives of each of the three groups into which retinal ganglion cells had been classified. Small HRP-cells clearly constituted the majority of the HRP-cell population. When the injection site was restricted to the superior colliculus, medium HRP-cells as large as 19 μm were only occasionally observed, the 15 to 18 μm range being predominant over the medium cell population.
-
4.
Medium HRP-cells larger than 20 μm were a common finding only when the injection site involved the pretectal nuclei and were never observed when the injection site was restricted to superior colliculus.
-
5.
Possibility of a correspondence between the large, medium and small HRP-cells of the present study with, respectively, the physiological types Y-, X- and W- of cat retinal ganglion cells is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apter, J.T.: Projection of the retina on the superior colliculus of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 8, 123–134 (1945)
Boycott, B.B., Wässle, H.: The morphological types of ganglion cells of the domestic cat's retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 240, 397–419 (1974)
Cleland, B.G., Dubin, M.W., Levick, W.R.: Sustained and transient neurones in the cat's retina and lateral geniculate body. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 217, 473–496 (1971)
Cleland, B.G., Levick, W.R.: Brisk and sluggish concentrically organized ganglion cells in the cat's retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 240, 421–456 (1974a)
Cleland, B.G., Levick, W.R.: Properties of rarely encountered types of ganglion cells in the cat's retina and an overall classification. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 240, 457–492 (1974b)
Enroth-Cugell, C., Robson, J.G.: The contrast sensitivity of retinal ganglion cells of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 187, 517–552 (1966)
Feldon, S., Feldon, P., Kruger, L.: Topography of the retinal projection upon the superior colliculus of the cat. Vision Res. 10, 135–143 (1970)
Fukuda, Y.: Receptive field organization of cat optic nerve fibres with special reference to conduction velocity. Vision Res. 11, 209–226 (1971)
Fukuda, Y., Stone, J.: Retinal distribution and central projections of Y-, X-, and W-cells of the cat's retina. J. Neurophysiol. 37, 749–772 (1974)
Hoffmann, K.-P.: The retinal input to the superior colliculus in the cat. Invest. Ophthal. 11, 467–470 (1972)
Hoffmann, K.-P.: Conduction velocity in pathways from retina to superior colliculus in the cat: a correlation with receptive field properties. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 409–424 (1973)
Hoffmann, K.-P., Stone, J., Sherman, M.S.: Relay of receptive-field properties in dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 35, 518–531 (1972)
Kuffler, S.W.: Discharge patterns and functional organization of mammalian retina. J. Neurophysiol. 16, 37–68 (1953)
LaVail, J.H., LaVail, M.M.: The retrograde axonal transport in the central nervous system. Science 176, 1416–1417 (1972)
Levick, W.R., Cleland, B.G.: Selectivity of microelectrodes in recordings from the cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Neurophysiol. 37, 1387–1393 (1974)
Magalhães-Castro, H.H., Saraiva, P.E.S., Magalhães-Castro, B.: Identification of corticotectal cells of the visual cortex of cats by means of horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 83, 474–479 (1975)
Saito, H., Shimahara, T., Fukada, Y.: Four types of responses to light and dark spots stimuli in the cat optic nerve. Tohoku J. exp. Med. 102, 127–133 (1965)
Stone, J.: A quantitative analysis of distribution of ganglion cells in the cat's retina. J. comp. Neurol. 124, 337–352 (1965)
Stone, J.: The naso-temporal division of the cat's retina. J. comp. Neurol. 126, 585–600 (1966)
Stone, J., Fukuda, Y.: The naso-temporal division of the cat's retina re-examined in terms of Y-, X-, and W-cells. J. comp. Neurol. 155, 377–394 (1974a)
Stone, J., Fukuda, Y.: Properties of cat retinal ganglion cells: a comparison of W-cells with X- and Y-cells. J. Neurophysiol. 37, 722–748 (1974b)
Stone, J., Hoffmann, K.-P.: Very slow conducting ganglion cells in the cat's retina: a major new functional type? Brain Res. 43, 610–616 (1972)
Straschill, M., Hoffmann, K.-P.: Functional aspects of localization in the cat's tectum opticum. Brain Res. 13, 274–283 (1969)
Wässle, H., Levick, W.R., Cleland, B.G.: The distribution of the alpha type of ganglion cells in the cat's retina. J. comp. Neurol. 159, 419–437 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magalhães-Castro, H.H., Murata, L.A. & Magalhães-Castro, B. Cat retinal ganglion cells projecting to the superior colliculus as shown by the horseradish peroxidase method. Exp Brain Res 25, 541–549 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239786
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239786