Summary
-
1.
In chloralose anaesthetised cats the receptive field organisation and response properties of neurones of the spinal trigeminal nucleus were examined and compared with the discharge characteristics of afferent units from vibrissae.
-
2.
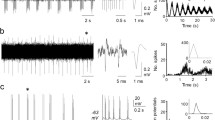
The response properties of the primary afferent discharges were preserved in at least a proportion of the second order cells, 82% of those which responded to movements of the maxillary vibrissae had phasic discharges and 18% had tonic discharges.
-
3.
The discharge characteristics of the two main types of primary afferent slowly-adapting units (St I and St II) were distinguishable in the tonically active cells of the nucleus. These two groups showed (i) substantially different interspike interval distributions, (ii) different adaptive properties and (iii) different directional sensitivity. The two categories were designated nuclear type I and type II in accordance with the classification of primary afferent slowly-adapting units.
-
4.
A loss of stimulus information was deduced from a consistent increase in the variability of the second order discharges compared with their presumed afferent input, but this information loss may be important in allowing the linear summation of discharges at the level of the thalamus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres, K.H.: Über die Feinstruktur der Rezeptoren an Sinushaaren. Z. Zellforsch. 75, 339–365 (1966)
Chambers, M.R., Andres, K.H., von Duering, M., Iggo, A.: The structure and function of the slowly-adapting type II mechanoreceptor in hairy skin. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 57, 417–445 (1972)
Cox, D.R., Lewis, P.A.W.: The statistical analysis of series of events. New York: Wiley (1966)
Darian-Smith, I., Phillips, G., Ryan, R.D.: Functional organisation in trigeminal main sensory and rostral spinal nuclei of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 168, 129–146 (1963)
Gottschaldt, K.-M., Iggo A., Young, D.W.: Functional characteristics of mechanoreceptors in sinus hair follicles of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 235, 287–315 (1973)
Hellon, R.F.: The marking of electrode tip in nervous tissue. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 214, 12P (1971)
Iggo, A., Muir, A.R.: The structure and function of a slowly-adapting touch corpuscle in hairy skin. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 200, 763–796 (1969)
Iggo, A., Gottschaldt, K.-M.: Cutaneous mechanoreceptors in simple and complex sensory structures. In: “Symposium-Mechanoreception” (ed. J. Schwartzkopff), pp. 153–176. Düsseldorf: Westdeutscher Verlag 1974.
Kruger, L., Michel, F.: A morphological and somatotopic analysis of single unit activity in the trigeminal sensory complex of the cat. Exp. Neurol. 5, 139–156 (1962)
Mosso, J.A., Kruger, L.: Receptor categories represented in spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 472–488 (1973)
Perkel, D.H., Gerstein, G.L., Moore, G.P.: Neuronal spike trains and stochastic point processes I. The single spike train. Biophys. J. 7, 391–418 (1967)
Rodieck, R.W., Kiang, N.Y-S., Gerstein, G.L.: Some quantitative methods for the study of single activity of single neurons. Biophys. J. 2, 351–368 (1962)
Schultz, W., Galbraith, G.C., Gottschaldt, K.-M., Creutzfeldt, O.D.: A comparison of primary afferent and cortical neurone activity coding sinus hair movements in the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 24, 365–381 (1976)
Shipley, M.T.: Response characteristics of single units in the rat's trigeminal nuclei to vibrissae displacements. J. Neurophysiol. 37, 73–90 (1974)
Stein, R.B., French, A.S.: Models for the transmission of information by nerve cells. In: Excitatory Synaptic Mechanisms (eds. P. Anderson and J.K.S. Jansen). Oslo: Universitetsförlaget 1970
Wall, P.D., Taub, A.: Four aspects of the trigeminal nucleus and a paradox. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 25 110–126 (1962)
Young, D.W.: Tactile information processing within a trigemino-cerebellar pathway. Doctoral Thesis, University of Edinburgh 1974
Young, D.W.: Some properties of neurones in the spinal trigeminal nucleus responding to movements of the vibrissae. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 244, 75–76P (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, D.W., Iggo, A. Neurones in the spinal trigeminal nucleus of the cat responding to movement of the vibrissae. Exp Brain Res 28, 457–467 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236470
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236470