Summary
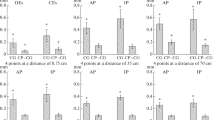
Displacements of the center of foot pressure, the hip and the head were recorded in six subjects standing on a platform, sinusoidally tilting in pitch(anterior-posterior).Stimulusfrequenciesranged between 0.01 and 1 Hz. Stimulus amplitudes were 2, 4 and 6 °. With eyes open the displacements were minimal at 0.3 Hz. With eyes closed, however, induced sway was maximal at this frequency. The apparent lack of visual stabilization at the lowest frequency (0.01 Hz) might be attributed to a subthreshold velocity of the retinal image motion induced by the swaying body. A similar absence of visual stabilization at 1 Hz is assumed to indicate the limit of the working range of visual stabilization of posture. Independent of stimulus amplitude a phase lead of about 90 ° was found at 0.01 Hz. This decreased with increasing frequency up to a phase lag of 100 ° at the highest frequency (1 Hz). Head stabilization was generally more effective than hip stabilization. EMG recordings from the leg muscles suggest that with eyes closed the center of force is mainly stabilized by leg muscle activity, while with eyes open this stabilization is best, when vision allows for stabilization of body posture by intersegmental movements between head, trunk and legs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amblard B, Cremieux J (1976) Role of visual information in the maintenance of postural equilibrium in man. Agressologie 17C: 25–36
Burke D (1980) Muscle spindle function during movement. Trends Neurosci 11: 251–253
Dichgans J, Mauritz KH, Allum JH, Brandt T (1976) Postural sway in normals and atactic patients. Analysis of stabilizing and destabilizing effects of vision. Agressologie 17C: 15–24
Dichgans J, Brandt T (1978) Visual-vestibular interaction. Effects on self-motion perception and postural control. In: Held R, Leibowitz HW, Teuber HL (eds) Handbook of sensory physiology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 755–804
Diener HC (1975) Der räumliche Frequenzeffekt auf das Bewegungssehen beim Menschen. Thesis, Freiburg
Gantchev GN, Dunev S, Draganova N (1972) On the problem of the induced oscillations of the body. Agressologie 13B: 51–54
Gurfinkel VS (1973) Muscle afferentation and postural control in man. Agressologie 14C: 1–8
Gurfinkel VS, Lipshits MI, Mori S, Popov KE (1976a) The state of stretch reflex during quiet standing in man. Prog Brain Res 44: 473–486
Gurfinkel VS, Lipshits MI, Mori S, Popov KE (1976b) Postural reactions to the controlled sinusoidal displacement of the supporting platform. Agressologie 17B: 71–76
Leibowitz HW, Johnson CA, Isabelle E (1972) Peripheral motion detection and refractive error. Science 177: 1207–1208
Lestienne F, Soechting J, Berthoz A (1977) Postural readjustments induced by linear motion of visual scenes. Exp Brain Res 28: 363–384
Mauritz KH, Dichgans J, Hufschmidt A (1977) The angle of visual roll motion determines the displacement of subjective visual vertical. Percept Psychophys 22: 557–562
Nashner LM (1970) Sensory feedback in human posture control. Thesis, Cambridge, Mass. Man Vehicle Laboratory, MIT
Poppele RE, Kennedy WR (1974) Comparison between behaviour of human and cat muscle spindles recorded in vitro. Brain Res 75: 316–319
Tracey DJ (1980) Joint receptors and the control of movement. Trends Neurosci 11: 253–255
Vallbo AB, Hagbarth KE, Torebjörk HE, Wallin BG (1979) Somatosensory, proprioceptive and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves. Physiol Rev 59: 919–957
Walsh EG (1973) Standing man, slow rhythmic tilt, importance of vision. Agressologie 14C: 79–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Di 278/1-1)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diener, H.C., Dichgans, J., Bruzek, W. et al. Stabilization of human posture during induced oscillations of the body. Exp Brain Res 45, 126–132 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235771
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235771