Summary
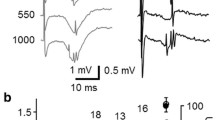
The contribution of ephaptic interactions to potentiation of the hippocampal CA1 extracellular population spike during paired pulse or frequency stimulation of stratum radiatum (SR) inputs was investigated using the in vitro hippocampal slice preparation. Records of the transmembrane potential revealed a depolarizing wave with an amplitude and latency that varied directly with that of the extracellular population spike. Paired pulse or repetitive stimulation of SR resulted in a potentiation of the population spike amplitude and a corresponding increase in the amplitude of the TMP depolarizing wave. Action potentials generated during the stimulus train consistently arose from the peak of the depolarizing wave. It is proposed that ephaptic interactions contribute to potentiation of the extracellular population spike through recruitment of subthreshold neurons within the population during repetitive afferent stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P, Lømo T (1967) Control of hippocampal output by afferent volley frequency. In: Adey WR, Tokizane T (eds) Progress in brain research, vol 27, pp 400–412. Structure and function of the limbic system. Elsevier Publ Co, Amsterdam
Buzsaki G, Czeh G (1981) Commissural and perforant path interactions in the rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res 43: 429–438
Buzsaki G, Eidelberg E (1982) Convergence of associational and commissural pathways on CA1 pyramidal cells of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 237: 283–295
Creager R, Dunwiddie T, Lynch G (1980) Paired pulse and frequency facilitation in the CA1 region of the in vitro rat hippocampus. J Physiol (Lond) 299: 409–424
Ranck JB Jr (1981) Extracellular stimulation. In: Patterson MM, Kesner RP (eds) Electrical stimulation research techniques. Academic Press, New York, pp 2–34
Richardson TL, Turner RW, Miller JJ (1983) Extracellular fields influence transmembrane potentials and synchronization of hippocampal neuronal activity. Brain Res (in press)
Steward O, White WF, Cotman CW, Lynch G (1976) Potentiation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the normal and in the reinnervated dentate gyrus of the rat. Exp Brain Res 26: 423–441
Steward O, White FW, Cotman CW (1977) Potentiation of the excitatory synaptic action of commissural, associational and entorhinal afferents to dentate granule cells. Brain Res 134: 551–560
Taylor CP, Dudek FE (1982) Synchronous neural afterdischarges in rat hippocampal slices without active chemical synapses. Science 218: 810–812
Turner RW, Baimbridge KG, Miller JJ (1982) Calcium-induced long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 7: 1411–1416
Turner RW, Miller JJ (1982) Effects of extracellular calcium on low frequency induced potentiation and habituation in the in vitro hippocampal slice preparation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60: 266–275
White WF, Nadler JV, Cotman CW (1979) Analysis of short-term plasticity at the perforant path — granule cell synapse. Brain Res 178: 41–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Medical Research Council of Canada to JJM. RWT supported by a MRC Studentship and TLR by a BCHCRF Training Fellowship
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turner, R.W., Richardson, T.L. & Miller, J.J. Ephaptic interactions contribute to paired pulse and frequency potentiation of hippocampal field potentials. Exp Brain Res 54, 567–570 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235482
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235482