Summary
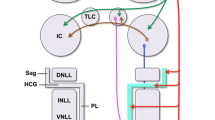
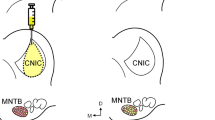
This study investigated afferent projections to the cerebellum, in particular those from the auditory cerebral cortex. The parafloccular lobule of the rat cerebellum is shown to be a primary target for the auditory cortical information with the midvermal region being a receiving area from the inferior colliculus. The method of anterograde transport of tritiated amino acids was employed to determine projections of the auditory cortex to the pons. Autoradiography showed that the site of termination of efferents from the auditory cortex corresponds to the location of neurons that project to the paraflocculus. Histogram analysis of neuronal activity in halothane anesthetized rats was employed to determine the response characteristics of neurons in paraflocculus and midvermis following cortical and tectal electrical stimulation. In addition, unit recordings of parafloccular neurons in immobilized, locally anesthetized animals demonstrated general characteristics of the responses of these neurons to auditory field stimulation. Electrical stimulation of the auditory cortex evoked mixed, excitatory-inhibitory and pure inhibitory mossy fiber responses in 33% of neurons in the paraflocculus, with no responses evident in the midvermis. Following inferior collicular stimulation, 12.6% of the neurons in the midvermis elicited a response. Recordings from parafloccular neurons in unanesthetized, immobilized rats showed evidence for excitatory and inhibitory mossy fiber responses, following auditory field stimulation. This spectrum of basic studies establishes the existence of a pathway in which the paraflocculus is revealed as an integrating target for cortical auditory information.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitkin LM, Boyd J (1975) Responses of single units in cerebellar vermis of the cat to monaural and binaural stimuli. J Neurophysiol 38: 418–429
Allen GI, Azzena GB, Ohno T (1974) Cerebellar Purkinje cell responses to inputs from sensorimotor cortex. Exp Brain Res 30: 239–245
Allen GI, Tsukahara N (1974) Cerebrocerebellar communication systems. Physiol Rev 54: 957–1006
Altman JA, Bechterev NN, Radionova EA, Shimigdina GN, Syka J (1976) Electrical responses of the auditory area of the cerebellar cortex to acoustic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 26: 285–298
Asanuma H, Arnold AP (1975) Noxious effects of excessive currents used for intracortical microstimulation. Brain Res 96: 103–107
Azizi SA, Mihailoff GA, Burne RA, Woodward DJ (1981) The pontocerebellar system in the rat: An HRP study. I. Posterior vermis. J Comp Neurol 197: 543–558
Azizi SA, Woodward DJ (1983) Specific interactions of different sensory modalities in the paraflocculus of the rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 9: 224
Belcari P, Guglielmino S (1976) Electrophysiological investigations on the projections from the cerebral cortex to the vermal posterior lobe of the cerebellum. Pflügers Arch 363: 149–153
Bloedel JR (1973) Cerebellar afferent systems. A review. Prog Neurobiol 2: 1–68
Brodal A, Jansen J (1946) The pontocerebellar projection in the rabbit and cat. Experimental investigations. J Comp Neurol 84: 31–118
Brodal P (1972a) The corticopontine projections in the cat, The projection from the auditory cortex. Arch Ital Biol 110: 119–144
Brodal P (1972b) The corticopontine projection from the visual cortex in the cat. I. The total projection and projection from area 17. Brain Res 390: 297–317
Brodal P (1972c) The corticopontine projection from the visual cortex in the cat. II. The projection from areas 18 and 19. Brain Res 39: 319–335
Brodal P (1978) The corticopontine projection in the rhesus monkey. Origin and principles of organization. Brain 101: 251–238
Brodal P (1979) The pontocerebellar projection in the rhesus monkey: An experimental study with retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Neuroscience 4: 193–205
Brodal P (1982) The corticopontocerebellar pathway: Salient features of its organization. Exp Brain Res Suppl 6: 108–133
Burne RA (1978) Visual input to the paraflocculus of the cerebellum in the rat. Ph. D. dissertation, The University of Rochester, Rochester, New York
Burne RA, Mihailoff GA, Woodward DJ (1978) Visual corticopontine input to the paraflocculus: a combined autoradiographic and horseradish peroxidase study. Brain Res 143: 139–146
Burne RA, Azizi SA, Mihailoff GA, Woodward DJ (1981) The tectopontine projections in rat with comments on visual pathways to the basilar pons. J Comp Neurol 202: 287–307
Burne RA, Woodward DJ (1983) Visual cortical projection to the paraflocculus in the rat. An electrophysiologic Study. Exp Brain Res 49: 55–67
Buser P, Franchel H (1960) Existence d'un foyer de projection sensorielle acoustique au niveau du lobe ansiforme du cervelet chez le chat. Comp Rend 251: 791–793
Chapin JK, Waterhouse BD, Woodward DJ (1981) Differences in cutaneous sensory response properties of single somatosensory cortical neurons in awake and halothane anesthetized rats. Brain Res Bull 6: 63–70
Crispino L (1983) Modification of responses from specific sensory systems in midbrain by cerebellar stimulation: experiments on a teleost fish. J Neurophysiol 49: 3–15
Crispino L, Bullock TH (1984) Cerebellum mediates modality-specific modulation of sensory responses of midbrain and forebrain in rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 291–292
Eccles JC, Faber DS, Murphy JT, Sabah NH, Táboříková H (1971a) Afferent volleys in limb nerves influencing impulse discharges in cerebellar cortex. II. In Purkinje cells. Exp Brain Res 13: 36–53
Eccles JC, Faber DS, Murphy JT, Sabah NH, Táboříková H (1971b) Investigations on integration of mossy fiber inputs to Purkinje cells in the anterior lobe. Exp Brain Res 13: 54–77
Eccles JC, Ito M, Szentágothai J (1967) The cerebellum as a neuronal machine. Springer, New York New York
Evarts EV, Thach WT (1969) Motor mechanisms of the CNS: Cerebro-cerebellar interrelationships. Ann Rev Physiol 31: 451–498
Fadiga E, Pupilli GC (1964) Teleceptive components of the cerebellar function. Physiol Rev 44: 432–486
Freeman JA (1970) Responses of cat cerebellar Purkinje cells to convergent inputs from cerebral cortex and peripheral sensory systems. J Neurophysiol 33: 697–712
Hellweg FC, Koch R, Vollrath M (1977) Representation of the cochlea in the neocortex of Guinea Pigs. Exp Brain Res 29: 467–474
Jansen J (1957) Afferent impulses to the cerebellar hemispheres from the cerebral cortex and certain subcortical nuclei. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 143: 1–99
Kawamura K (1975) The pontine projection from the inferior colliculus in the cat: an experimental anatomical study. Brain Res 95: 309–322
Krieg WJS (1946a) Connections of the cerebral cortex I. The albino rat A. Topography of the cortical areas. J Comp Neurol 84: 221–275
Krieg WJS (1946b) Connections of the cerebral cortex I. The albino rat B. Structure of the cortical areas. J Comp Neurol 84: 277–323
Larsell O (1952) The morphogenesis and adult pattern of the lobules and fissures of the cerebellum of the white rat. J Comp Neurol 97: 281–356
Lorenzo D, Velluti JC, Crispino L, Velluti R (1977) Cerebellar sensory functions: Rat auditory evoked potentials. Exp Neurol 55: 629–636
Massion J, Sasaki K (1979) Cerebro-cerebellar interactions. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam New York Oxford
Merzenich MM, Kaas JH, Roth GL (1976) Auditory cortex in grey squirrel: tonotopic organization and architectonic fields. J Comp Neurol 166: 387–402
Merzenich MM, Knight PL, Roth GL (1974) Cochleotopic organization of primary auditory cortex in the cat. Brain Res 63: 343–346
Mihailoff GA, Burne RA, Azizi SA, Norell G, Woodward DJ (1981) The pontocerebellar system in the rat: an HRP study. II. Hemispheral components. J Comp Neurol 197: 559–557
Mitra J, Snider RS (1969) Cerebellar modification of unitary discharges in auditory system. Exp Neurol 23: 341–352
Mortimer JA (1973) Temporal sequence of cerebellar Purkinje cell and nuclear activity in relation to the acoustic startle response. Brain Res 50: 457–462
Mortimer JA (1975) Cerebellar responses to teleceptive stimuli in alert monkeys. Brain Res 83: 369–390
Shofer RJ, Nahvi MJ, Strom M (1969) Frequency sensitive auditory responses in the cat cerebellum with surface and microelectrode recordings. Electroenceph Clin Neurol 26: 633
Snider RS, Stowell A (1944) Receiving areas of tactile, auditory and visual systems in the cerebellum. J Neurophysiol 1: 331–357
Teramoto S, Snider RS (1966) Modification of auditory responses by cerebellar stimulation. Exp Neurol 16: 191–200
Trouche E, Beaubaton D (1980) Initiation of a goal-directed movement in the monkey. Role of the cerebellar dentate nucleus. Exp Brain Res 40: 311–321
Velluti R, Crispino L (1979) Cerebellar actions on cochlear microphonics and on auditory nerve action potentials. Brain Res Bull 4: 621–624
Watson PJ (1978) Nonmotor functions of the cerebellum. Psychol Bull 85: 944–967
Wiesendanger R, Weisendanger M (1982a) The corticopontine system in the rat. I. Mapping of the corticopontine neurons. J Comp Neurol 208: 215–226
Wiesendanger R, Weisendanger M (1982b) The corticopontine system in the rat. II. The projection pattern. J Comp Neurol 208: 227–238
Wolfe JW (1972) Responses of the cerebellar auditory area to pure tone stimuli. Exp Neurol 36: 295–309
Wolfe JW, Kos CM (1975) Cerebellar inhibition of auditory function. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 80: 314–318
Woodward DJ (1972) PISH-postimulus time and interspike interval histogram. Digital Equipment Co Users Society-Program Library, Decus no. 12-65, Maynard, MA, USA
Woodward DJ, Hoffer BJ, Lapham LW (1969) Postnatal development of electrical and enzyme histochemical activity in Purkinje cells in rat. Exp Neurol 23: 12–139
Woolsey CN (1961) Organization of the cortical auditory system. In: Rosenblith WA (ed) Sensory communications. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 235–257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizi, S.A., Burne, R.A. & Woodward, D.J. The auditory corticopontocerebellar projection in the rat: inputs to the paraflocculus and midvermis. An anatomical and physiological study. Exp Brain Res 59, 36–49 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237663
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237663