Summary
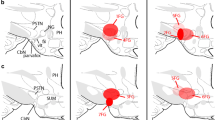
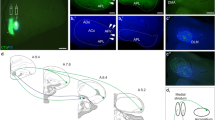
The destruction of th central amygdaloid nucleus (Ce), which contains a large group of neurons with leucine-enkephalin (L-ENK)-like immunoreactivity (L-ENKI), resulted in a marked ipsilateral reduction of these fibers in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST) suggesting that L-ENKI neurons in the Ce project ipsilaterally to the BST. This was supported by the finding that injection of biotin-wheat germ agglutinin into the BST labeled many neurons in the Ce. Simultaneous staining with antiserum showed that some of these neurons are L-ENKI. The L-ENKI fibers from the Ce reach the BST via two pathways; one from the ventral amygdalofugal pathway (VA), which terminate in the ventral subdivision of the BST pars lateralis (BSTL), and the other from the stria terminalis (ST), which terminates in the lateral subdivision of the BSTL, because (1) accumulation of L-ENKI structures appeared in the axons of these two systems on the amygdaloid side, (2) transection or destruction of the ST alone caused only a slight reduction of ENKI fibers in the lateral subdivision of the BSTL ipsilaterally and (3) transection or destruction of VA alone markedly reduced the number of L-ENKI fibers in the ventral subdivision of the ipsilateral BSTL. Thus, the VA L-ENKI fiber system is the major source of L-ENKI fibers in the ventral subdivision, while the ST L-ENKI fiber system is a minor source of the L-ENKI fibers in the lateral subdivision. The presence of an intrinsic L-ENKI system in the BST which may innervate the lateral subdivision was also suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ac:
-
anterior commissure
- AHy:
-
anterior hypothalamic nucleus
- AM:
-
anteromedial thalamic nucleus
- AV:
-
anteroventral thalamic nucleus
- BST:
-
bed nucleus of stria terminalis
- BSTL:
-
BST pars lateralis
- BSTM:
-
BST pars medialis
- Ce:
-
central amygdaloid nucleus
- f:
-
fornix
- GP:
-
globus pallidus
- HDB:
-
horizontal limb of diagonal band of Broca
- ic:
-
internal capsule
- l:
-
lateral subdivision of the BSTL
- LH:
-
lateral hypothalamus
- LPO:
-
lateral preoptic area
- LS:
-
lateral septal nucleus
- m:
-
medial subdivision of the BSTL
- Mfb:
-
medial forebrain bundle
- MPO:
-
medial preoptic area
- MS:
-
medial septal nucleus
- ox:
-
optic chiasma
- Re:
-
reuniens thalamic nucleus
- Rt:
-
reticular thalamic nucleus
- SI:
-
substantia innominata
- sm:
-
stria medularis thalami
- st:
-
stria terminalis
- v:
-
ventral subdivision of the BSTL
- va:
-
ventral amygdalofugal pathway
- VDB:
-
vertical limb of diagonal band of Broca
- VP:
-
ventral pallium
- 2n:
-
optic nerve
- 3v:
-
third ventricle
References
Brodal A (1947) The amygdaloid nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 87: 1–16
Coons AH (1958) Fluorescent antibody method. In: Danielli JF (ed) General cytochemical methods. Academic Press, New York, pp 399–422
Cowan M, Raisman G, Powell TPS (1965) The connections of the amygdala. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 28: 137–151
Dahlstrøm A (1968) Effect of colchicine on transport of amine storage granules in sympathetic nerve of rat. Eur J Pharmacol 5: 111–112
Eiden LE, Hökfelt T, Brownstein MJ, Palkovits M (1985) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide afferents to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat: an immunohistochemical and biochemical study. Neuroscience 15: 999–1013
Elde R, Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Terenius L (1976) Immunohis-tochemical studies using antibodies to leu-enkephalin: initial observation on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience 1: 349–355
Finley JCM, Maderut JL, Petrusz P (1981) The immunocytochemical localization of enkephalin in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol 198: 541–565
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson O, Terenius L, Stein L (1977) The distribution of enkephalin-immunoreactive cell bodies in the rat central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 5: 25–31
Inagaki S, Kawai Y, Matsuzaki T, Shiosaka S, Tohyama M (1983) Precise terminal fields of the descending somatostatinergic neuron system from the amygdaloid complex of the rat. J Hirnforsch 24: 345–356
Kawai Y, Inagaki S, Shiosaka S, Senba E, Hara Y, Sakanaka M, Takatsuki K, Tohyama M (1982) Long descending projections from amygdaloid somatostatin-containing cells to the lower brain stem. Brain Res 239: 603–607
Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Watson SJ (1983) Enkephalin system in diencephalon and brainstem of the rat. J Comp Neurol 220: 310–320
König JFR, Klippel RA (1967) The rat brain: asterotaxic atlas of the forebrain and lower brain stem. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Krettek JE, Price JL (1978a) Amygdaloid projections to subcortical structures within the basal forebrain and brainstem in the rat and cat. J Comp Neurol 178: 225–254
Krettek JE, Price JL (1978b) A description of the amygdaloid complex in the rat and cat, with observations on intraamygdaloid axonal connections. J Comp Neurol 178: 255–280
Kreutzberg G (1969) Neuronal dynamics and flow. IV. Blockage of intraaxonal enzyme transport by colchicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 62: 722–728
Mesulam M-M (1978) Tetramethylbenzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction products with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem 26: 106–117
Moga MM, Gray TS (1985) Evidence for corticotropin-releasing factor, neurotensin, and somatostatin in the neural pathway from the central nucleus of the amygdala to the parabrachial nucleus. J Comp Neurol 241: 275–284
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Price JL, Amaral DG (1981) An autoradiographic study of the projections of the central nucleus of the monkey amygdala. J Neurosci 1: 1242–1259
Sakanaka M, Shiosaka S, Takatsuki K, Inagaki S, Takagi H, Senba E, Kawai Y, Matsuzaki T, Tohyama M (1981) Experimental immunohistochemical studies on the amygdalofugal peptidergic (substance P and somatostatin) fibers in the stria terminalis of the rat. Brain Res 221: 231–242
Senba E, Shiosaka S, Hara Y, Inagaki S, Kawai Y, Takatsuki K, Sakanaka M, Takagi H, Minagawa H, Tohyama M (1982) Ontogeny of leucine-enkephalin system of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis. I. Lower brain stem. J Comp Neurol 203: 173–188
Shiosaka S, Sakanaka M, Inagaki S, Senba E, Hara Y, Takatsuki K, Takagi H, Kawai Y, Tohyama M (1983) Putative neurotransmitters in the amygdaloid complex with special reference to peptidergic pathways. In: Emson PC (ed) Chemical neuroanatomy. Raven Press, New York, pp 359–389
Shiosaka S, Shibasaki T, Tohyama M (1984) Bilateral α-melanocyte stimulating hormonergic fiber system zona incerta to cerebral cortex: combined retrograde axonal transport and immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 309: 350–353
Shiosaka S, Shimada S, Tohyama M (1986a) Sensitive doublelabeling technique of retrograde biotinized tracer (biotinWGA) and immunocytochemistry: light and electron microscopic analysis. J Neurosci Methods 16: 9–18
Shiosaka S, Tohyama M (1986b) Immunohistochemical techniques. In: Emson PC, Rosser M, Tohyama M (eds) Peptides and neurological disease. Prog Brain Res 66: 3–32
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ, Snyder SH (1978) Enkephalin-containing pathway: amygdaloid efferents in the stria terminalis. Brain Res 149: 223–228
Weller KL, Smith DA (1982) Afferent connections to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Brain Res 232: 255–270
Woodhams PL, Roberts GW, Polak JM, Crow TJ (1983) Distribution of neuropeptides in the limbic system of the rat: the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and preoptic area. Neuroscience 8: 677–703
Zamboni L, De Martino C (1967) Buffered picric acid formaldehyde: a new rapid fixative for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 35: 148A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, Z.R., Yamano, M., Shiosaka, S. et al. Origin of leucine-enkephalin fibers and their two main afferent pathways in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat. Exp Brain Res 65, 411–420 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236314
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236314