Summary
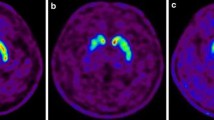
Positron emission tomography following intravenous administration of 6-[18F]-L-fluorodopa was used to investigate the usefulness of PET for the assessment of normal and abnormal dopaminergic function. For this purpose, the incracerebral distribution of 6-[18F]-L-fluorodopa and its metabolites was evaluated in normal control and asymptomatic MPTP-treated rhesus monkeys. MPTP is a neurotoxic compound which destroys selectively the dopaminergic neurons of the nigrostriatal pathways in primates. The 18F accumulation was found to be significantly reduced in the striatum, putamen more than caudate, of the MPTP-treated animals compared to the normal controls. The 18F accumulation in dopamine-poor areas did not differ between the two groups. The ratios of striatum to dopamine-poor brain area were highly correlated to the concentrations of the dopamine metabolite, homovanillic acid, in the cerebrospinal fluid of the same animals. The findings are consistent with the hypothesis that “silent damage” to the dopaminergic nigral neurons may precede the onset of parkinsonism by many years and that PET scanner examination using 6-[18F]-L-fluorodopa may be useful in the detection of subtle dopaminergic dysfunctions as may exist in DA-related motor syndromes and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam MJ, Ruth TJ, Grierson JR, Abeysekera B, Pate BD (1986) Routine synthesis of L-[18F]6-fluorodopa with F-18 acetyl hypofluorite. J Nucl Med 27:1462–1466
Alexander GE, Delong MR, Strick PL (1986) Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Ann Rev Neurosci 9:357–381
Burns RS, Chiueh CC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Jacobowitz DM, Kopin IJ (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra by N-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4546–4550
Calne DB, Langston JW (1983) Aetiology of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Vol. 2:1457–1459
Calne DB, Langston JW, Martin WRW, Stoessl AJ, Ruth TJ, Adam MJ, Pate BD, Schultzer M (1985) Positron emission tomography after MPTP: observations relating to the cause of Parkinson's disease. Nature 317:246–248
Carpenter MB (1981) Anatomy of the corpus striatum and brain stem integrating systems. In: Brookhart JM, Mountcastle VB (eds) Handbook of physiology: the nervous system. Am Physiol Soc, Bethesda, pp 947–995
Chirakal R, Firnau G, Couse J, Garnett ES (1984) Radiofluorination with 18F-labelled acetyl fluorite: [18F]L-6-fluorodopa. Int J Appl Radiat Isot 35:651–653
Chiueh CC, Zubowska-Grojec Z, Kirk KL, Kopin IJ (1983) 6-fluorocatecholamines as false adrenergic neurotransmitters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:529–533
Chiueh CC, Burns RS, Kopin IJ, Kirk KL, Firnau G, Nahmias C, Chirakal R, Garnett ES (1986) 6-18F-Dopa/positron emission tomography visualized degree of damage to brain dopamine in basal ganglia of monkeys with MPTP-induced parkinsonism. In: Markey SP, Castagnoli N Jr, Trevor AJ, Kopin IJ (eds) MPTP: a neurotoxin producing a parkinsonian syndrome. Academic Press, London, pp 327–338
Davis GC, Williams AC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Caine ED, Reichert CM, Kopin IJ (1979) Chronic parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiat Res 1:249–254
Degryse AD, Colpaert FC (1986) Symptoms and behavioral features induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in an old Java monkey [Macaca fascicularis (Raffles)]. Brain Res Bull 16:561–571
Doudet DJ, Gross C, Lebrun-Grandie P, Bioulac B (1985) MPTP primate model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 335:194–199
Eisenhofer G, Goldstein D, Stull R (1986) Simultaneous liquid Chromatographic determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol, catecholamines and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in plasma and their response to inhibition of monoamine oxydase. Clin Chem 32:2030–2033
Fallon JH, Loughlin SE (1986) Monoamine innervation of cerebral cortex and a theory of the role of monoamines in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. In: Jones EG, Peters A (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol 6. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–26
Firnau G, Garnett ES, Chirakal R, Sood S, Nahmias C, Schrobilgen G (1986) [18F]Fluoro-L-Dopa for the in vivo study of intracerebral dopamine. Appl Radiat Isot 37:669–676
Firnau G, Sood S, Chirakal R, Nahmias C, Garnett ES (1987) Cerebral metabolism of 6-18F-fluoro-L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in the primate. J Neurochem 48:1077–1082
Forno LS (1982) Pathology of Parkinson's disease. In: Marsden CD, Fahn S (eds) Movement disorders. Butterworth Scientific, London, pp 25–40
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Chan PKH, Sood S, Belbeck LW (1978) 18F fluorodopa, an analogue of dopa, and its use in direct external measurements of storage, degradation and turnover of intracerebral dopamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:464–467
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Nahmias C, Sood S, Belbeck LW (1980) Blood-brain barrier transport and cerebral utilization of dopa in living monkeys. Am J Physiol 238:R318–327
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Nahmias C (1983a) Dopamine visualized in the basal ganglia of living man. Nature 305:137–138
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Nahmias C, Chirakal R (1983b) Striatal dopamine metabolism in living monkeys examined in positron emission tomography. Brain Res 280:169–171
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Nahmias C, Carbotte R, Bartolucci G (1984a) Reduced striatal glucose consumption and prolonged reaction time are early features in Huntington's disease. J Neurol Sci 65:231–237
Garnett ES, Nahmias C, Firnau G (1984b) Central dopaminergic pathways in hemiparkinsonism examined by positron emission tomography. Can J Neurol Sci 11:174–179
Guttman M, Yong VW, Kim SU, Calne DB, Martin WRW, Adam MJ, Ruth TJ (1988) Asymptomatic striatal dopamine depletion: PET scans in unilateral MPTP monkeys. Synapse 2:469–473
Hefti F, Melamed E, Wurtman RJ (1981) The site of dopamine formation in rat striatum after L-Dopa administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 217:189–197
Horne MK, Cheng CH, Wooten GF (1984) The cerebral metabolism of L-dihydroxyphenylalanine. Pharmacology 28:12–26
Hornykiewicz O (1982) Brain neurotransmitters changes in Parkinson's disease. In: Marsden CD, Fahn S (eds) Movement disorders. Butterworth Scientific, London, pp 41–58
Jewett DM, Potocki JF, Ehrenkaufer RE (1984) A gas-solidphase microchemical method for the synthesis of acetyl fluorite. J Fluor Chem 24:477–484
Kuhl DE, Metter EJ, Riege WH (1984) Patterns of local cerebral glucose utilization determined in Parkinson's disease by the 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose method. Ann Neurol 15:419–424
Langston JW, Ballard PA, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980
Langston JW, Ballard PA (1984) Parkinsonism induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): implication for treatment and the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Can J Neurol Sci 11:160–165
Langston JW, Irwin I (1986) MPTP: current concepts and controversies. Clin Neuropharmacol 9:485–507
Langston JW (1986) MPTP-induced parkinsonism: how good a model is it? In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Jenner P, Teychenne P (eds) Recent advances in Parkinson's disease. Raven Press, New York, pp 119–126
Leenders KL, Palmer AJ, Quinn N, Clark JC, Firnau G, Garnett ES, Nahmias C, Jones T, Marsden CD (1986) Brain dopamine metabolism in patients with Parkinson's disease measured with positron emission tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 49:853–860
Lenzi GL, Jones T, Reid JL, Moss S (1979) Regional impairment of cerebral oxydative metabolism in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 42:59–62
Marsden CD (1982) The mysterious motor function of the basal ganglia: the Robert Wartenberg lecture. Neurology 32:514–539
Martin WRW, Stoessl AJ, Adam MJ, Grierson JR, Ruth TJ, Pate BD, Calne DB (1986a) Imaging of dopamine systems in human subjects exposed to MPTP. In: Markey SP, Castagnoli N Jr, Trevor AJ, Kopin IJ (eds) MPJP: a neurotoxin producing a parkinsonian syndrome. Academic Press, London, pp 315–325
Martin WRW, Stoessl AJ, Adam MJ, Ammann W, Bergstrom M, Harrop R, Laihinen A, Rogers JG, Ruth TJ, Sayre CI, Pate BD, Calne DB (1986b) Positron emission tomography in Parkinson's disease: glucose and DOPA metabolism. In: Yahr MD, Bergmann KJ (eds) Advances in neurology, Vol 45. Raven Press, New York, pp 95–98
Melamed E, Globus M, Mildworf B (1986) Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with Parkinson's disease under chronic levodopa therapy: measurements during “on” and “off” response fluctuations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 49:1301–1304
Mitchell IJ, Cross AJ, Sambrook MA, Crossman AR (1986) N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in the monkey: neurochemical pathology and regional brain metabolism. J Neural Transm Suppl 20:41–46
Nahmias C, Garnett ES, Firnau G, Lang AE (1985) Striatal dopamine distribution in parkinsonian patients during life. J Neurol Sci 69:223–230
Rougemont D, Baron JC, Collard P, Bustany P, Comar D, Agid Y (1984) Local cerebral glucose utilization in treated and untreated patients with Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 47:824–830
Scheinin M, Chang WH, Kirk KL, Linnoila M (1983) Simultaneous determination of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol, 5-hydroxy-indolacetic acid and homovanillic acid in cerebrospinal fluid with high-performance liquid chromatography using electrochemical detection. Analyt Biochem 131:246–253
Schwartzman RJ, Alexander GM (1985) Changes in the local cerebral metabolic rate for glucose in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) primate model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 358:137–143
Taylor AE, Saint Cyr JA, Lang AE (1986) Frontal lobe dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: the cortical focus of neostriatal outflow. Brain 109:845–883
Wolfson LI, Leenders KL, Brown LL, Jones T (1985) Alterations of regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 35:1399–1405
Wooten GF, Horne MK (1982) A new autoradiographic approach for imaging forebrain dopamine distribution. Ann Neurol 12:163–168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doudet, D.J., Miyake, H., Finn, R.T. et al. 6-18F-L-DOPA imaging of the dopamine neostriatal system in normal and clinically normal MPTP-treated rhesus monkeys. Exp Brain Res 78, 69–80 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230688
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230688