Summary
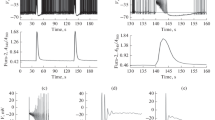
Penicillin-induced paroxysmal depolarization shifts (PDS) are followed by prolonged afterhyperpolarizations of about 2 seconds duration. Intracellular injection of EGTA blocked a late component of the afterhyperpolarizations; an early one lasting up to one second was only slightly reduced by EGTA. It is concluded that afterhyperpolarizations following penicillininduced PDS comprise different components: an initial one lasting up to one second which is not Ca2+-dependent and a slow one lasting up to two seconds which is caused by a Ca2+-dependent K+ current.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmone-Marsan C (1969) Acute effects of topical epileptogenic agents. In: Jasper HH, Ward AA, Pope A (eds) Basic mechanisms of the epilepsies. Little Brown, Boston, pp 299–319
Alger BE (1984) Hippocampus: electrophysiological studies of epileptiform activity in vitro. In: Dingledine R (ed) Brain slices. Plenum Publ, New York, pp 155–200
Alger BE, Nicoll RA (1980) Epileptiform burst afterhyperpolarization: calcium-dependent potassium potential in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Science 210:1122–1124
Bingmann D, Speckmann E-J, Elger CE, Lehmenkühler A, Lensing J, Lipinsky G (1983) Local penicillin activity and neuronal epileptiform discharges in brain slices. In: Speckmann E-J, Elger CE (ed) Epilepsy and motor system. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München Wien Baltimore, pp 139–151
Hablitz JJ (1981) Effects of intracellular injections of chloride and EGTA on post epileptiform-burst hyperpolarization in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 22:159–163
Knowles WD, Schneiderman JH, Wheal HV, Stafstrom CE, Schwartzkroin PA (1984) Hyperpolarizing potentials in guinea pig hippocampal CA3 neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 4:207–230
Newberry NR, Nicoll RA (1984) A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 348:239–254
Schwartzkroin PA, Stafstrom CE (1980) Effects of EGTA on the calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Science 210:1125–1126
Witte OW (1988) Cl--dependent afterpotentials of penicillininduced paroxysmal depolarizations shifts in the motor cortex of the rat in vivo. Pflügers Arch 411: R119
Witte OW, Speckmann E-J, Walden J (1987) Motorcortical epileptic foci in vivo: actions of a calcium channel blocker on paroxysmal neuronal depolarizations. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66:43–55
Witte OW, Uhlig S, Valle E (1989) Separation of different types of afterpotentials following penicillin-induced paroxysmal depolarization shifts of neurones in the motor cortex of the rat. Neurosci Lett 101:51–56
Wong RKS, Prince DA (1978) Participation of calcium spikes during intrinsic burst firing in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 159:385–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domann, R., Dorn, T. & Witte, O.W. Calcium-dependent potassium current following penicillin-induced epileptiform discharges in the hippocampal slice. Exp Brain Res 78, 646–648 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230253
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230253