Abstract
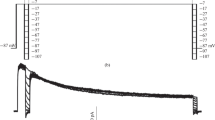
Macroscopic potassium currents were studied in cell-attached and inside-out patches from rat cerebellar granule cells. They were related with transient IA type potassium channels. Currents activated rapidly at potentials higher than -40 mV and did not inactivate completely. The magnitude of the current diminished when the membrane patches were excised. No differences in the activation and inactivation properties were found between patches in the integral cells and cell free membrane patches. A biophysical description of the currents is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong D, Ackert R (1987) Voltage-activated calcium channels must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2518–2522.
Baldwin TJ, Tsaur M-L, Lopez GA, Jan YN, Jan LY (1991) Characterizarion of mammalian cDNA for an inactivating voltage-sensitive K+ channel. Neuron 7:471–483.
Carignani C, Robello M, Marchetti C, Maga L (1991) A transient outward current depends on external calcium in rat cerebellar granule cells. J Membr Biol 122:259–265.
Choi KL, Aldrich RW, Yellen G (1991) Tetraethylammonium blockade distinguished two inactivation mechanisms in voltage-activated K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5092–5095.
Connor JA, Stevens CF (1971) Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol (Lond) 213:21–23.
Cull-Candy SG, Marshall CG, Odgen D (1989) Voltage-activated membrane currents in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 414:179–199.
Galdzicki Z, Lin F, Moran O, Novelli A, Puia G, Sciancalepore M (1991) Development of voltage-dependent ionic currents in rat cerebellar granule cells grown in primary culture. Int J Neurosci 56:193–200.
Grupe A, Scroeter KH, Ruppersberg JP, Stocker M, Drewes T, Beckh S, Pongs O (1990) Cloning and expression of a human voltage gated potassium channel. A novel member of the RCK potassium channel family. EMBO J 9:1749–1756.
Hamill O, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth F (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100.
Hockberger PE, Tseng HY, Connor JA (1987) Immunochemical and electrophysiological differentiation of rat cerebellar granule cells explant cultures. J Neurosci 7:1370–1383.
Hoshi T, Zagota WN, Aldrich RW (1991) Two types of inactivation in Shaker K+ channels: effects of alterations in the carboxy-terminal region. Neuron 7:547–556.
Hwang PM, Glatt CE, Bredt DS, Yellen G, Snyder SH (1992) A novel K+ channel with unique localizations in mammalian brain: molecular cloning and characterization. Neuron 8:473–481.
Isakoff EY, Jan YN, Jan LY (1990) Evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric potassium channels in Xenopus oocytes. Nature 345:530–534.
Jalonen T, Johansson S, Holopainen I, Oja AA, Arhem P (1990) Single-channel and whole-cell currents in rat cerebellar granule cells. Brain Res 535:33–38.
Levi G, Aloisi M, Ciotti M, Gallo V (1984) Autoradiographic localization and depolarization-induced release of acidic amino acids in differentiating cerebellar granule cells cultures. Brain Res 290:77–86.
Moran O, Conti F (1990) Sodium ionic and gating currents in mammalian cells. Eur Biophys J 18:25–32.
Moran O, Lin F, Zegarra-Moran O, Sciancalepore M (1991) Voltage dependent calcium channels in cerebellar granule cell primary cultures. Eur Biophys J 20:157–164.
Nilius B (1988) Modal gating behaviour of cardiac sodium channels in cell-free membrane patches. Biophys J 53:857–862.
Robello M, Carignani C, Marchetti C (1989) A transient voltage-dependent outward current in cultured cerebellar granules. Biosci Rep 9:451–457.
Rudy B (1988) Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neurosci 25:729–749.
Ruppersberg JP, Stocker M, Heinemann SH, Frank R, Koenen M (1991) Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature 352:711–714.
Sheng M, Tsaur M-L, Jan YN, Jan LY (1992) Subcellular segregation of two A-type K+ channel proteins in rat central neurons. Neuron 9:271–284.
Wang H, Kunkel, DD, Martin TM, Schwartzkroin PA, Tempel BL (1993) Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons. Nature 365:75–79.
Wei A, Covarrubias M, Butler A, Baker K, Pak M, Falkoff L (1990) K+ current diversity is produced by an extended gene family conserved in Drosophila and mouse. Science 248:599–603.
Zagotta WN, Hoshi T, Aldrich RW (1989) Gating of single Shaker K+ channels in Drosophila muscle and in Xenopus oocytes injected with Shaker mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7243–7247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zegarra-Moran, O., Moran, O. Properties of the transient potassium currents in cerebellar granule cells. Exp Brain Res 98, 298–304 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228417
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228417