Abstract
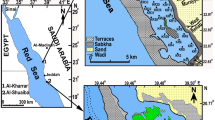
The relationship between the distribution of benthic diatoms and sediment characteristics of the Mangyung-Dongjin tidal flat on the west coast of Korea was investigated during June and July 1988. Diatoms were collected from the upper 5 mm of sediments at 60 sites along eight transect lines running perpendicular to the shore line. Of the 371 taxa encountered in the study area, 88% were pennate diatoms. Genera represented by the greatest number of species were Navicula, Nitzschia, Amphora, Cocconeis, Fragilaria and Achnanthes. The most abundant species were Paralia sulcata, Navicula sp. #1, N. arenaria and Cymatosira belgica; all were broadly distributed across the tidal flats. The 60 sites could be assigned to eight clusters with respect to similarity in species composition. Discriminant analysis showed that separation cluster was primarily related to the mean grain size of the sediment. The species could not be separated into groups based on similarities in occurrence; a high degree of spatial overlap was observed. The preferences of the more abundant species for grain size were, therefore, analysed by plotting numerical abundance against mean grain size. There were at least four patterns: species groups could be associated with finegrained sediments, those of intermediate size and coarser sediments and the last group showed no discernible pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiraal W (1984) The ecology of estuarine sediment-inhabiting diatoms. Prog phycol Res 3:269–322
AdmiraalW, Peletier H (1979) Influence of organic compounds and light limitation on the growth rate of estuarine benthic diatoms. Br Phycol J 14:197–206
Admiraal W, Peletier H, Brouwer T (1984) The seasonal succession patterns of diatom species on an intertidal mudflat: an experimental analysis. Oikos 42:30–40
Amspoker MC (1977) The distribution of intertidal epipsammic diatoms on Scripps Beach, La Jolla, California, USA. Bot mar 20:227–232
Amspoker MC, McIntire CD (1978) Distribution of intertidal diatoms associated with sediments in Yaquina estuary. Oregon. J Phycol 14:387–395
Aston SR (1980) Nutrients, dissolved gases and general biogeochemistry in estuaries. In: Olausson E, Cato I (eds) Chemistry and biogeochemistry of estuaries. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., London, pp 223–262
Ballie PW, Welsh BL (1980) The effect of tidal resuspension on the distribution of intertidal epipelic algae in an estuary. Estuar cstl mar Sci 10:165–180
Brockmann C (1950) Die Watt-Diatomeen der Schleswig-Holsteinischen Westküste. Abh senkenb naturforsch Ges 478:1–26
Carver RE (ed) (1971) Procedures in sedimentary petrology. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Choi JK, Shim JH (1986) The ecological study of phytoplankton in Kyeonggi Bay, Yellow Sea. III. Phytoplankton. J Oceanogr Soc Korea 21:156–170
Colijn F, Jonge VN de (1984) Primary production of microphytobenthos in the Ems-Dollard estuary. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 14:185–196
Cook LL, Whipple SA (1982) The distribution of edaphic diatoms along environmental gradients of a Louisiana salt marsh. J Phycol 18:64–71
Cooley WW, Lohnes PR (1971) Multivariate data analysis. Wiley, New York
Folk RL (1954) The distinction between grain size and mineral composition in sedimentary rock nomenclature. J Geol 62:334–359
Folk RL, Ward WC (1957) Brazos River bar, a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J sedim Petrol 27:3–26
Jonge VN de (1985) The occurrence of ‘epipsammic’ diatom populations: a result of interaction between physical sorting of sediment and certain properties of diatom species. Estuar cstl Shelf Sci 21:607–622
Jonge VN de, Bergs J van den (1987) Experiments on the resuspension of estuarine sediments containing benthic diatoms. Estuar cstl Shelf Sci 24:725–740
Jonge VN de, Beusekom JEE van (1992) Contribution of resuspended microphytobenthos to total phytoplankton in the Ems estuary and its possible role for grazers. Neth J Sea Res 30:91–105
Kim JH, Cho KJ (1985) The physico-chemical properties of sediment, the species composition and biomass of benthic diatoms in the intertidal zone of Keum River estuary. Korean J Ecol 8:199–207
Kosugi M (1987) Limiting factors on the distribution of benthic diatoms in coastal regions — salinity and substratum. Diatom 3:21–31
Lohman KE (1972) A procedure for the microscopical study of diatomaceous sediments. Nova Hedwigia (Beih) 39:267–283
McIntire CD (1973) Diatom associations in Yaquina estuary, Oregon: a multivariate analysis. J Phycol 9:254–259
McIntire CD (1978) The distribution of estuarine diatoms along environmental gradients: a canonical correlation. Estuar cstl mar Sci 6:447–457
McIntire CD, Moore WM (1977) Marine littoral diatoms-ecological considerations. In: Werner D (ed) The biology of diatoms. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 333–371
McIntire CD, Wulff BL (1969) A laboratory method for the study of marine benthic diatoms. Limnol Oceanogr 14:667–668
Norusis MJ (1986) SPSS/PC+ for the IBM PC/XT/AT. SPSS Inc. Chicago
Oh JS (1994) Ecological and taxonomical study of phytoplankton in the estuarine system of the Mangyung and Dongjin Rivers. M.Sc. thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul
Oh SH, Koh CH (1991) Distribution pattern of dominant benthic diatoms on the Mangyung-Dongjin tidal flat, west coast of Korea. J oceanol Soc Korea 26:24–37
OHAROK: Office of Hydrographic Affairs, Republic Of Korea (1987) Tide tables, Vol. 1. OHAROK, Fusan
Oppenheim DR (1988) The distribution of epipelic diatoms along an intertidal shore in relation to principal physical gradients. Bot mar 31:65–72
Rizynk RZ, Phinney HK (1972) The distribution of intertidal phytopsammon in an Oregon estuary. Mar Biol 13:318–324
Roelofs AK (1984) Distributional patterns and variation of valve diameter of Paralia sulcata in surface sediments of southern British Columbia inlets. Estuar cstl Shelf Sci 18:165–176
Round FE (1971) Benthic marine diatoms. Oceanogr mar biol A Rev 9:83–139
Round FE (1979) A diatom assemblage living below the surface of intertidal sand flats. Mar Biol 54:219–223
Shaffer GP, Sullivan MJ (1988) Water column productivity attributable to displaced benthic diatoms in well-mixed shallow estuaries. J Phycol 24:132–140
Shim JH, Shin YK, Yeo HG (1991) Abiotic environment and primary producers of estuarine pelagic ecosystem in the lower water of the Mangyung River and the Dongjin River. J oecanogr Soc Korea 26:155–168
Shim JH, Yang JS (1982) The community structure and distribution of phytoplankton of the Keum River estuary. J oceanogr Soc Korea 17:1–11
Simonsen R (1974) The diatom plankton of the Indian Ocean expedition of R.V. “Meteor” 1964–65. “Meteor” ForschErgebn 19:1–66
Sullivan MJ (1975) Diatom communities from a Delaware salt marsh. J Phycol 11:384–390
Sullivan MJ (1978) Diatom community structure: taxonomic and statistical analysis of a Mississippi salt marsh. J Phycol 14:468–475
Sullivan MJ (1982) Distribution of edaphic diatoms in a Mississippi salt marsh: a canonical correlation analysis. J Phycol 18:130–133
Sullivan MJ, Moncreiff CA (1988a) A multivariate analysis of diatom community structure and distribution in a Mississippi salt marsh. Bot mar 31:93–99
Sullivan MJ, Moncreiff CA (1988b) Primary production of edaphic algal communities in a Mississippi salt marsh. J Phycol 24:49–58
Whitting MC, McIntire CD (1985) An investigation of distributional patterns in the diatom flora of Netarts Bay, Oregon by correspondence analysis. J Phycol 21:655–661
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by T. Ikeda, Nagasaki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, S.H., Koh, C.H. Distribution of diatoms in the surficial sediments of the Mangyung-Dongjin tidal flat, west coast of Korea (Eastern Yellow Sea). Marine Biology 122, 487–496 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350883
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350883