Abstract
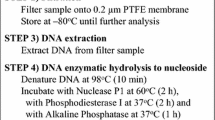
A simple technique is described for de-salting and concentrating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) extracted from seawater or marine sediment samples prior to assays with the standard luciferin-luciferase procedure. The technique involves chromatography of H2SO4 extracts on columns of activated carbon. The efficiency of ATP recovery from marine sediments using this pre-treatment was superior to that attained with either boiling “Tris” extraction or with H2SO4 extraction without subsequent purification. All ions which interfere with the luciferase reaction or precipitate ATP upon neutralization of acid extracts are removed with this procedure, thus eliminating the 50- to 100-fold dilutions required with other acid-extraction procedures. In addition, the purified ATP extracts may be concentrated up to 100-fold, thus greatly improving the sensitivity of ATP measurement in samples containing very low biomass. This procedure has been applied to ATP determination in marine sediments in the upwelling area off northwest Africa. The average ATP concentrations in the upper 6 cm of sediment from 1000 and 200 m were 195 and 545 ng per ml wet sediment, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Atkinson, D.E.: Regulation of enzyme function. A. Rev. Microbiol. 23, 47–68 (1969)
Ausmus, B.S.: The use of the ATP assay in terrestrial decomposition studies. In: Modern methods in the study of microbial ecology, pp 223–234. Ed. by T. Rosswall. Stockholm: Swedish Natural Science Research Council (NRF) 1972
Birkett, L. and A.D. McIntyre: Treatment and sorting of samples. In: IBP Handbook No. 16. Methods for the study of marine benthos, pp 156–168. Ed. by N.A. Holme and A.D. McIntyre. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications 1971
Carlucci, A.F. and D. Pramer: Factors influencing the plate method for determining abundance of bacteria in sea water. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 96, 392–394 (1957)
Christian, R.R., K. Bancroft and W.J. Wiebe: Distribution of microbial adenosine triphosphate in salt marsh sediments at Sapelo Island, Georgia. Soil Sci. 119, 89–97 (1975)
Ehrlich, H.: Bacteriology of manganese nodules. I. Bacterial action on manganese nodule enrichments. Appl. Microbiol. 11, 15–19 (1963)
Ernst, W.: ATP als Indikator für die Biomasse mariner Sedimente. Oecologia (Berl.) 5, 55–60 (1970)
Ferguson, R.L. and M.B. Murdoch: On the estimation of microbial ATP in estuarine sediments and water. Bull. ecol. Soc. Am. 54, p. 27 (1973)
Griggs, G.B., A.G. Carey and L.D. Kulm: Deep-sea sedimentation and sediment-fauna interaction in Cascadia Channel and on Cascadia Abyssal Plain. Deep-Sea Res. 16, 157–170 (1969)
Holm-Hansen, O.: ATP levels in algal cells as influenced by environmental conditions. Pl. Cell Physiol., Tokyo 11, 689–700 (1970)
— Determination of total microbial biomass by measurement of adenosine triphosphate. In: Estuarine microbial ecology, pp 73–89. Ed. by L.H. Stevenson and R.R. Colwell. Columbia, S.C.: University of South Carolina Press 1973
— and C.R. Booth: The measurement of adenosine triphosphate in the ocean and its ecological significance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 510–519 (1966)
— and H.W. Paerl: The applicability of ATP determination for estimation of microbial biomass and metabolic activity. In: Detritus and its ecological role in aquatic ecosystems, pp 149–168. Ed. by U. Melchiorri. Pallanza: Istituto Italiano di Idrobiologia 1972
Ireland, D.M. and D.C.B. Mills. Detection and determination of adenosine diphosphate and related substances in plasma. Biochem. J. 99, 283–296 (1966)
Jannasch, H., K. Eimhjellen, C. Wirson and A. Farmanfarmaian: Microbial degradation of organic matter in the deep sea. Science, N.Y. 171, 672–675 (1971)
Johnson, R.W. and J. Calder: Early diagenesis of fatty acids and hydrocarbon in a salt marsh environment. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 37, 1943–1955 (1973)
Karl, D.M. and P.A. LaRock: Adenosine triphosphate measurements in soil and marine sediments. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 32, 599–607 (1975)
Karl, D.M. P.A. LaRock, J.W. Morse and W. Sturges: Adenosine triphosphate in the North Atlantic Ocean and its relationship to the oxygen minimum. Deep-Sea Res. (1975). (In press)
Lee, C.C., R.F. Harris, J.D.H. Williams, D.E. Armstrong and J.K. Syers: ATP in lake sediments; determination. Proc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 35, 82–86 (1971a)
——, J.K. Syers and D.E. Armstrong: ATP in lake sediments: II-origin and significance. Proc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 35, 86–91 (1971b)
Litchfield, C.: Interactions of amino acids and marine bacteria. In: Estuarine microbial ecology, pp 145–168. Ed. by L.H. Stevenson and R.R. Colwell. Columbia, S.C.: University of South Carolina Press 1973
Menzies, R.J. and G.T. Rowe: The LUBS, a large undisturbed bottom sampler. Limnol. Oceanogr. 13, 708–714 (1968)
Patterson, J.W., P.L. Brezonik and H.D. Putman: Measurement and significance of ATP in activated sludge. Envir. Sci. Technol. 4, 569–575 (1970)
Sugahara, I., M. Sugiyama and A. Kawai: Distribution and activity of nitrogen-cycle bacteria in water-sediment systems with different concentrations of oxygen. In: Effect of the ocean environment on microbial activities, pp 327–340. Ed. by R.R. Colwell and R. Morita. Baltimore: University Park Press 1974
Temple, K.: Syngenesis of sulfide ores: an evaluation of biochemical aspects. Econ. Geol. 59, 1473–1491 (1964)
Weddle, C.L. and D. Jenkins: The viability and activity of activated sludge. Wat. Res. 5, 621–640 (1971)
Wright, R.: Mineralization of organic solutes by heterotrophic bacteria. In: Effect of the ocean environment on microbial activities, pp 546–565. Ed. by R.R. Colwell and R. Morita. Baltimore: University Park Press 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.S. Pearse, Santa Cruz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodson, R.E., Holm-Hansen, O. & Azam, F. Improved methodology for ATP determination in marine environments. Marine Biology 34, 143–149 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390756
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390756