Abstract
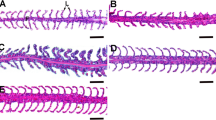
By means of scanning and transmission electron microscopy, the influence of the red tide species Chattonella antiqua was examined with respect to the surface ultrastructures of chloride cells of the yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata. Conspicuous ultrastructural alterations occurred on the apical surface of these cells. The majority of chloride cells in the control gills showed an apical surface with numerous cellular extensions, while more than half the chloride cells affected by red tide organisms exhibited an apical surface with fewer and smaller extensions, a wrinkled apical surface, or a protruded apical surface. These ultrastructural alterations of chloride cell surface may be due to the partial disturbance of salinity by C. antiqua, and reflect the changes of the ion-transport function in yellowtail gills exposed to red tide water.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Berridge, M. J. and J. L. Oschman: Transporting Epithelia, pp 32–75. New York: Academic Press 1972
Brown, P. C., L. Hutching and D. Horstman: A red-water out-break and associated fish mortality at Gordons Bay near Cape Town. Fish. Bull. S. Afr. 11, 46–52 (1979)
Doi, A., O. Hatase, M. Shimada, T. H. Murakami and T. Okaichi: Ultrastructural changes in gill epithelia of a yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata, exposed to sea bloom. Cell Str. Func. 6, 375–383 (1981)
Dunel-Erb, S. and P. Laurent: Ultrastructures of marine teleost gill epithelia, SEM and TEM study of chloride cell apical membrane. J. Morphol. 165, 175–186 (1980)
Epstein, F. H., P. Silva and G. Kormanic: Role of Na−K-ATPase in chloride cell function. Am. J. Physiol. 7, 246–250 (1980)
Hoar, W. S. and D. J. Randall: Fish physiology, pp 253–292. New York: Academic Press, 1970
Hootman, S. R. and G. W. Philpott: Accessory cells in teleost branchial epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. 7, 199–206 (1980)
Hossler, F. E.: Gill arch of the mullet, Mugi cephalus III. Rate of response to salinity change. Am. J. Physiol. 7, 160–170 (1980)
Karnaky, K. J. Jr.: Ion-secreting epithelia; chloride cells in the head region of Fundulus heteroclitus. Am. J. Physiol. 7, 185–198 (1980)
Kobayashi, H.: Sakana no Kokyu to Junkan: In: Respiration and circulation in fish, pp 111–124. Ed. by Japan Soc. Sci. Fish., Suisangaku series 24 Tokyo: Koseisha-Koseikaku 1978 (in Japanese)
Laurent, P., and S. Dunel: Morphology of gill epithelia in fish. Am. J. Physiol. 7, 149–159 (1980)
Maetz, J.: Fish gills: mechanisms of salt transfer in fresh water and sea water. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 262, 209–249 (1971)
Maetz, J. and M. Bornanchin: Biochemical and biophysical aspects of salt excretion by chloride cells in teleosts. Forsch. Zool. 23, 323–363 (1975)
Motais, R. and F. Garcia Romeu: Transport mechanisms in the teleostean gill and amphibian skin. A. Rev. Physiol. 34, 141–176 (1972)
Potts, W. T. W.: Fish gills. In: Transport of ion and water in animals, pp 453–480. Ed. by B. L. Gupta, R. B. Moreton, J. L. Oschman and B. J. Wall. New York: Academic Press 1977
Sardet, C., M. Pisam and J. Maetz: The surface epithelium of teleostean fish gills. Cellular and junctional adaptations of the chloride cell in relation to salt adaptation. J. Cell. Biol. 80, 96–117 (1979)
Seki, H., T. Tsuji and A. Hattori: Effect of zooplankton grazing on the formation of the anoxic layer in Tokyo Bay. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 2, 145 (1974)
Shimada, M., T. H. Murakami, A. Doi, S. Abe, T. Okaichi and M. Watanabe: A morphological and histochemical study on gill primary lamellae of the teleost, Seriola quinqueradiata, exposed to sea bloom. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 497–507 (1982)
Shimada, M., T. H. Murakami, T. Imahayashi, H. S. Ozaki, T. Toyoshima and T. Okaichi: Effects of sea bloom, Chattonella antiqua, on gill primary lamellae of the young yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata, Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 232–244 (1983)
Yanagida, T.: The red tide, pp 50–175 Tokyo: Kodansha Scientific 1980 (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toyoshima, T., Ozaki, H.S., Shimada, M. et al. Ultrastructural alterations on chloride cells of the yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata, following exposure to the red tide species Chattonella antiqua . Mar. Biol. 88, 101–108 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393048
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393048