Summary
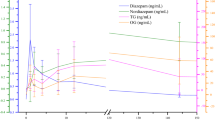
The concentration of free and conjugated diazepam, of its major demethylated metabolite, N-demethyldiazepam, and of its hydroxylated metabolites, N-methyloxazepam and oxazepam, were measured by a GLC-method in plasma, bile and urine following four nightly doses of diazepam 10 mg. Ten patients with a T-tube in the common bile duct after choledochotomy (Group I) were studied and 12 patients after cholecystectomy (Group II). Twelve hours after drug administration, the mean total concentration of diazepam in bile was 1/23 that in plasma. Similarly, during 9–10 h only low concentrations of diazepam were found in the urine, and in both urine and bile only the unconjugated drug was found. The principal metabolite of diazepam in plasma was N-demethyldiazepam. In bile an average of 77% of the total amount of N-demethyldiazepam was in the conjugated form, and its total concentration was half that in plasma. In urine N-demethyldiazepam was mainly in the conjugated form. No hydroxylated metabolites of diazepam were found in plasma. Oxazepam was the metabolite found in bile and urine in the next highest concentration after N-demethyldiazepam. In the urine it was mainly conjugated, but in bile only a mean of 35% was conjugated. Both in bile and urine, N-methyloxazepam was found only intermittently and in low concentration. Diazepam and all of its common metabolites were measured in human bile, and the concentrations found were too low to produce a clinically significant enterohepatic circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, E.: A simple method for determining diazepam and its major metabolites in biological fluids: Application in bioavailability studies. Acta pharmacol. toxicol.36, 335–352 (1975)
Baird, E.S., Hailey, D.M.: Delayed recovery from a sedative: correlation of the plasma levels of diazepam with clinical effects after oral and intravenous administration. Brit. J. Anaesth.44, 803–808 (1972)
Bertagni, B., Marcucci, F., Mussini, E., Garattini, S.: Biliary excretion of conjugated hydroxyl benzodiazepines after administration of several benzodiazepines to rats, guinea pigs, and mice. J. Pharm. Sci.61, 965–966 (1972)
Eustace, P.W., Hailey, D.M., Baird, E.S.: Biliary excretion of diazepam in man. Brit. J. Anaesth.47, 983–985 (1975)
Kangas, L., Pekkarinen, A., Sourander, C., Raijola, E.: A comparative gas chromatographic study on absorption of diazepam tablets in man. Ann. clin. Res.6, Suppl. 11, 12–20 (1974)
Kanto, J., Iisalo, E., Lehtinen, V., Salminen, J.: The concentrations of diazepam and its metabolites in the plasma after an acute and chronic administration. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.)36, 123–131 (1974)
van der Kleijn, E., van Rossum, J.M., Muskens, A.T.J.M., Rijntjes, N.V.M.: Pharmacokinetics of diazepam in dogs, mice and man. Acta pharmacol. toxicol.29, 109–129 (1971)
Klotz, U., Antonin, K.H., Bieck, P.R.: Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of diazepam after single and subchronic doses. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.10, 121–126 (1976)
Mahon, W., Inaba, T., Umeda, T., Tsutsumi, E., Stone, R.: Biliary elimination of diazepam in man. J. clin. Pharmacol. Ther.19, 443–450 (1976)
Sellman, R., Kanto, J., Pekkarinen, J.: Biliary excretion of diazepam and its metabolites in man. Acta pharmacol. toxicol.37, 242–249 (1975)
Zingales, J. A.: Diazepam metabolism during chronic medication. Unbound fraction in plasma, erythrocytes and urine. J. Chromatogr.75, 55–78 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sellman, R., Hurme, M. & Kanto, J. Biliary excretion of diazepam and its metabolites in man after repeated oral doses. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 12, 209–212 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609863
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609863