Summary
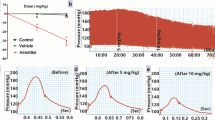
The acute and long-term hypotensive effects of low doses of nifedipine, and the correlation between the fall in the blood pressure (BP) and the plasma nifedipine concentration, were investigated in patients with essential hypertension. The oral administration of nifedipine 5 mg rapidly decreased BP from 163±22/101±10 to 127±12/82±9 mmHg (mean±SD; p<0.001), and increased heart rate from 72±8 to 76±6 beats/min (p<0.05), plasma renin activity rose from 1.2±0.6 to 1.4±0.8 ng/ml/h (p<0.05), and plasma nifedipine concentration was 75.6±22.0 ng/ml 30 min after administration (n=7). The nifedipine concentration was significantly correlated both with the fall in BP (r=0.410, p<0.02, n=31) and the rise in the heart rate (r=0.412, p<0.02, n=31). Treatment with nifedipine 5 mg t.d.s. alone or in combination either with propranolol 10 mg t.d.s., or thiazide 1 tablet daily, or propranolol and thiazide, controlled BP in 36 patients during the 22 week study period. During the long-term nifedipine therapy, the plasma nifedipine level was significantly correlated with the fall in systolic (r=0.577, p<0.01, n=20) and diastolic (r=0.595, p<0.01, n=20) BP. It was concluded that the plasma nifedipine concentration could be correlated with the fall in BP, and that low doses of nifedipine, either as monotherapy or in combination, were effective in the acute and long-term treatment of patients with essential hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grün G, Fleckenstein A (1972) Die elektromechanische Entkoppelung der glatten Gefäßmuskulatur als Grundprinzip der Coronardilation durch 4-(2′-nitrophenyl)-2, 6-dimethyl-1, 4-dihydropyridin-3, 5-dicarbonsäure-dimethylester (BAY a 1040, Nifedipine). Arzneim Forsch 22: 334–344
Murakami M, Murakami E, Takekoshi N, Tsuchiya M, Kin T, Onoe T, Takeuchi N, Funatsu T, Hara S, Ishise S, Mifune J, Maeda M (1972) Antihypertensive effect of 4(-2′-Nitrophenyl)-2, 6-Dimethyl-1, 4-Dihydropyridine-3, 5-Dicarbonic acid dimethylester (Nifedipine Bay-a 1040), a new coronary dilator. Jpn Heart J 13: 128–135
Aoki K, Yoshida T, Kato S, Tazumi K, Sato I, Takikawa K, Hotta K (1976) Hypotensive action and increased plasma renin activity by Ca2+ antagonist (nifedipine) in hypertensive patients. Jpn Heart J 17: 479–484
Aoki K, Kondo S, Mochizuki A, Yoshida T, Kato K, Takikawa K (1978) Antihypertensive effect of cardiovascular Ca2+-antagonist in hypertensive patients in the absence and presence of beta-adrenergic blockade. Am Heart J 96: 218–226
Aoki K, Kondo S, Mochizuki A, Sato K, Yoshida T, Kato S, Kato K (1979) Ca2+-antagonist therapy for hypertension in combination with beta-blockade: A new concept of essential hypertension. In: Yamori Y, Lovenberg W, Freis ED (eds) Prophylactic approach to hypertensive diseases. Raven Press, New York, pp 377–386
Aoki K, Kondo S, Sato K, Kato K, Kawaguchi Y, Mochizuki A, Yamamoto M (1981) Hypotensive action of nifedipine (Ca2+-antagonist) and propranolol in acute trials and its long-term therapy of hypertensive coronary heart disease patients. Jpn Heart J 22: 575–584
Guazzi M, Olivari MT, Polese A, Fiorentini C, Magrini F, Moruzzi P (1977) Nifedipine, a new antihypertensive with rapid action. Clin Pharmacol Ther 22: 528–532
Olivari MT, Bartorelli C, Polese A, Fiorentini C, Moruzzi P, Guazzi MD (1979) Treatment of hypertension with nifedipine, a calcium antagonist agent. Circulation 59: 1056–1062
Guazzi MD, Fiorentini C, Olivari MT, Bartorelli A, Necchi G, Polese A (1980) Short- and long-term efficacy of a calcium-antagonistic agent (nifedipine) combined with methyldopa in the treatment of severe hypertension. Circulation 61: 913–919
Pedersen OL, Mikkelsen E (1978) Acute and chronic effects of nifedipine in arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 14: 375–381
Pedersen OL, Mikkelsen E, Christensen NJ, Kornerup HJ, Pedersen EB (1979) Effect of nifedipine on plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines in arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15: 235–240
Thibonnier M, Bonnet F, Corvol P (1980) Antihypertensive effect of fractionated sublingual administration of nifedipine in moderate essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17: 161–164
Koch-Weser J (1974) Vasodilator drugs in the treatment of hypertension. Arch Intern Med 133: 1017–1027
Ishii H, Itoh K, Nose T (1980) Different antihypertensive effects of nifedipine in conscious experimental hypertensive and normotensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 64: 21–29
Kondo S, Kuchiki A, Yamamoto K, Akimoto K, Takahashi K, Awata N, Sugimoto I (1980) Identification of nifedipine metabolites and their determination by gas chromatography. Chem Pharm Bull 28: 1–7
O'Malley K, Velasco M, Wells J, McNay JL (1975) Control plasma renin activity and changes in sympathetic tone as determination of minoxidil-induced increase in plasma renin activity. J Clin Invest 55: 230–235
Gilmore E, Weil J, Chidsey C (1970) Treatment of essential hypertension with a new vasodilator in combination with beta-adrenergic blockade. N Engl J Med 282: 521–527
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, K., Sato, K., Kawaguchi, Y. et al. Acute and long-term hypotensive effects and plasma concentrations of nifedipine in patients with essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23, 197–201 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00547553
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00547553