Summary
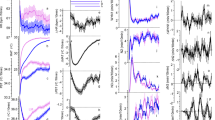
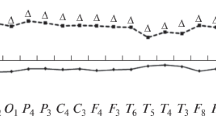
The influence of a benzodiazepine (triazolam) on the body temperature of poor sleepers during nights disturbed by airplane noises has been examined. Subjects were divided into 3 groups each of 8 men. Following a double-blind design, Group A (controls) received a placebo for 6 consecutive nights, Group B received 0.25 mg triazolam, and Group C received 0.5 mg triazolam on nights N3, N4 and N5. On all other nights Group B and C subjects received placebo. For all 3 groups, nights N3 and N5 were disturbed by 32, semi-randomly distributed airplane noises. Air and wall temperatures (To=20°C), and air humidity (Tdp=10°C), were kept constant. Rectal temperature and 4 local skin temperatures were recorded from each subject. Urine samples were collected each morning for measurement of cortisol and catecholamine levels. Noise was found to cause an increase in body heat storage, but only in Group A. Both drug groups showed impairment of body heat balance. The hypothermic action of triazolam could be explained both by a central action of the drug on the thermoregulatory controller and by a peripheral action on blood vessels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braestrup C, Albrechtsen R, Squires RF (1977) High densities of benzodiazepine receptor in human cortical areas. Nature 269: 702–704
Candas V, Libert JP, Vogt JJ, Ehrhart J, Muzet A (1979) Body temperature during sleep under different thermal conditions. In: Fanger PO, Valbjorn O (eds) Indoor climate: effects on human comfort, performance and health. JJ Trykteknik, Copenhagen, pp 763–776
Church MW, Johnson LC, Seales DM, Rossiter VS (1978) Bedtime and morning oral temperatures, evoked cardiovascular responses, and spontaneous skin potential responses in good and poor sleepers and the effects of flurazepam. Sleep Res 7: 65
Côté P, Noble J, Bourassa MG (1976) Systemic vasodilatation following diazepam after combined sympathetic and parasympathetic blockade in patients with coronary heart disease. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 2: 369–380
Follenius M, Brandenberger G, Lecornu C, Simeoni M, Reinhardt B (1980) Plasma catecholamines and pituitary adrenal hormones in response to noise exposure. Eur J Appl Physiol 43: 253–261
Henkins RI, Knigge KM (1963) Effect of sound on the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis. Am J Physiol 204: 710–714
Irvine RE (1966) Hypothermia due to diazepam. Br Med J 2: 1007
Knipschild P (1977) Medical effects of aircraft noise. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 40: 185–204
Muzet A, Johnson LC, Spinweber CL (1982) Benzodiazepine hypnotics increase heart rate during sleep. Sleep 5: 256–261
Ogle CW, Lockett MF (1968) The urinary changes induced in rats by high pitched sounds (20 kcyc./sec). J Endocrinol 42: 253–260
Passon PG, Peuler JD (1973) A simplified radiometric assay for plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. Anal Biochem 51: 618–631
Peuler JD, Johnson GA (1977) Simultaneous single isotope radioenzymatic assay of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. Life Sci 21: 625–636
Ramanathan NL (1964) A new weighting system for mean surface temperature of the human body. J Appl Physiol 19: 531–533
Slob A, Wink A, Radder JJ (1973) The effect of acute noise exposure on the secretion of corticosteroids, adrenalin and noradrenalin in man. Int Arch Arbeitsmed 31: 225–235
Stolwijk JAJ, Hardy JD (1966) Partitional calorimetric studies of responses of man to thermal transients. J Appl Physiol 21: 967–977
Vecsei P, Penke B, Katzy R, Baek L (1972) Radioimmunological determination of plasma cortisol. Experientia 8: 1104–1106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Libert, J.P., Weber, L.D., Amoros, C. et al. Influence of triazolam on thermal heat balance in poor sleepers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27, 173–179 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544042
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544042